Abstract
Purpose of Review
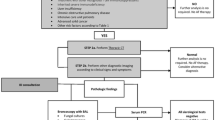
Invasive aspergillosis is a frequent opportunistic infection in the intensive care unit. Diagnostic strategies within this setting are not well-defined.
Recent Findings
In the absence of histopathological proof, estimation of likelihood of disease is required, based on a combination of host factors with clinical, microbiological and radiologic findings. Importantly, the at-risk critically ill population has expanded beyond the classical immunosuppressed patients. Clinical features are non-specific, yet overt organ failure is associated with an increased risk and should raise the suspicion of invasive fungal disease. Validation of serological and molecular diagnostics is complicated by the lack of universal definitions in critically ill patients.
Summary
Improved awareness of novel risk groups can promote early diagnosis. Development of novel, host immune response driven biomarkers and universal definitions of invasive fungal disease in intensive care units is urgently needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/invasive fungal infections cooperative group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases mycoses study group (EORTC/MSG) consensus group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(12):1813–21.
•• Donnelly JP, Chen SC, Kauffman CA, Steinbach WJ, Baddley JW, Verweij PE, et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz1008Updated definitions of invasive fungal disease, incorporating evidence onAspergillusPCR.
Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Maertens J, Van Wijngaerden E. Invasive aspergillosis in the intensive care unit. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(2):205–16.
Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, Misset B, Meersseman W, Cardoso T, et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit Care. 2015;19(1):7.
Vandewoude K, Blot S, Benoit D, Depuydt P, Vogelaers D, Colardyn F. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: analysis of risk factors for acquisition and mortality. Acta Clin Belg. 2004;59(5):251–7.
Garnacho-Montero J, Amaya-Villar R, Ortiz-Leyba C, Leon C, Alvarez-Lerma F, Nolla-Salas J, et al. Isolation of Aspergillus spp. from the respiratory tract in critically ill patients: risk factors, clinical presentation and outcome. Crit Care. 2005;9(3):R191–9.
Bulpa P, Dive A, Sibille Y. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2007;30(4):782–800.
Vandewoude KH, Blot SI, Depuydt P, Benoit D, Temmerman W, Colardyn F, et al. Clinical relevance of Aspergillus isolation from respiratory tract samples in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2006;10(1):R31.
Blot SI, Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, Meersseman W, Brusselaers N, et al. A clinical algorithm to diagnose invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(1):56–64.
Husain S, Sole A, Alexander BD, Aslam S, Avery R, Benden C, et al. The 2015 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation guidelines for the management of fungal infections in mechanical circulatory support and cardiothoracic organ transplant recipients: executive summary. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35(3):261–82.
Schroeder M, Simon M, Katchanov J, Wijaya C, Rohde H, Christner M, et al. Does galactomannan testing increase diagnostic accuracy for IPA in the ICU? A prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):139.
Koulenti D, Garnacho-Montero J, Blot S. Approach to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014;27(2):174–83.
• Tejerina EE, Abril E, Padilla R, Rodriguez Ruiz C, Ballen A, Frutos-Vivar F, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: an autopsy study. Mycoses. 2019;62(8):673–9 Recent autopsy study showing frequent misdiagnosis of IA in critically ill patients.
Cornillet A, Camus C, Nimubona S, Gandemer V, Tattevin P, Belleguic C, et al. Comparison of epidemiological, clinical, and biological features of invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic and nonneutropenic patients: a 6-year survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43(5):577–84.
Chakrabarti A, Kaur H, Savio J, Rudramurthy SM, Patel A, Shastri P, et al. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of invasive mould infections in Indian intensive care units (FISF study). J Crit Care. 2019;51:64–70.
•• Cavayas YA, Yusuff H, Porter R. Fungal infections in adult patients on extracorporeal life support. Crit Care. 2018;22(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-018-2023-zRetrospective cohort study of adult patients on ECMO between 2006 and 2016, showing association betweenAspergillusinvolvement and use of ECMO as respiratory support as well as an association betweenAspergillusand influenza in this study cohort.
