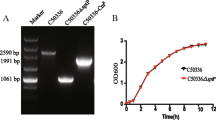
Abstract
Salmonella enterica is a major human pathogen that causes invasive non-typhoidal Salmonellosis (iNTS), resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. Although a number of pre-clinical and clinical studies have reported on the feasibility of developing a safe and effective vaccine against iNTS, there have been no licensed Salmonella vaccines available to protect against NTS strains. Vaccine formulations of highest priority for NTS are live attenuated vaccines, which can elicit effective induction of intestinal mucosal and intracellular bacteria-specific cell mediated immune responses. Since glucose is crucial for intracellular survival and replication in host cells, we constructed strains with mutations in components of the glucose uptake system, called the phosphotransferase system (PTS), and compared the relative virulence and immune responses in mice. In this study, we found that the strain with mutations in both ptsI and crr (KST0556) was the most attenuated strain among the tested strains, and proved to be highly effective in inducing a mucosal immune response that can protect against NTS infections in mice. Thus, we suggest here that KST0556 (ΔptsIΔcrr) is a potential live vaccine candidate for NTS, and may also be a candidate for a live delivery vector for heterologous antigens. Moreover, since PTS is a well-conserved glucose transporter system in both Gramnegative and Gram-positive bacteria, the ptsI and crr genes may be potential targets for creating live bacterial vectors or vaccine strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao, T.T., Feasey, N.A., Gordon, M.A., Keddy, K.H., Angulo, F.J., and Crump, J.A. 2015. Global burden of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella disease, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 21, 941.
Batz, M.B., Hoffmann, S., and Morris, J.G. 2012. Ranking the disease burden of 14 pathogens in food sources in the United States using attribution data from outbreak investigations and expert elicitation. J. Food Prot. 75, 1278–1291.
Bowden, S.D., Hopper-Chidlaw, A.C., Rice, C.J., Ramachandran, V.K., Kelly, D.J., and Thompson, A. 2014. Nutritional and metabolic requirements for the infection of HeLa cells by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. PLoS One 9, e96266.
Bowden, S.D., Rowley, G., Hinton, J.C., and Thompson, A. 2009. Glucose and glycolysis are required for the successful infection of macrophages and mice by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 77, 3117–3126.
Church, J.A., Parker, E.P., Kosek, M.N., Kang, G., Grassly, N.C., Kelly, P., and Prendergast, A.J. 2018. Exploring the relationship between environmental enteric dysfunction and oral vaccine responses. Future Microbiol. 13, 1055–1070.
Coombes, B.K., Coburn, B.A., Potter, A.A., Gomis, S., Mirakhur, K., Li, Y., and Finlay, B.B. 2005. Analysis of the contribution of Salmonella pathogenicity islands 1 and 2 to enteric disease progression using a novel bovine ileal loop model and a murine model of infectious enterocolitis. Infect. Immun. 73, 7161–7169.
Crump, J.A., Kretsinger, K., Gay, K., Hoekstra, R.M., Vugia, D.J., Hurd, S., Segler, S.D., Megginson, M., Luedeman, L.J., Shiferaw, B., et al. 2008. Clinical response and outcome of infection with Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi with decreased susceptibility to fluoroquinolones: a United States foodnet multicenter retrospective cohort study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 1278–1284.
Cryz, S.J.Jr., Vanprapar, N., Thisyakorn, U., Olanratmanee, T., Losonsky, G., Levine, M.M., and Chearskul, S. 1993. Safety and immunogenicity of Salmonella Typhi Ty21a vaccine in young Thai children. Infect. Immun. 61, 1149–1151.
Curtiss, R. and Kelly, S.M. 1987. Salmonella Typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect. Immun. 55, 3035–3043.
Datsenko, K.A. and Wanner, B.L. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6640–6645.
De Reuse, H. and Danchin, A. 1988. The ptsH, ptsI, and crr genes of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: a complex operon with several modes of transcription. J. Bacteriol. 170, 3827–3837.
