Abstract
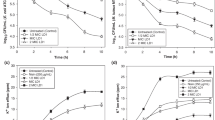
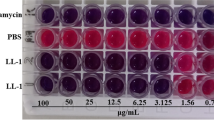
The detailed antibacterial mechanism of cordycepin efficacy against food-borne germs remains ambiguous. In this study, the antibacterial activity and action mechanism of cordycepin were assessed. The results showed that cordycepin effectively inhibited the growth of seven bacterial pathogens including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens; the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were 2.5 and 1.25 mg/ml against Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, respectively. Scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope examination confirmed that cordycepin caused obvious damages in the cytoplasmatic membranes of both E. coli and B. subtilis. Outer membrane permeability assessment indicated the loss of barrier function and the leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Propidium iodide and carboxyfluorescein diacetate double staining approach coupled with flow cytometry analysis indicated that the integrity of cell membrane was severely damaged during a short time, while the intracellular enzyme system still remained active. This clearly suggested that membrane damage was one of the reasons for cordycepin efficacy against bacteria. Additionally, results from circular dichroism and fluorescence analysis indicated cordycepin could insert to genome DNA base and double strand, which disordered the structure of genomic DNA. Basis on these results, the mode of bactericidal action of cordycepin against E. coli and B. subtilis was found to be a dual mechanism, disrupting bacterial cell membranes and binding to bacterial genomic DNA to interfere in cellular functions, ultimately leading to cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, Y.J., Park, S.J., Lee, S.G., Shin, S.C., and Choi, D.H. 2000. Cordycepin: selective growth inhibitor derived from liquid culture of Cordyceps militaris against Clostridium spp. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 2744–2748.
Baase, W.A. and Johnson, W.C. 1979. Circular dichroism and DNA secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 6, 797–814.
Babii, C., Bahrin, L.G., Neagu, A.N., Gostin, I., Mihasan, M., Birsa, L.M., and Stefan, M. 2016. Antibacterial activity and proposed action mechanism of a new class of synthetic tricyclic flavonoids. J. Appl. Microbiol. 120, 630–637.
Bajpai, V.K., Baek, K.H., and Kang, S.C. 2012. Control of Salmonella in foods by using essential oils: A review. Food Res. Int. 45, 722–734.
Caddy, C., Giaroli, G., White, T.P., Shergill, S.S., and Tracy, D.K. 2014. Ketamine as the prototype glutamatergic antidepressant: pharmacodynamic actions, and a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 4, 75–79.
Chang, L., Wang, J., Tong, C., Zhang, X., Zhao, L., and Liu, X. 2016. Antibacterial mechanism of polyacrylonitrile fiber with organophosphorus groups against Escherichia coli. Fibers Polym. 17, 721–728.
Cunningham, K. 1951. 508. Cordycepin, a metabolic product from cultures of Cordyceps militaris(Linn.) link. Part I. Isolation and characterisation. J. Chem. Soc. 2, 2299–2300.
Denyer, S.P. 1991. Mechanisms of action of chemical biocides. Their study and exploitation. In Denyer, S.P. and Hugo, W.B. (eds.), Society for Applied Bacteriology Technical Series 27.
Denyer, S.P. 1995. Mechanisms of action of antibacterial biocides. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 36, 227–245.
Dewey, T.G. 1991. Biophysical and biochemical aspects of fluorescence spectroscopy. Plenum, New York, USA.
Dong, B., Almassalha, L.M., Stypula-Cyrus, Y., Urban, B.E., Chandler, J.E., Nguyen, T.Q., Sun, C., Zhang, H.F., and Backman, V. 2016. Superresolution intrinsic fluorescence imaging of chromatin utilizing native, unmodified nucleic acids for contrast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 9716–9721.
Dorsey, J., Yentsch, C.M., Mayo, S., and Mckenna, C. 1989. Rapid analytical technique for the assessment of cell metabolic activity in marine microalgae. Cytometry 10, 622–628.
Fehlbaum, P., Bulet, P., Chernysh, S., Briand, J.P., Roussel, J.P., Letellier, L., Hetru, C., and Hoffmann, J.A. 1996. Structure-activity analysis of thanatin, a 21-residue inducible insect defense peptide with sequence homology to frog skin antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 1221–1225.
Guerra-Rosas, M.I., Morales-Castro, J., Cubero-Márquez, M.A., Salvia-Trujillo, L., and Martín-Belloso, O. 2017. Antimicrobial activity of nanoemulsions containing essential oils and high methoxyl pectin during long-term storage. Food Control. 77, 131–138.
Hossain, M., Giri, P., and Kumar, G.S. 2008. DNA intercalation by quinacrine and methylene blue: a comparative binding and thermodynamic characterization study. DNA Cell Biol. 27, 81–90.
