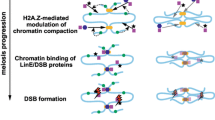
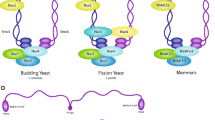
Abstract
During meiosis, crossing over allows for the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, enabling their segregation and leading to genetic variation in the resulting gametes. Spo11, a topoisomerase-like protein expressed in eukaryotes, and diverse accessory factors induce programmed double-strand breaks (DSBs) to initiate meiotic recombination during the early phase of meiosis after DNA replication. DSBs are further repaired via meiosis-specific homologous recombination. Studies on budding yeast have provided insights into meiosis and genetic recombination and have improved our understanding of higher eukaryotic systems. Cohesin, a chromosome-associated multiprotein complex, mediates sister chromatid cohesion (SCC), and is conserved from yeast to humans. Diverse cohesin subunits in budding yeast have been identified in DNA metabolic pathways, such as DNA replication, chromosome segregation, recombination, DNA repair, and gene regulation. During cell cycle, SCC is established by multiple cohesin subunits, which physically bind sister chromatids together and modulate proteins that involve in the capturing and separation of sister chromatids. Cohesin components include at least four core subunits that establish and maintain SCC: two structural maintenance chromosome subunits (Smc1 and Smc3), an α-kleisin subunit (Mcd1/Scc1 during mitosis and Rec8 during meiosis), and Scc3/Irr1 (SA1 and SA2). In addition, the cohesin-associated factors Pds5 and Rad61 regulate structural modifications and cell cyclespecific dynamics of chromatin to ensure accurate chromosome segregation. In this review, we discuss SCC and the recombination pathway, as well as the relationship between the two processes in budding yeast, and we suggest a possible conserved mechanism for meiotic chromosome dynamics from yeast to humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, S. and Roeder, G.S. 2000. Zip3 provides a link between recombination enzymes and synaptonemal complex proteins. Cell 102, 245–255.
Bishop, D.K. and Zickler, D. 2004. Early decision: Meiotic crossover interference prior to stable strand exchange and synapsis. Cell 117, 9–15.
Börner, G.V., Kleckner, N., and Hunter, N. 2004. Crossover/noncrossover differentiation, synaptonemal complex formation, and regulatory surveillance at the leptotene/zygotene transition of meiosis. Cell 117, 29–45.
Brar, G.A., Kiburz, B.M., Zhang, Y., Kim, J.E., White, F., and Amon, A. 2006. Rec8 phosphorylation and recombination promote the step-wise loss of cohesins in meiosis. Nature 441, 532–536.
Brooker, A.S. and Berkowitz, K.M. 2014. The roles of cohesins in mitosis, meiosis, and human health and disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 1170, 229–266.
Brown, M.S., Grubb, J., Zhang, A., Rust, M.J., and Bishop, D.K. 2015. Small Rad51 and Dmc1 complexes often co-occupy both ends of a meiotic DNA double strand break. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005653.
Cejka, P., Cannavo, E., Polaczek, P., Masuda-Sasa, T., Pokharel, S., Campbell, J.L., and Kowalczykowski, S.C. 2010. DNA end resection by Dna2-Sgs1-RPA and its stimulation by Top3-Rmi1 and Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2. Nature 467, 112–116.
Challa, K., Lee, M.S., Shinohara, M., Kim, K.P., and Shinohara, A. 2016. Rad61/Wpl1 (Wapl), a cohesin regulator, controls chromosome compaction during meiosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 3190–3203.
Chan, K.L., Gligoris, T., Upcher, W., Kato, Y., Shirahige, K., Nasmyth, K., and Beckouët, F. 2013. Pds5 promotes and protects cohesin acetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 13020–13025.
Cheng, C.H., Lo, Y.H., Liang, S.S., Ti, S.C., Lin, F.M., Yeh, C.H., Huang, H.Y., and Wang, T.F. 2006. SUMO modifications control assembly of synaptonemal complex and polycomplex in meiosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 20, 2067–2081.
Choi, D.H., Lee, R., Kwon, S.H., and Bae, S.H. 2013. Hrq1 functions independently of Sgs1 to preserve genome integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Microbiol. 51, 105–112.
Chua, P.R. and Roeder, G.S. 1998. Zip2, a meiosis-specific protein required for the initiation of chromosome synapsis. Cell 93, 349–359.
