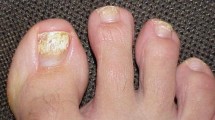
Abstract
Purpose of Review
The incidence of onychomycosis by Aspergillus has shown an increase in recent years, representing 34–60% of onychomycosis due to non-dermatophyte molds. At least 26 species of Aspergillus causing onychomycosis have been reported, some of which may be morphologically indistinguishable but genetically distinct, even in their susceptibility profile to antifungals. So in the diagnosis of this pathology, it is necessary to use both conventional and molecular methods to get to the identification of the fungus at the species level and thus establish the appropriate treatment.
Recent Findings
The current taxonomy of the genus Aspergillus includes sections that are made up of species whose morphology is almost identical but have different patterns of susceptibility to antifungals. Advances in the taxonomy of these fungi reveal the need to combine phenotypic methods (analysis of microscopic and macroscopic characteristics) with molecular ones (amplification and sequencing of fragments of the β-tubulin and calmodulin genes) to achieve their correct identification at the level of species.
Summary
From the demonstration of Aspergillus as the primary agent of onychomycosis, an increase in the incidence of this pathology worldwide has been reported, whose treatment is usually complicated. Various species of Aspergillus can cause nail infection but may respond differently to antifungal treatment, so it is important to know their epidemiology, clinical characteristics, etiologic agents, diagnostic methods, and treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Martínez-Herrera EO, Arroyo-Camarena S, Tejada-García DL, Porras-López CF, Arenas R. Onychomycosis due to opportunistic molds. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3):334–7. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• López-Jodra O, Torres-Rodríguez JM. Unusual fungal species causing onychomycosis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1999;16(S):S11–5. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• Wijesuriya T, Kottahachchi J, Gunasekara TDCP, Bulugahapitiya U, Ranasinghe KNP, Neluka Fernando S, et al. Aspergillus species: An emerging pathogen in onychomycosis among diabetics. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;19(6):811. This paper reports clinical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
de Magalhães LK, Machado Barbosa de Castro CM, Nogueira Cambuim F II, de Oliveira JC, Delgado M, de Melo Rego RS. Hongos filamentosos no dermatofitos: onicomicosis en cuatro pacientes infectados con el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2008;25(1):45–9.
•• Nouripour-Sisakht S, Mirhendi H, Shidfar MR, Ahmadi B, Rezaei-Matehkolaei A, Geramishoar M, et al. Aspergillus species as emerging causative agents of onychomycosis. J Mycol Med. 2015;25(2):101–7. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Ballesté R, Mousqués N, Gezuele E. Onicomicosis. Revisión del tema. Rev Medica Urug. 2003;19:93–106.
Baran R, Tosti A, Piraccini BM. Uncommon clinical patterns of Fusarium nail infection: report of three cases. Br J Dermatol. 1997;136(3):424–7.
• Escobar ML, Carmona-Fonseca J. Onicomicosis por hongos ambientales no dermatofíticos. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2003;20:6–10. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Cavallera E, Asbati M. Onicomicosis por hongos filamentosos no dermatófitos en Cádiz. Dermatol Venezol. 2006;44(1):4–10.
Palacio A, Pazos C, Cuétara S. Onicomicosis por hongos filamentosos no dermatófitos en Cádiz. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2001;19(7):345–6.
• Bonifaz A, Cruz-Aguilar P, Ponce RM. Onychomycosis by molds. Report of 78 cases. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17(1):70–2. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Ramirez Hobak L, Gomez-Stenz A, Vega Sanchez DC, Arenas R. Onicomicosis por mohos no dermatofitos. Una revisión. Dermatol CMQ. 2017;15(3):184–94.
•• Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C, Cooper EA, Brintnell W, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. Systematic review of nondermatophyte mold onychomycosis: Diagnosis, clinical types, epidemiology, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(3):494–502. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Negroni R, Arechavala A, Bohnvel P. Hongos miceliales no dermatofitos en onicodistrofias. Experiencia de un centro médico privado en Buenos Aires. Dermatol Argent. 2008;14(2):118–23. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Mahmoudabadi AZ, Zarrin M. Onychomycosis with Aspergillus flavus; a case report from Iran. Pak J Med Sci. 2005;21(4):497–8. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Godoy-Martinez P, Nunes FG, Tomimori-Yamashita J, Urrutia M, Zaror L, Silva V, et al. Onychomycosis in São Paulo, Brazil. Mycopathologia. 2009;168(3):111–6. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Hilmioǧlu-Polat S, Metin DY, Inci R, Dereli T, Kilinç I, Tümbay E. Non-dermatophytic molds as agents of onychomycosis in Izmir, Turkey—a prospective study. Mycopathologia. 2005;160(2):125–8. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Bereston MES, Waring WS. Onychomycosis and dermatomycosis caused by Trichophyton Rubrum and Aspergillus nidulans. Arch Dermatol Syphilol. 1945;52(3):162–5.
• Nkondjo Minkoumou S, Fabrizi V, Papini M. Onychomycosis in Cameroon: A clinical and epidemiological study among dermatological patients. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51(12):1474–7. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Chadeganipour M, Nilipour S, Ahmadi G. Study of onychomycosis in Isfahan, Iran. Mycoses. 2010;53(2):153–7. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Ranawaka RR, de Silva N, Ragunathan RW. Non-dermatophyte mold onychomycosis in Sri Lanka. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18(1):7. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Hajoui ZM, Zeroual Z, Ghfir B, Moustachi A, Lyagoubi M, Aoufi S. The mold onychomycosis in Morocco: About 150 isolated cases in 20 years. J Mycol Med. 2012;22(3):221–4. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• Gupta AK, Nakrieko KA. Molecular determination of mixed infections of dermatophytes and nondermatophyte molds in individuals with onychomycosis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2014;104(4):330–6. This paper reports diagnostic methods for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Raghavendra K, Yadav D, Kumar A, Sharma M, Bhuria J, Chand A. The nondermatophyte molds: Emerging as leading cause of onychomycosis in south-east Rajasthan. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(2):92. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• Ramani R, Srinivas CR, Ramani A, Kumari TGR, Shivananda PG. Molds in Onychomycosis. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32(12):877–8. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Romano C, Gianni C, Difonzo EM. Retrospective study of onychomycosis in Italy: 1985–2000. Mycoses. 2005;48(1):42–4. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Leelavathi M, Tzar MN, Adawiah J. Common microorganisms causing onychomycosis in tropical climate. Sains Malays. 2012;41(6):697–700. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Bokhari MA, Hussain I, Jahangir M, Haroon TS, Aman S, Khurshid K. Onychomycosis in Lahore, Pakistan. Int J Dermatol. 1999;38(8):591–5. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Hashemi SJ, Gerami M, Zibafar E, Daei M, Moazeni M, Nasrollahi A. Onychomycosis in Tehran: Mycological study of 504 patients. Mycoses. 2010;53(3):251–5. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• English MP, Atkinson R. Onychomycosis in elderly chiropody patients. Br J Dermatol. 1974;91(1):67–72. This paper reports clinical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Soltani M, Khosravi AR, Shokri H, Sharifzadeh A, Balal A. A study of onychomycosis in patients attending a dermatology center in Tehran, Iran. J Mycol Med. 2015;25(2):e81–7. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Bereston MES, Keil H. Onychomycosis due to Aspergillus flavus. Arch Dermatol Syphilol. 1941;44(3):420–5.