•• Blot S, Rello J, Koulenti D. Diagnosing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients: putting the puzzle together. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2019;25(5):430–7 Comprehensive review of IPA in intensive care setting, attributing degrees of likelihood for invasive pulmonary fungal disease to different pillars of diagnosis.
Patterson TF, Thompson GR 3rd, Denning DW, Fishman JA, Hadley S, Herbrecht R, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(4):e1–e60.
Meersseman W, Vandecasteele SJ, Wilmer A, Verbeken E, Peetermans WE, Van Wijngaerden E. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients without malignancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(6):621–5.
Prodanovic H, Cracco C, Massard J, Barrault C, Thabut D, Duguet A, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with decompensated cirrhosis: case series. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007;7:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-7-2.
Levesque E, Ait-Ammar N, Dudau D, Clavieras N, Feray C, Foulet F, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in cirrhotic patients: analysis of a 10-year clinical experience. Ann Intensive Care. 2019;9(1):31.
Baddley JW, Stephens JM, Ji X, Gao X, Schlamm HT, Tarallo M. Aspergillosis in intensive care unit (ICU) patients: epidemiology and economic outcomes. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-29.
• Danion F, Rouzaud C, Dureault A, Poiree S, Bougnoux ME, Alanio A, et al. Why are so many cases of invasive aspergillosis missed? Med Mycol. 2019;57(Supplement_2):S94–s103 Elaborate review of causes of IA misdiagnosis in a general population, focussing on the different aspects of diagnosis (host factors, radiology and microbiological tests).
Wauters J, Baar I, Meersseman P, Meersseman W, Dams K, De Paep R, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is a frequent complication of critically ill H1N1 patients: a retrospective study. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(11):1761–8.
van de Veerdonk FL, Kolwijck E, Lestrade PP, Hodiamont CJ, Rijnders BJ, van Paassen J, et al. Influenza-associated Aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(4):524–7.
• Schauwvlieghe AFAD, Rijnders BJA, Philips N, Verwijs R, Vanderbeke L, Van Tienen C, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6(10):782–92 This retrospective cohort study of multiple ICUs in Belgium and the Netherlands showed for the first time that severe influenza in critically ill patients is an independent risk factor for IPA development.
Baron M, Zini JM, Challan Belval T, Vignon M, Denis B, Alanio A, et al. Fungal infections in patients treated with ibrutinib: two unusual cases of invasive aspergillosis and cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017;58(12):2981–2.
Fujita K, Kim YH, Kanai O, Yoshida H, Mio T, Hirai T. Emerging concerns of infectious diseases in lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Respir Med. 2019;146:66–70.
Salmon-Ceron D, Tubach F, Lortholary O, Chosidow O, Bretagne S, Nicolas N, et al. Drug-specific risk of non-tuberculosis opportunistic infections in patients receiving anti-TNF therapy reported to the 3-year prospective French RATIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(4):616–23.
Prebil SE, Andrews J, Cribbs SK, Martin GS, Esper A. Safety of research bronchoscopy in critically ill patients. J Crit Care. 2014;29(6):961–4.
Prattes J, Flick H, Pruller F, Koidl C, Raggam RB, Palfner M, et al. Novel tests for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with underlying respiratory diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(8):922–9.
He H, Ding L, Sun B, Li F, Zhan Q. Role of galactomannan determinations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from critically ill patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: a prospective study. Crit Care. 2012;16(4):R138.
Ullmann AJ, Aguado JM, Arikan-Akdagli S, Denning DW, Groll AH, Lagrou K, et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24(Suppl 1):e1–e38.
Bulpa P, Bihin B, Dimopoulos G, Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Misset B, et al. Which algorithm diagnoses invasive pulmonary aspergillosis best in ICU patients with COPD? Eur Respir J. 2017;50(3):1700532. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00532-2017.