Chung, W.H. 2014. To peep into Pif1 helicase: Multifaceted all the way from genome stability to repair-associated DNA synthesis. J. Microbiol. 52, 89–98.
Cloud, V., Chan, Y.L., Grubb, J., Budke, B., and Bishop, D.K. 2012. Rad51 is an accessory factor for Dmc1-mediated joint molecule formation during meiosis. Science 337, 1222–1225.
Deardorff, M.A., Wilde, J.J., Albrecht, M., Dickinson, E., Tennstedt, S., Braunholz, D., Mönnich, M., Yan, Y., Xu, W., Gil-Rodríguez, M.C., et al. 2012. RAD21 mutations cause a human cohesinopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 90, 1014–1027.
DeMare, L.E., Leng, J., Cotney, J., Reilly, S.K., Yin, J., Sarro, R., and Noonan, J.P. 2013. The genomic landscape of cohesin-associated chromatin interactions. Genome Res. 23, 1224–1234.
Denison, S.H., Käfer, E., and May, G.S. 1993. Mutation in the bimD gene of Aspergillus nidulans confers a conditional mitotic block and sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. Genetics 134, 1085–1096.
Gligoris, T.G., Scheinost, J.C., Bürmann, F., Petela, N., Chan, K.L., Uluocak, P., Beckouët, F., Gruber, S., Nasmyth, K., and Löwe, J. 2014. Closing the cohesin ring: structure and function of its Smc3- kleisin interface. Science 346, 963–967.
Gruber, S., Haering, C.H., and Nasmyth, K. 2003. Chromosomal cohesin forms a ring. Cell 112, 765–777.
Guacci, V., Yamamoto, A., Strunnikov, A., Kingsbury, J., Hogan, E., Meluh, P., and Koshland, D. 1993. Structure and function of chromosomes in mitosis of budding yeast, pp. 677–685. In Cold spring harbor symposia on quantitative biology Vol. 58. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Gullerova, M. and Proudfoot, N.J. 2008. Cohesin complex promotes transcriptional termination between convergent genes in S. pombe. Cell 132, 983–995.
Haering, C.H., Farcas, A.M., Arumugam, P., Metson, J., and Nasmyth, K. 2008. The cohesin ring concatenates sister DNA molecules. Nature 454, 297–301.
Haering, C.H., Löwe, J., Hochwagen, A., and Nasmyth, K. 2002. Molecular architecture of SMC proteins and the yeast cohesin complex. Mol. Cell 9, 773–788.
Haering, C.H., Schoffnegger, D., Nishino, T., Helmhart, W., Nasmyth, K., and Löwe, J. 2004. Structure and stability of cohesin’s Smc1-kleisin interaction. Mol. Cell 15, 951–964.
Hartman, T., Stead, K., Koshland, D., and Guacci, V. 2000. Pds5p is an essential chromosomal protein required for both sister chromatid cohesion and condensation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Biol. 151, 613–626.
Hirano, M. and Hirano, T. 2002. Hinge-mediated dimerization of SMC protein is essential for its dynamic interaction with DNA. EMBO J. 21, 5733–5744.
Hong, S., Sung, Y., Yu, M., Lee, M., Kleckner, N., and Kim, K.P. 2013. The logic and mechanism of homologous recombination partner choice. Mol. Cell 51, 440–453.
Horsfield, J.A., Print, C.G., and Mönnich, M. 2012. Diverse developmental disorders from the one ring: distinct molecular pathways underlie the cohesinopathies. Front. Genet. 3, 171.
Hunter, N. and Kleckner, N. 2001. The single-end invasion: an asymmetric intermediate at the double-strand break to double-Holliday junction transition of meiotic recombination. Cell 106, 59–70.
Jin, H., Guacci, V., and Yu, H.G. 2009. Pds5 is required for homologue pairing and inhibits synapsis of sister chromatids during yeast meiosis. J. Cell Biol. 186, 713–725.
Katis, V.L., Lipp, J.J., Imre, R., Bogdanova, A., Okaz, E., Habermann, B., Mechtler, K., Nasmyth, K., and Zachariae, W. 2010. Rec8 phosphorylation by casein kinase 1 and Cdc7-Dbf4 kinase regulates cohesin cleavage by separase during meiosis. Dev. Cell 18, 397–409.
Keeney, S. 2001. Mechanism and control of meiotic recombination initiation. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 52, 1–53.