DeRoeck, D., Clemens, J.D., Nyamete, A., and Mahoney, R.T. 2005. Policymakers’ views regarding the introduction of new-generation vaccines against typhoid fever, shigellosis and cholera in Asia. Vaccine 23, 2762–2774.
DeRoeck, D., Ochiai, R.L., Yang, J., Anh, D.D., Alag, V., and Clemens, J.D. 2008. Typhoid vaccination: the Asian experience. Expert Rev. Vaccines 7, 547–560.
Deutscher, J., Francke, C., and Postma, P.W. 2006. How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70, 939–1031.
Dills, S.S., Apperson, A., Schmidt, M.R., and Saier, M.H.Jr. 1980. Carbohydrate transport in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 44, 385–418.
Engels, E.A., Falagas, M.E., Lau, J., and Bennish, M.L. 1998. Typhoid fever vaccines: a meta-analysis of studies on efficacy and toxicity. BMJ 316, 110–116.
Feasey, N.A., Dougan, G., Kingsley, R.A., Heyderman, R.S., and Gordon, M.A. 2012. Invasive non-typhoidal salmonella disease: an emerging and neglected tropical disease in Africa. Lancet 379, 2489–2499.
Fraser, A., Paul, M., Goldberg, E., Acosta, C.J., and Leibovici, L. 2007. Typhoid fever vaccines: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Vaccine 25, 7848–7857.
Galen, J.E., Simon, R., and Ernst, R.K. 2011. Salmonella expressing detoxified lipopolysaccharide is immunogenic and protective both as an attenuated vaccine and for delivery of foreign antigens. Expert Rev. Vaccines 10, 1679–1682.
Garcia-Del Portillo, F., Pucciarelli, M.G., and Casadesus, J. 1999. DNA adenine methylase mutants of Salmonella Typhimurium show defects in protein secretion, cell invasion, and M cell cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 11578–11583.
Girard, M.P., Steele, D., Chaignat, C.L., and Kieny, M.P. 2006. A review of vaccine research and development: human enteric infections. Vaccine 24, 2732–2750.
Hindle, Z., Chatfield, S.N., Phillimore, J., Bentley, M., Johnson, J., Cosgrove, C.A., Ghaem-Maghami, M., Sexton, A., Khan, M., Brennan, F.R., et al. 2002. Characterization of Salmonella enterica derivatives harboring defined aroC and Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system (ssaV) mutations by immunization of healthy volunteers. Infect. Immun. 70, 3457–3467.
Hoiseth, S.K. and Stocker, B.A. 1981. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella Typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature 291, 238–239.
Kantele, A., Pakkanen, S.H., Siitonen, A., Karttunen, R., and Kantele, J.M. 2012. Live oral typhoid vaccine Salmonella Typhi Ty21a-a surrogate vaccine against non-typhoid salmonella? Vaccine 30, 7238–7245.
Khan, M.I., Soofi, S.B., Ochiai, R.L., Habib, M.A., Sahito, S.M., Nizami, S.Q., Acosta, C.J., Clemens, J.D., Bhutta, Z.A., and Group, D.T.K.V.E.S. 2012. Effectiveness of Vi capsular polysaccharide typhoid vaccine among children: a cluster randomized trial in Karachi, Pakistan. Vaccine 30, 5389–5395.
LaRock, D.L., Chaudhary, A., and Miller, S.I. 2015. Salmonellae interactions with host processes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13, 191–205.
Le Bouguenec, C. and Schouler, C. 2011. Sugar metabolism, an additional virulence factor in enterobacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 301, 1–6.
Lim, S., Han, A., Kim, D., and Seo, H.S. 2015. Transcriptional profiling of an attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium ptsI mutant strain under low-oxygen conditions using microarray analysis. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 45, 200–214.
Lundin, B.S., Johansson, C., and Svennerholm, A.M. 2002. Oral immunization with a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi vaccine induces specific circulating mucosa-homing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in humans. Infect. Immun. 70, 5622–5627.