Chong GM, Maertens JA, Lagrou K, Driessen GJ, Cornelissen JJ, Rijnders BJ. Diagnostic performance of Galactomannan antigen testing in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54(2):428–31.
Leeflang MM, Debets-Ossenkopp YJ, Wang J, Visser CE, Scholten RJ, Hooft L, et al. Galactomannan detection for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(12):Cd007394. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007394.pub2
Mercier T, Guldentops E, Lagrou K, Maertens J. Galactomannan, a surrogate marker for outcome in invasive Aspergillosis: finally coming of age. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:661. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00661.
Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Maertens J, Wilmer A, Hermans G, Vanderschueren S, et al. Galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: a tool for diagnosing aspergillosis in intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(1):27–34.
Fortun J, Martin-Davila P, de la Gomez Garcia Pedrosa E, Silva JT, Garcia-Rodriguez J, Benito D, et al. Galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in non-hematological patients. J Inf Secur. 2016;72(6):738–44.
Khodavaisy S, Hedayati MT, Alialy M, Habibi MR, Badali H. Detection of galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage of the intensive care unit patients at risk for invasive aspergillosis. Curr Med Mycol. 2015;1(1):12–7.
Acosta J, Catalan M, del Palacio-Perez-Medel A, Lora D, Montejo JC, Cuetara MS, et al. A prospective comparison of galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in medical patients under intensive care: comparison with the diagnostic performance of galactomannan and of (1--> 3)-beta-d-glucan chromogenic assay in serum samples. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(7):1053–60.
Petraitiene R, Petraitis V, Witt JR 3rd, Durkin MM, Bacher JD, Wheat LJ, et al. Galactomannan antigenemia after infusion of gluconate-containing plasma-Lyte. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(12):4330–2.
Spriet I, Lagrou K, Maertens J, Willems L, Wilmer A, Wauters J. Plasmalyte: no longer a culprit in causing false-positive Galactomannan test results. J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54(3):795–7.
Aigner M, Wanner M, Kreidl P, Lass-Florl C, Lackner M. Candida in the Respiratory Tract Potentially Triggers Galactomannan Positivity in Nonhematological Patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(6):e00138–19.
• Hage CA, Carmona EM, Epelbaum O, Evans SE, Gabe LM, Haydour Q, et al. Microbiological Laboratory Testing in the Diagnosis of Fungal Infections in Pulmonary and Critical Care Practice. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(5):535–50 Novel guideline of the American Thoracic Society focussing on microbiological aspects of invasive fungal disease in pulmonary and critical care setting. This paper entails specific recommendations on use of galactomannan andAspergillusPCR for IA diagnosis.
Acosta J, Catalan M, del Palacio-Perez-Medel A, Montejo JC, De-La-Cruz-Bertolo J, Moragues MD, et al. Prospective study in critically ill non-neutropenic patients: diagnostic potential of (1,3)-beta-D-glucan assay and circulating galactomannan for the diagnosis of invasive fungal disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;31(5):721–31.
• Boch T, Reinwald M, Spiess B, Liebregts T, Schellongowski P, Meybohm P, et al. Detection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients by combined use of conventional culture, galactomannan, 1–3-beta-D-glucan and Aspergillus specific nested polymerase chain reaction in a prospective pilot study. J Crit Care. 2018;47:198–203 Prospective pilot study of a combination biomarker diagnostic strategy in 44 critically ill patients, both hematological as non-hematological, showing a benefit of integrating BAL and blood sample biomarkers for diagnosis of IPA.
De Vlieger G, Lagrou K, Maertens J, Verbeken E, Meersseman W, Van Wijngaerden E. Beta-D-glucan detection as a diagnostic test for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised critically ill patients with symptoms of respiratory infection: an autopsy-based study. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(11):3783–7.
Lahmer T, Neuenhahn M, Held J, Rasch S, Schmid RM, Huber W. Comparison of 1,3-beta-d-glucan with galactomannan in serum and bronchoalveolar fluid for the detection of Aspergillus species in immunosuppressed mechanical ventilated critically ill patients. J Crit Care. 2016;36:259–64.