Kim, K.P. and Mirkin, E.V. 2018. So similar yet so different: The two ends of a double strand break. Mutat. Res. 809, 70–80.
Kim, K.P., Weiner, B.M., Zhang, L., Jordan, A., Dekker, J., and Kleckner, N. 2010. Sister cohesion and structural axis components mediate homolog bias of meiotic recombination. Cell 143, 924–937.
Klein, F., Mahr, P., Galova, M., Buonomo, S.B., Michaelis, C., Nairz, K., and Nasmyth, K. 1999. A central role for cohesins in sister chromatid cohesion, formation of axial elements, and recombination during yeast meiosis. Cell 98, 91–103.
Kowalec, P., Fronk, J., and Kurlandzka, A. 2017. The Irr1/Scc3 protein implicated in chromosome segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a dual nuclear-cytoplasmic localization. Cell Div. 12, 1.
Krantz, I.D., McCallum, J., DeScipio, C., Kaur, M., Gillis, L.A., Yaeger, D., Jukofsky, L., Wasserman, N., Bottani, A., Morris, C.A., et al. 2004. Cornelia de Lange syndrome is caused by mutations in NIPBL, the human homolog of Drosophila melanogaster Nipped- B. Nat. Genet. 36, 631–635.
Kueng, S., Hegemann, B., Peters, B.H., Lipp, J.J., Schleiffer, A., Mechtler, K., and Peters, J.M. 2006. Wapl controls the dynamic association of cohesin with chromatin. Cell 127, 955–967.
Kulemzina, I., Schumacher, M.R., Verma, V., Reiter, J., Metzler, J., Failla, A.V., Lanz, C., Sreedharan, V.T., Rätsch, G., and Ivanov, D. 2012. Cohesin rings devoid of Scc3 and Pds5 maintain their stable association with the DNA. PLoS Genet. 8, e1002856.
Lao, J.P., Cloud, V., Huan, C.C., Grubb, J., Thacker, D., Lee, C.Y., Dresser, M.E., Hunter, N., and Bishop, D.K. 2013. Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003978.
Lao, O., Lu, T.T., Nothnagel, M., Junge, O., Freitag-Wolf, S., Caliebe, A., Balascakova, M., Bertranpetit, J., Bindoff, L.A., Comas, D., et al. 2008. Correlation between genetic and geographic structure in Europe. Curr. Biol. 18, 1241–1248.
Lara-Pezzi, E., Pezzi, N., Prieto, I., Barthelemy, I., Carreiro, C., Martínez, A., Maldonado-Rodríguez, A., López-Cabrera, M., and Barbero, J.L. 2004. Evidence of a transcriptional co-activator function of cohesin STAG/SA/Scc3. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 6553–6559.
Larionov, V., Karpova, T., Kouprina, N., and Jouravleva, G. 1985. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with impaired maintenance of centromeric plasmids. Curr. Genet. 10, 15–20.
Laurent, J.M., Young, J.H., Kachroo, A.H., and Marcotte, E.M. 2016. Efforts to make and apply humanized yeast. Brief Funct. Genomics 15, 155–163.
Lee, J., Okada, K., Ogushi, S., Miyano, T., Miyake, M., and Yamashita, M. 2006. Loss of Rec8 from chromosome arm and centromere region is required for homologous chromosome separation and sister chromatid separation, respectively, in mammalian meiosis. Cell Cycle 5, 1448–1455.
Li, Y., Muir, K.W., Bowler, M.W., Metz, J., Haering, C.H., and Panne, D. 2018. Structural basis for Scc3-dependent cohesin recruitment to chromatin. Elife 7, e38356.
Lin, W., Jin, H., Liu, X., Hampton, K., and Yu, H.G. 2011. Scc2 regulates gene expression by recruiting cohesin to the chromosome as a transcriptional activator during yeast meiosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 22, 1985–1996.
Liu, J., Feldman, R., Zhang, Z., Deardorff, M.A., Haverfield, E.V., Kaur, M., Li, J.R., Clark, D., Kline, A.D., Waggoner, D.J., et al. 2009. SMC1A expression and mechanism of pathogenicity in probands with X-linked Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 30, 1535–1542.
Longhese, M.P., Bonetti, D., Guerini, I., Manfrini, N., and Clerici, M. 2009. DNA double-strand breaks in meiosis: checking their formation, processing and repair. DNA Repair (Amst.) 8, 1127–1138.