Luo, Y., Kong, Q., Yang, J., Golden, G., Wanda, S.Y., Jensen, R.V., Ernst, P.B., and Curtiss, R. 3rd 2011. Complete genome sequence of the universal killer Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium UK-1 (ATCC 68169). J. Bacteriol. 193, 4035–4036.
Majowicz, S.E., Musto, J., Scallan, E., Angulo, F.J., Kirk, M., O’Brien, S.J., Jones, T.F., Fazil, A., Hoekstra, R.M., and International Collaboration on Enteric Disease’Burden of Illness, S. 2010. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 50, 882–889.
Maze, A., Glatter, T., and Bumann, D. 2014. The central metabolism regulator EIIAGlc switches Salmonella from growth arrest to acute virulence through activation of virulence factor secretion. Cell Rep. 7, 1426–1433.
Meiring, J.E., Gibani, M., and Ty, V.A.C.C.M.G. 2017. The typhoid vaccine acceleration consortium (TyVAC): Vaccine effectiveness study designs: Accelerating the introduction of typhoid conjugate vaccines and reducing the global burden of enteric fever. Report from a meeting held on 26–27 October 2016, Oxford, UK.Vaccine 35, 5081–5088.
O’Callaghan, D., Maskell, D., Liew, F.Y., Easmon, C.S., and Dougan, G. 1988. Characterization of aromatic-and purine-dependent Salmonella Typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect. Immun. 56, 419–423.
Paterson, G.K., Cone, D.B., Peters, S.E., and Maskell, D.J. 2009. Redundancy in the requirement for the glycolytic enzymes phosphofructokinase (Pfk) 1 and 2 in the in vivo fitness of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 46, 261–265.
Poncet, S., Milohanic, E., Maze, A., Nait Abdallah, J., Ake, F., Larribe, M., Deghmane, A.E., Taha, M.K., Dozot, M., De Bolle, X., et al. 2009. Correlations between carbon metabolism and virulence in bacteria. Contrib. Microbiol. 16, 88–102.
Postma, P.W., Lengeler, J.W., and Jacobson, G.R. 1993. Phosphoenolpyruvate: carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 57, 543–594.
Solans, L., Uranga, S., Aguilo, N., Arnal, C., Gomez, A.B., Monzon, M., Badiola, J.J., Gicquel, B., and Martin, C. 2014. Hyper-attenuated MTBVAC erp mutant protects against tuberculosis in mice. Vaccine 32, 5192–5197.
Steeb, B., Claudi, B., Burton, N.A., Tienz, P., Schmidt, A., Farhan, H., Maze, A., and Bumann, D. 2013. Parallel exploitation of diverse host nutrients enhances Salmonella virulence. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003301.
Tennant, S.M. and Levine, M.M. 2015. Live attenuated vaccines for invasive Salmonella infections. Vaccine 33 Suppl 3, C36–41.
Thomas, M.K., Perez, E., Majowicz, S.E., Reid-Smith, R., Olea, A., Diaz, J., Solari, V., and McEwen, S.A. 2011. Burden of acute gastrointestinal illness in the Metropolitan region, Chile, 2008. Epidemiol. Infect. 139, 560–571.
Varki, A. 2017. Biological roles of glycans. Glycobiology 27, 3–49.
Wahid, R., Zafar, S.J., McArthur, M.A., Pasetti, M.F., Levine, M.M., and Sztein, M.B. 2014. Live oral Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi vaccines Ty21a and CVD 909 induce opsonophagocytic functional antibodies in humans that cross-react with S. Paratyphi A and S. Paratyphi B. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 21, 427–434.
Wiedemann, A., Virlogeux-Payant, I., Chausse, A.M., Schikora, A., and Velge, P. 2014. Interactions of Salmonella with animals and plants. Front. Microbiol. 5, 791.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, Y., Lin, S.M., Jang, AY. et al. Effective mucosal live attenuated Salmonella vaccine by deleting phosphotransferase system component genes ptsI and crr. J Microbiol. 57, 64–73 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8416-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8416-0