Abstract
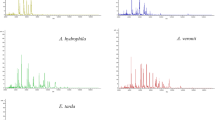
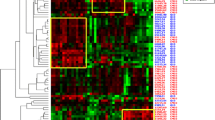
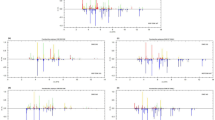
Streptococcus iniae causes severe mortalities among cultured marine species, especially in the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), which is economically important in Korea and Japan. Recently, there has been growing concern regarding the emergence of S. iniae as a zoonotic pathogen. Here, 89 S. iniae isolates obtained from diseased olive flounders collected from 2003 to 2008 in Jeju Island, South Korea, were characterized using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). The results were aligned both with the available Bruker Daltonics data-base and with a new set of S. iniae data entries developed in our laboratory, and the results were compared. When we used the Bruker Daltonics database, the 89 isolates yielded either “no reliable identification” or were incorrectly identified as Streptococcus pyogenes at the genus level. When we used the new data entries from our laboratory, in contrast, all of the isolates were correctly identified as S. iniae at the genus (100%) and species (96.6%) levels. We performed proteomic analysis, divided the 89 isolates into cluster I (51.7%), cluster II (20.2%), and cluster III (28.1%), and then used the MALDI Biotyper software to identify specific mass peaks that enabled discrimination between clusters and between Streptococcus species. Our results suggest that the use of MALDI TOF MS could outperform the conventional methods, proving easier, faster, cheaper and more efficient in properly identifying S. iniae. This strategy could facilitate the epidemiological and taxonomical study of this important fish pathogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alatoom, A.A., Cunningham, S.A., Ihde, S.M., Mandrekar, J., and Patel, R. 2011. Comparison of direct colony method versus extraction method for identification of Gram-positive cocci by use of Bruker Biotyper matrix-assisted laser desorption ionizationtime of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 2868–2873.
Alispahic, M., Christensen, H., Hess, C., Razzazi-Fazeli, E., Bisgaard, M., and Hess, M. 2012. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry confirms clonal lineages of Gallibacterium anatis between chicken flocks. Vet. Microbiol. 160, 269–273.
Barbuddhe, S.B., Maier, T., Schwarz, G., Kostrzewa, M., Hof, H., Domann, E., Chakraborty, T., and Hain, T. 2008. Rapid identification and typing of Listeria species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 5402–5407.
Bizzini, A., Durussel, C., Bille, J., Greub, G., and Prod'hom, G. 2010 Performance of matrx-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of bacterial strains routinely isolated in a clinical microbiology laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48, 1549–1554
Bizzini, A., Jaton, K., Romo, D., Bille, J., Prod'hom, G., and Greub, G. 2011. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry as an alternative to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for identification of difficult to identify bacterial strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 693–696.
Böhme, K., Fernández-No, I.C., Gallardo, J.M., Cañas, B., and Calo-Mata, P. 2010. Safety assessment of fresh and processed seafood products by MALDI-TOF mass fingerprinting. Food Bioprocess Tech. 4, 907–918.
Chen, M., Li, L., Wang, R., Liang, W., Huang, Y., Li, J., Lei, A., and Huang, W. 2012. PCR detection and PFGE genotype analyses of streptococcal clinical isolates from tilapia in China. Vet. Microbiol. 159, 526–530.
Cherkaoui, A., Hibbs, J., Emonet, S., Tangomo, M., Girard, M., Francois, P., and Schrenzel, J. 2010. Comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry methods with conventional phenotypic identification for routine identification of bacteria to the species level. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48, 1169–1175.
Chou, L., Griffin, M.J., Fraites, T., Ware, C., Ferguson, H., Keirstead, N., Brake, J., Wiles, J., Hawke, J.P., and Kearney, M.T. 2014. Phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity among Streptococcus iniae isolates recovered from cultured and wild fish in North America, Central America and the Caribbean islands. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 26, 263–271.