Lopez-Serra, L., Lengronne, A., Borges, V., Kelly, G., and Uhlmann, F. 2013. Budding yeast Wapl controls sister chromatid cohesion maintenance and chromosome condensation. Curr. Biol. 23, 64–69.
Losada, A. and Hirano, T. 2005. Dynamic molecular linkers of the genome: the first decade of SMC proteins. Genes Dev. 19, 1269–1287.
Lukaszewicz, A., Shodhan, A., and Loidl, J. 2015. Exo1 and Mre11 execute meiotic DSB end resection in the protist Tetrahymena. DNA Repair 35, 137–143.
Makrantoni, V. and Marston, A.L. 2018. Cohesin and chromosome segregation. Curr. Biol. 28, R688–R693.
Mannini, L., Liu, J., Krantz, I.D., and Musio, A. 2010. Spectrum and consequences of SMC1A mutations: the unexpected involvement of a core component of cohesin in human disease. Hum. Mutat. 31, 5–10.
Marcon, E. and Moens, P.B. 2005. The evolution of meiosis: recruitment and modification of somatic DNA-repair proteins. Bioessays 27, 795–808.
Markowitz, T.E., Suarez, D., Blitzblau, H.G., Patel, N.J., Markhard, A.L., MacQueen, A.J., and Hochwagen, A. 2017. Reduced dosage of the chromosome axis factor Red1 selectively disrupts the meiotic recombination checkpoint in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006928.
Marston, A.L. 2014. Chromosome segregation in budding yeast: sister chromatid cohesion and related mechanisms. Genetics 196, 31–63.
Melby, T.E., Ciampaglio, C.N., Briscoe, G., and Erickson, H.P. 1998. The symmetrical structure of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) and MukB proteins: long, antiparallel coiled coils, folded at a flexible hinge. J. Cell Biol. 142, 1595–1604.
Misulovin, Z., Pherson, M., Gause, M., and Dorsett, D. 2018. Brca2, Pds5 and Wapl differentially control cohesin chromosome association and function. PLoS Genet. 14, e1007225.
Molnar, M., Bahler, J., Sipiczki, M., and Kohli, J. 1995. The rec8 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is involved in linear element formation, chromosome pairing and sister-chromatid cohesion during meiosis. Genetics 141, 61–73.
Monnich, M., Kuriger, Z., Print, C.G., and Horsfield, J.A. 2011. A zebrafish model of Roberts syndrome reveals that Esco2 depletion interferes with development by disrupting the cell cycle. PLoS One 6, e20051.
Morin, I., Ngo, H.P., Greenall, A., Zubko, M.K., Morrice, N., and Lydall, D. 2008. Checkpoint-dependent phosphorylation of Exo1 modulates the DNA damage response. EMBO J. 27, 2400–2410.
Moynahan, M.E. and Jasin, M. 2010. Mitotic homologous recombination maintains genomic stability and suppresses tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 196–207.
Muir, K.W., Kschonsak, M., Li, Y., Metz, J., Haering, C.H., and Panne, D. 2016. Structure of the Pds5-Scc1 complex and implications for cohesin function. Cell Rep. 14, 2116–2126.
Musio, A., Selicorni, A., Focarelli, M.L., Gervasini, C., Milani, D., Russo, S., Vezzoni, P., and Larizza, L. 2006. X-linked Cornelia de Lange syndrome owing to SMC1L1 mutations. Nat. Genet. 38, 528–530.
Nanbu, T., Nguyễn, L.C., Habib, A.G., Hirata, N., Ukimori, S., Tanaka, D., Masuda, K., Takahashi, K., Yukawa, M., Tsuchiya, E., et al. 2015. Fission yeast Exo1 and Rqh1-Dna2 redundantly contribute to resection of uncapped telomeres. PLoS One 10, e0140456.
Nasmyth, K. and Haering, C.H. 2009. Cohesin: its roles and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Genet. 43, 525–558.
Nasmyth, K., Peters, J.M., and Uhlmann, F. 2000. Splitting the chromosome: Cutting the ties that bind sister chromatids. Science 288, 1379–1385.
Neale, M.J., Pan, J., and Keeney, S. 2005. Endonucleolytic processing of covalent protein-linked DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 436, 1053–1057.
New, J.H., Sugiyama, T., Zaitseva, E., and Kowalczykowski, S.C. 1998. Rad52 protein stimulates DNA strand exchange by Rad51 and replication protein A. Nature 391, 407–410.