Hoenigl M, Prattes J, Spiess B, Wagner J, Prueller F, Raggam RB, et al. Performance of galactomannan, beta-d-glucan, Aspergillus lateral-flow device, conventional culture, and PCR tests with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(6):2039–45.
Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Spriet I, Maertens J, Verbeken E, Peetermans WE, et al. Significance of the isolation of Candida species from airway samples in critically ill patients: a prospective, autopsy study. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35(9):1526–31.
Digby J, Kalbfleisch J, Glenn A, Larsen A, Browder W, Williams D. Serum glucan levels are not specific for presence of fungal infections in intensive care unit patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003;10(5):882–5.
Alexander BD, Smith PB, Davis RD, Perfect JR, Reller LB. The (1,3){beta}-D-glucan test as an aid to early diagnosis of invasive fungal infections following lung transplantation. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(11):4083–8.
Hummel M, Spiess B, Kentouche K, Niggemann S, Bohm C, Reuter S, et al. Detection of Aspergillus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with cerebral aspergillosis by a nested PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(11):3989–93.
Imbert S, Brossas JY, Palous M, Joly I, Meyer I, Fekkar A. Performance of Aspergillus PCR in cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of cerebral aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(11):889.e1–4.
White PL, Wingard JR, Bretagne S, Loffler J, Patterson TF, Slavin MA, et al. Aspergillus polymerase chain reaction: systematic review of evidence for clinical use in comparison with antigen testing. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61(8):1293–303.
Mengoli C, Cruciani M, Barnes RA, Loeffler J, Donnelly JP. Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9(2):89–96.
Imbert S, Gauthier L, Joly I, Brossas JY, Uzunov M, Touafek F, et al. Aspergillus PCR in serum for the diagnosis, follow-up and prognosis of invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic and nonneutropenic patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(6):562.e1–8.
Orsi CF, Gennari W, Venturelli C, La Regina A, Pecorari M, Righi E, et al. Performance of 2 commercial real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of Aspergillus and Pneumocystis DNA in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from critical care patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73(2):138–43.
Torelli R, Sanguinetti M, Moody A, Pagano L, Caira M, De Carolis E, et al. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis by a commercial real-time PCR assay for Aspergillus DNA in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from high-risk patients compared to a galactomannan enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(12):4273–8.
Thornton CR. Development of an immunochromatographic lateral-flow device for rapid serodiagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008;15(7):1095–105.
Eigl S, Prattes J, Lackner M, Willinger B, Spiess B, Reinwald M, et al. Multicenter evaluation of a lateral-flow device test for diagnosing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients. Crit Care. 2015;19:178.
Hoenigl M, Eigl S, Heldt S, Duettmann W, Thornton C, Prattes J. Clinical evaluation of the newly formatted lateral-flow device for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2018;61(1):40–3.
• Mercier T, Dunbar A, de Kort E, Schauwvlieghe A, Reynders M, Guldentops E, et al. Lateral flow assays for diagnosing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in adult hematology patients: A comparative multicenter study. Med Mycol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myz079Comparative study of current CE-marked lateral flow assays for IPA diagnosis, evaluated in a multicenter study of hematological patients.
Jenks JD, Mehta SR, Taplitz R, Aslam S, Reed SL, Hoenigl M. Point-of-care diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in non-neutropenic patients: Aspergillus Galactomannan lateral flow assay versus Aspergillus-specific lateral flow device test in bronchoalveolar lavage. Mycoses. 2019;62(3):230–6.
Kabbani D, Bhaskaran A, Singer LG, Bhimji A, Rotstein C, Keshavjee S, et al. Pentraxin 3 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of lung transplant recipients with invasive aspergillosis. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36(9):973–9.
Li H, Liu L, Zhou W, Rui Y, He B, Shi Y, et al. Pentraxin 3 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and plasma in non-neutropenic patients with pulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25(4):504–10.