• Tsang CC, Hui TWS, Lee KC, Chen JHK, Ngan AHY, Tam EWT, et al. Genetic diversity of Aspergillus species isolated from onychomycosis and Aspergillus hongkongensis sp. nov., with implications to antifungal susceptibility testing. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;84(2):125–34. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
•• Gianni C, Romano C. Clinical and histological aspects of toenail onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus spp.: 34 cases treated with weekly intermittent terbinafine. Dermatology. 2004;209(2):104–10. This paper mentions the treatment for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Kim DM, Suh MK, Ha GY, Sohng SH. Fingernail onychomycosis due to Aspergillus niger. Ann Dermatol. 2012;24(4):459–63. This paper mentions general aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Gugnani HC, Vijayan VK, Tyagi P, Sharma S, Stchigel AM, Guarro J. Onychomycosis due to Emericella quadrilineata. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42(2):914–6. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Garcia-Martos P, Guarro J, Gene J, Mira J, Linares M, Ortoneda M. Onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus sclerotiorum. J Mycol Med. 2001;11(4):222–4. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Zotti M, Machetti M, Persi A, Barabino G, Parodi A. Onychomycosis: First case due to Aspergillus nomius. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91(5):591–2. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Falahati M, Ghojoghi A, Abastabar M, Ghasemi Z, Farahyar S, Roudbary M, et al. The first case of total dystrophic onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus clavatus resistant to antifungal drugs. Mycopathologia. 2016;181(3–4):273–7. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Zarei F, Mirhendi H, Fakhim H, Geramishoar M. The first case of onychomycosis due to Aspergillus uvarum (section Nigri). Mycoses. 2015;58(4):239–42. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
Brasch J, Varga J, Jensen JM, Egberts F, Tintelnot K. Nail infection by Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis. Med Mycol. 2009;47(6):658–62. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Zotti M, Machetti M, Perotti M, Barabino G, Persi A. A new species, Aspergillus persii, as an agent of onychomycosis. Med Mycol. 2010;48(4):656–60. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Kristensen L, Stenderup J, Otkjær A. Onychomycosis due to Aspergillus tamarii in a 3-year-old boy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85:261–2. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
Nyongesa BW, Okoth S, Ayugi V. Identification key for Aspergillus species isolated from maize and soil of Nandi Country, Kenya. Adv Microbiol. 2015;5:205–29.
Chen AJ, Frisvad JC, Sun BD, Varga J, Kocsubé S, Dijksterhuis J, et al. Aspergillus section Nidulantes (formerly Emericella): Polyphasic taxonomy, chemistry and biology. Stud Mycol. 2016;84:1–118.
•• Balajee SA, Houbraken J, Verweij PE, Hong SB, Yaghuchi T, Varga J, et al. Aspergillus species identification in the clinical setting. Stud Mycol. 2007;59:39–46. This paper reports diagnostic methods for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Lee BJ, Kim IJ, Suh SB. Two cases of onychomycosis due to Aspergillus repens. Korean J Dermatol. 1981;19:881–6. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
Uribe B, Colin J, Arce M, Arenas R. Aspergillus niger. Dermatol CMQ. 2017;15(3):197–8.
• Moore M, Weiss RS. Onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus terreus. J Invest Dermatol. 1948;11(3):215–23. This paper mentions historical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Rosenthal SA, Stritzler R, Villafane J. Onychomycosis ca 52(3): used by Aspergillus fumigatus. Report of a case. Arch Derm. 1968;97:685–7. This paper mentions historical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Torres-Rodriguez JM, Madrenys-Brunet N, Siddat M, López-Jodra O, Jimenez T. Aspergillus versicolor as cause of onychomycosis: Report of 12 cases and susceptibility testing to antifungal drugs. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 1998;11(1):25–31. This paper mentions the treatment for onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Takahata Y, Hiruma M, Sugita T, Muto M. A case of onychomycosis due to Aspergillus sydowii diagnosed using DNA sequence analysis. Mycoses. 2008;51(2):170–3. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
Choudhary SV, Koley S, Mallick S, Bose S, Basak S. Proximal subungual onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus flavus in a HIV- positive patient. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75(4):410–2.