Niu, H., Chung, W.H., Zhu, Z., Kwon, Y., Zhao, W., Chi, P., Prakash, R., Seong, C., Liu, D., Lu, L., et al. 2010. Mechanism of the ATPdependent DNA end-resection machinery from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 467, 108–111.
Orgil, O., Matityahu, A., Eng, T., Guacci, V., Koshland, D., and Onn, I. 2015. A conserved domain in the Scc3 subunit of cohesin mediates the interaction with both Mcd1 and the cohesin loader complex. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005036.
Panizza, S., Tanaka, T., Hochwagen, A., Eisenhaber, F., and Nasmyth, K. 2000. Pds5 cooperates with cohesin in maintaining sister chromatid cohesion. Curr. Biol. 10, 1557–1564.
Remeseiro, S., Cuadrado, A., Kawauchi, S., Calof, A.L., Lander, A.D., and Losada, A. 2013. Reduction of Nipbl impairs cohesin loading locally and affects transcription but not cohesion-dependent functions in a mouse model of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1831, 2097–2102.
Remeseiro, S. and Losada, A. 2013. Cohesin, a chromatin engagement ring. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 25, 63–71.
Rogacheva, M.V., Manhart, C.M., Chen, C., Guarne, A., Surtees, J., and Alani, E. 2014. Mlh1-Mlh3, a meiotic crossover and DNA mismatch repair factor, is a Msh2-Msh3-stimulated endonuclease. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 5664–5673.
Rowland, B.D., Roig, M.B., Nishino, T., Kurze, A., Uluocak, P., Mishra, A., Beckouët, F., Underwood, P., Metson, J., Imre, R., et al. 2009. Building sister chromatid cohesion: Smc3 acetylation counteracts an antiestablishment activity. Mol. Cell 33, 763–774.
Sasanuma, H., Tawaramoto, M.S., Lao, J.P., Hosaka, H., Sanda, E., Suzuki, M., Yamashita, E., Hunter, N., Shinohara, M., Nakagawa, A., et al. 2013. A new protein complex promoting the assembly of Rad51 filaments. Nat. Commun. 4, 1676.
Sekigawa, M., Kunoh, T., Wada, S., Mukai, Y., Ohshima, K., Ohta, S., Goshima, N., Sasaki, R., and Mizukami, T. 2010. Comprehensive screening of human genes with inhibitory effects on yeast growth and validation of a yeast cell-based system for screening chemicals. J. Biomol. Screen 15, 368–378.
Serrentino, M.E., Chaplais, E., Sommermeyer, V., and Borde, V. 2013. Differential association of the conserved SUMO ligase Zip3 with meiotic double-strand break sites reveals regional variations in the outcome of meiotic recombination. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003416.
Shinohara, M., Oh, S.D., Hunter, N., and Shinohara, A. 2008. Crossover assurance and crossover interference are distinctly regulated by the ZMM proteins during yeast meiosis. Nat. Genet. 40, 299–309.
Storlazzi, A., Tesse, S., Ruprich-Robert, G., Gargano, S., Pöggeler, S., Kleckner, N., and Zickler, D. 2008. Coupling meiotic chromosome axis integrity to recombination. Genes Dev. 22, 796–809.
Strunnikov, A.V., Larionov, V.L., and Koshland, D. 1993. SMC1: An essential yeast gene encoding a putative head-rod-tail protein is required for nuclear division and defines a new ubiquitous family. J. Cell Biol. 123, 1635–1648.
Sugiyama, T., Zaitseva, E.M., and Kowalczykowski, S.C. 1997. A single-stranded DNA-binding protein is needed for efficient presynaptic complex formation by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 7940–7945.
Sumara, I., Vorlaufer, E., Gieffers, C., Peters, B.H., and Peters, J.M. 2000. Characterization of vertebrate cohesin complexes and their regulation in prophase. J. Cell Biol. 151, 749–762.
Sun, X., Huang, L., Markowitz, T.E., Blitzblau, H.G., Chen, D., Klein, F., and Hochwagen, A. 2015. Transcription dynamically patterns the meiotic chromosome-axis interface. Elife 10, 4.
Sung, P. 1994. Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein. Science 265, 1241–1243.