Hu, Z., Lee, C.I., Shah, V.K., Oh, E.H., Han, J.Y., Bae, J.R., Lee, K., Chong, M.S., Hong, J.T., and Oh, K.W. 2013. Cordycepin increases nonrapid eye movement sleep via adenosine receptors in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 840134.
Kiduk, P. and Sungjin, C. 2010. Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of 3-O-alkyl analogues of (+)-catechin: improvement of stability and proposed action mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 1028–1033.
Kim, J., Yang, C., and Dassarma, S. 1996. Analysis of left-handed Z-DNA formation in short d(CG)n sequences in Escherichia coli and Halobacterium halobium plasmids. Stabilization by increasing repeat length and DNA supercoiling but not salinity. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 9340–9346.
Kumar, C.V. and Asuncion, E.H. 1993. DNA binding studies and site selective fluorescence sensitization of an anthryl probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8547–8553.
Li, B., Hou, Y., Zhu, M., Bao, H., Nie, J., Zhang, G.Y., Shan, L., Yao, Y., Du, K., Yang, H., et al. 2016. 3′-Deoxyadenosine (cordycepin) produces a rapid and robust antidepressant effect via enhancing prefrontal AMPA receptor signaling pathway. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 19, pyv112.
Li, G., Wang, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, B., and Xia, X. 2013. Antimicrobial effect and mode of action of chlorogenic acid on Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 238, 589–596.
Lou, Z., Wang, H., Rao, S., Sun, J., Ma, C., and Li, J. 2012. p-Coumaric acid kills bacteria through dual damage mechanisms. Food Control 25, 550–554.
Lyles, J.T., Kim, A., Nelson, K., Bullard-Roberts, A.L., Hajdari, A., Mustafa, B., and Quave, C.L. 2017. The chemical and antibacterial evaluation of St. John’s wort oil macerates used in kosovar traditional medicine. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1639.
Mao, X.B., Eksriwong, T., Chauvatcharin, S., and Zhong, J.J. 2005. Optimization of carbon source and carbon/nitrogen ratio for cordycepin production by submerged cultivation of medicinal mushroom Cordyceps militaris. Process Biochem. 40, 1667–1672.
Mason, D.J., Dybowski, R., Larrick, J.W., and Gant, V.A. 1997. Antimicrobial action of rabbit leukocyte CAP18(106-137). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41, 624–629.
Moreira, D., Gullon, B., Gullon, P., Gomes, A., and Tavaria, F. 2016. Bioactive packaging using antioxidant extracts for the prevention of microbial food-spoilage. Food Funct. 7, 3273–3282.
Nikolis, N., Methenitis, C., and Pneumatikakis, G. 2003. Studies on the interaction of altromycin B and its platinum(II) and palladium(II) metal complexes with calf thymus DNA and nucleotides. J. Inorg. Biochem. 95, 177–193.
Niu, G. and Tan, H. 2015. Nucleoside antibiotics: biosynthesis, regulation, and biotechnology. Trends Microbiol. 23, 110–119.
Pinto, N.D.C.C., Campos, L.M., Evangelista, A.C.S., Lemos, A.S.O., Silva, T.P., Melo, R.C.N., de Lourenço, C.C., Salvador, M.J., Apolônio, A.C.M., Scio, E., et al. 2017. Antimicrobial Annona muricata L. (soursop) extract targets the cell membranes of Grampositive and Gram-negative bacteria. Ind. Crops Prod. 107, 332–340.
Radula-Janik, K., Kopka, K., Kupka, T., and Ejsmont, K. 2014. Substituent effect of nitro group on aromaticity of carbazole rings. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 50, 1244–1251.
Shrestha, B., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., and Liu, X. 2012. The medicinal fungus Cordyceps militaris: research and development. Mycol. Prog. 11, 599–614.
Stiefel, P., Schmidt-Emrich, S., Maniura-Weber, K., and Ren, Q. 2015. Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol. 15, 36–44.
Sugar, A.M. and Mccaffrey, R.P. 1998. Antifungal activity of 3′- deoxyadenosine (cordycepin). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42, 1424–1427.
Tang, Y.L., Shi, Y.H., Zhao, W., Hao, G., and Le, G.W. 2008. Insertion mode of a novel anionic antimicrobial peptide MDpep5 (Val-Glu-Ser-Trp-Val) from Chinese traditional edible larvae of housefly and its effect on surface potential of bacterial membrane. J. Pharm. Biomed Anal. 48, 1187–1194.
Tuli, H.S., Sharma, A.K., Sandhu, S.S., and Kashyap, D. 2013. Cordycepin: a bioactive metabolite with therapeutic potential. Life Sci. 93, 863–869.
Zhang, R., Pang, D., and Cai, R. 1999. Interactions between DNA and DNA-targeting molecules. Chem. J. Chinese U. 20, 1210–1217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., Lou, Z., Wang, H. et al. Antimicrobial effect and proposed action mechanism of cordycepin against Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Microbiol. 57, 288–297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8113-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8113-z