Heldt S, Eigl S, Prattes J, Flick H, Rabensteiner J, Pruller F, et al. Levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 are elevated in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of haematological patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2017;60(12):818–25.
Rawlings SA, Heldt S, Prattes J, Eigl S, Jenks JD, Flick H, et al. Using interleukin 6 and 8 in blood and Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid to predict survival in hematological malignancy patients with suspected pulmonary Mold infection. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1798.
Heldt S, Prattes J, Eigl S, Spiess B, Flick H, Rabensteiner J, et al. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in hematological malignancy patients: performance of cytokines, asp LFD, and Aspergillus PCR in same day blood and bronchoalveolar lavage samples. J Inf Secur. 2018;77(3):235–41.
Bacher P, Steinbach A, Kniemeyer O, Hamprecht A, Assenmacher M, Vehreschild MJ, et al. Fungus-specific CD4(+) T cells for rapid identification of invasive pulmonary mold infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191(3):348–52.
Steinbach A, Cornely OA, Wisplinghoff H, Schauss AC, Vehreschild JJ, Rybniker J, et al. Mould-reactive T cells for the diagnosis of invasive mould infection-a prospective study. Mycoses. 2019;62(7):562–9.
• Jenks JD, Rawlings SA, Garcia-Vidal C, Koehler P, Mercier T, Prattes J, et al. Immune parameters for diagnosis and treatment monitoring in invasive Mold infection. J Fungi (Basel). 2019;5(4):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5040116Elaborate review on recent advances in immunological diagnostic tools for invasive fungal disease.
Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, Casasnovas O, Denning DW, Mannone L, et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(1):253–9.
Park SY, Lim C, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, et al. Computed tomography findings in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in non-neutropenic transplant recipients and neutropenic patients, and their prognostic value. J Inf Secur. 2011;63(6):447–56.
Huang L, He H, Ding Y, Jin J, Zhan Q. Values of radiological examinations for the diagnosis and prognosis of invasive bronchial-pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Clin Respir J. 2018;12(2):499–509.
Krenke R, Grabczak EM. Tracheobronchial manifestations of Aspergillus infections. Sci World J. 2011;11:2310–29.
Thornton CR. Molecular imaging of invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis using ImmunoPET/MRI: the future looks bright. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:691.
Munoz P, Vena A, Ceron I, Valerio M, Palomo J, Guinea J, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in heart transplant recipients: two radiologic patterns with a different prognosis. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2014;33(10):1034–40.
Henzler C, Henzler T, Buchheidt D, Nance JW, Weis CA, Vogelmann R, et al. Diagnostic performance of contrast enhanced pulmonary computed tomography angiography for the detection of Angioinvasive pulmonary Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised patients. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04470-6.
•• Bassetti M, Scudeller L, Giacobbe DR, Lamoth F, Righi E, Zuccaro V, et al. Developing definitions for invasive fungal diseases in critically ill adult patients in intensive care units. Protocol of the FUNgal infections definitions in ICU patients (FUNDICU) project. Mycoses. 2019;62(4):310–9 Protocol of project aimed to develop definitions for invasive fungal diseases in intensive care setting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Lore Vanderbeke is a research fellow of the Research Foundation - Flanders (FWO Vlaanderen). Johan Maertens reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from MSD; grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Gilead Sciences; grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, Inc.; personal fees and non-financial support from Basilea; personal fees and non-financial support from Cidara; personal fees and non-financial support from F2G; grants from Immy; and grants from OLM outside the submitted work. Joost Wauters reports grants from MSD, other from Gillead, and grants from Pfizer outside the submitted work. Katrien Lagrou reports non-financial support from Pfizer, personal fees and non-financial support from MSD, personal fees from SMB Laboratoires, personal fees from Gilead, and personal fees from FUJIFILM Wako outside the submitted work. Eric Van Wijngaerden declares no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Advances in Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infections
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanderbeke, L., Van Wijngaerden, E., Maertens, J. et al. Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 14, 166–173 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-020-00383-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-020-00383-6