• Veraldi S, Chiaratti A, Harak H. Onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus versicolor. Mycoses. 2009;53(4):363–5. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Ahmadi B, Hashemi SJ, Zaini F, Shidfar MR, Moazeni M, Mousavi B, et al. A case of onychomycosis caused by Aspergillus candidus. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2012;1(1):45–8. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
•• Banu A, Anand M, Eswari L. A rare case of onychomycosis in all 10 fingers of an immunocompetent patient. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4(4):302–4. This paper reports clinical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
• Zotti M, Agnoletti AF, Vizzini A, Cozzani E, Parodi A. Onychomycosis from Aspergillus melleus, a novel pathogen for humans. Fungal identification and in vitro drug susceptibility. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24(12):966–8. This paper reports a new species in onychomycosis.
• Noguchi H, Hiruma M, Miyashita A, Makino K, Miyata K, Ihn H. A case of fingernail onychomycosis due to Aspergillus flavus. Jpn J Med Mycol. 2016;57(2):21–5. This paper reports clinical aspects of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
Matsuyama Y, Nakamura T, Hagi T, Asanuma K, Sudo A. Subungual onychomycosis due to Aspergillus niger mimicking a glomus tumor: A case report. Biomed Rep. 2017;6:532–4.
Álvarez-Salafranca M, Hernández-Ostiz S, Salvo Gonzalo S, Ara MM. Onicomicosis subungueal proximal por Aspergillus niger: un simulador de melanoma maligno subungueal. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;108(5):482–5.
Tamer F, Yuksel ME. Onychomycosis due to Aspergillus niger without black nail discoloration: A case report. Our Dermatol Online. 2017;8(2):233–4.
Akpinar Kara Y, Erdogan FG, Cologlu D. A case of onychomycosis due to Aspergillus flavus in all fingernails and toenails of an immunocompromised patient. J Clin Exp Dermatol Res. 2017;9(1):9–11.
Fernández MS, Rojas FD, Cattana ME, Sosa MA, Mangiaterra ML, Giusiano GE. Aspergillus terreus complex: An emergent opportunistic agent of Onychomycosis. Mycoses. 2013;56(4):477–8.
•• Grover C, Reddy BSN, Chaturvedi KU. Onychomycosis and the diagnostic significance of nail biopsy. J Dermatol. 2003;30(2):116–22. This paper reports diagnostic methods for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
• Afshar P, Khodavaisy S, Kalhori S, Ghasemi M, Razavyoon T. Onychomycosis in North-East of Iran. Iran J Microbiol. 2014;6(2):98–103. This paper mentions aspects of the epidemiology of onychomycosis by Aspergillus.
•• Bonifaz A, Rios-Yuil JM, Arenas R, Araiza J, Fernández R, Mercadillo-Pérez P, et al. Comparison of direct microscopy, culture and calcofluor white for the diagnosis of onychomycosis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2013;30(2):109–11. This paper reports diagnostic methods for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
Frías-De-León MG, Rosas-de Paz E, Arenas R, Atoche C, Duarte-Escalante E, Molina de Soschin D, et al. Identification of Aspergillus tubingensis in a primary skin infection. J Mycol Med. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2018.02.013.
• Tupaki-Sreepurna A, Jishnu B, Thanneru V, Sharma S, Gopi A, Sundaram M, et al. An assessment of in vitro antifungal activities of efinaconazole and itraconazole against common non-dermatophyte fungi causing onychomycosis. J Fungi. 2017;3(2):20. This paper mentions the treatment for onychomycosis by Aspergillus .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This paper is part of the Topical Collection on Fungal Infections of Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frías-De-León, M.G., Espinosa-Hernández, V.M., Bonifaz, A. et al. Onychomycosis Due to Aspergillus spp.: a Current Review. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 12, 112–119 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-018-0319-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-018-0319-8