Sutani, T., Kawaguchi, T., Kanno, R., Itoh, T., and Shirahige, K. 2009. Budding yeast Wpl1(Rad61)-Pds5 complex counteracts sister chromatid cohesion-establishing reaction. Curr. Biol. 19, 492–427.
Sym, M., Engebrecht, J.A., and Roeder, G.S. 1993. ZIP1 is a synaptonemal complex protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell 72, 365–378.
Symington, L.S., Rothstein, R., and Lisby, M. 2014. Mechanisms and regulation of mitotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 198, 795–835.
Szankasi, P. and Smith, G.R. 1995. A role for exonuclease I from S. pombe in mutation avoidance and mismatch correction. Science 267, 1166–1169.
Tanaka, K., Hao, Z., Kai, M., and Okayama, H. 2001. Establishment and maintenance of sister chromatid cohesion in fission yeast by a unique mechanism. EMBO J. 20, 5779–5790.
Tonkin, E.T., Wang, T.J., Lisgo, S., Bamshad, M.J., and Strachan, T. 2004. NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Nat. Genet. 36, 636–641.
Tran, P.T., Erdeniz, N., Symington, L.S., and Liskay, R.M. 2004. EXO1- A multi-tasking eukaryotic nuclease. DNA Repair 3, 1549–1559.
Tsubouchi, H. and Ogawa, H. 2000. Exo1 roles for repair of DNA double-strand breaks and meiotic crossing over in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 2221–2233.
Tsutsumi, M., Fujiwara, R., Nishizawa, H., Ito, M., Kogo, H., Inagaki, H., Ohye, T., Kato, T., Fujii, T., and Kurahashi, H. 2014. Age-related decrease of meiotic cohesins in human oocytes. PLoS One 9, e96710.
van Heemst, D., James, F., Pöggeler, S., Berteaux-Lecellier, V., and Zickler, D. 1999. Spo76p is a conserved chromosome morphogenesis protein that links the mitotic and meiotic programs. Cell 98, 261–271.
Vega, H., Waisfisz, Q., Gordillo, M., Sakai, N., Yanagihara, I., Yamada, M., van Gosliga, D., Kayserili, H., Xu, C., Ozono, K., et al. 2005. Roberts syndrome is caused by mutations in ESCO2, a human homolog of yeast ECO1 that is essential for the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Nat. Genet. 37, 468–470.
Wold, M.S. 1997. Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, singlestranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 61–92.
Xu, B., Lu, S., and Gerton, J.L. 2014. A deficit in acetylated cohesin leads to nucleolar dysfunction. Rare Dis. 2, e27743.
Yoon, S.W., Lee, M.S., Xaver, M., Zhang, L., Hong, S.G., Kong, Y.J., Cho, H.R., Kleckner, N., and Kim, K.P. 2016. Meiotic prophase roles of Rec8 in crossover recombination and chromosome structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 9296–9314.
Yu, H.G. and Koshland, D.E. 2003. Meiotic condensin is required for proper chromosome compaction, SC assembly, and resolution of recombination-dependent chromosome linkages. J. Cell Biol. 163, 937–947.
Zakharyevich, K., Ma, Y., Tang, S., Hwang, P.Y., Boiteux, S., and Hunter, N. 2010. Temporally and biochemically distinct activities of Exo1 during meiosis: double-strand break resection and resolution of double holliday junctions. Mol. Cell 40, 1001–1015.
Zhang, B., Chang, J., Fu, M., Huang, J., Kashyap, R., Salavaggione, E., Jain, S., Shashikant, K., Deardorff, M.A., Uzielli, M.L., et al. 2009. Dosage effects of cohesin regulatory factor PDS5 on mammalian development: implications for cohesinopathies. PLoS One 4, e5232.
Zhang, B., Jain, S., Song, H., Fu, M., Heuckeroth, R.O., Erlich, J.M., Jay, P.Y., and Milbrandt, J. 2007. Mice lacking sister chromatid cohesion protein PDS5B exhibit developmental abnormalities reminiscent of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Development 134, 3191–3201.
Zhang, Z., Ren, Q., Yang, H., Conrad, M.N., Guacci, V., Kateneva, A., and Dresser, M.E. 2005. Budding yeast PDS5 plays an important role in meiosis and is required for sister chromatid cohesion. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 670–680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S., Joo, J.H., Yun, H. et al. The nature of meiotic chromosome dynamics and recombination in budding yeast. J Microbiol. 57, 221–231 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8541-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8541-9