Croxatto, A., Prod'hom, G., and Greub, G. 2011. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 36, 380–407.
Dodson, S., Maurer, J., and Shotts, E. 1999. Biochemical and molecular typing of Streptococcus iniae isolated from fish and human cases. J. Fish Dis. 22, 331–336.
Dubois, D., Leyssene, D., Chacornac, J.P., Kostrzewa, M., Schmit, P.O., Talon, R., Bonnet, R., and Delmas, J. 2009. Identification of a variety of Staphylococcus species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48, 941–945.
El Khéchine, A., Couderc, C., Flaudrops, C., Raoult, D., and Drancourt, M. 2011. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry identification of mycobacteria in routine clinical practice. PLoS One 6, e24720.
Erler, R., Wichels, A., Heinemeyer, E.A., Hauk, G., Hippelein, M., Reyes, N.T., and Gerdts, G. 2015. VibrioBase: a MALDI-TOF MS database for fast identification of Vibrio spp. that are potentially pathogenic in humans. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 38, 16–25.
Fernández-No, I.C., Böhme, K., Calo-Mata, P., Cañas, B., Gallardo, J.M., and Barros-Velázquez, J. 2012. Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus parauberis from vacuum-packaging refrigerated seafood products. Food Microbiol. 30, 91–97.
Figueiredo, H.C.P., Nobrega Netto, L., Leal, C.A.G., Pereira, U.P., and Mian, G.F. 2012. Streptococcus iniae outbreaks in Brazillian Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) farms. Braz. J. Mirobiol. 43, 576–580.
Goh, S.H., Driedger, D., Gillett, S., Low, D.E., Hemmingsen, S.M., Amos, M., Chan, D., Lovgren, M., Willey, B.M., and Shaw, C. 1998. Streptococcus iniae, a human and animal pathogen: specific identification by the chaperonin 60 gene identification method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36, 2164–2166.
Haenen, O., Evans, J., and Berthe, F. 2013. Bacterial infections from aquatic species: potential for and prevention of contact zoonoses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 32, 497–507.
Kim, S.W., Jang, H.B., Lee, J.S., Im, S.P., Lazarte, J.M.S., Seo, J.P., Lee, W.J., Kim, J.S., and Jung, T.S. 2015. Comparison of proteome typing and serotyping of Streptococcus parauberis isolates from olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J. Microbiol. Methods 118, 168–172.
Kurokawa, S., Kabayama, J., Fukuyasu, T., Hwang, S.D., Park, C.I., Park, S.B., del Castillo, C.S., Hikima, J., Jung, T.S., and Kondo, H. 2013. Bacterial classification of fish-pathogenic Mycobacterium species by multigene phylogenetic analyses and MALDI Biotyper identification system. Mar. Biotechnol. 15, 340–348.
Marvin, L.F., Roberts, M.A., and Fay, L.B. 2003. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry in clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 337, 11–21.
Nawawi, R., Baiano, J., and Barnes, A. 2008. Genetic variability amongst Streptococcus iniae isolates from Australia. J. Fish Dis. 31, 305–309.
Nho, S.W., Shin, G.W., Park, S.B., Jang, H.B., Cha, I.S., Ha, M.A., Kim, Y.R., Park, Y.K., Dalvi, R.S., and Kang, B.J. 2009. Phenotypic characteristics of Streptococcus iniae and Streptococcus parauberis isolated from olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 293, 20–27.
Nomura, F. 2014. Proteome-based bacterial identification using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS): a revolutionary shift in clinical diagnostic microbiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Proteins Proteomics 1854, 528–537.
Park, S.B., Kwon, K., Cha, I.S., Jang, H.B., Nho, S.W., Fagutao, F.F., Kim, Y.K., Yu, J.E., and Jung, T.S. 2014. Development of a multiplex PCR assay to detect Edwardsiella tarda, Streptococcus parauberis, and Streptococcus iniae in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J. Vet. Sci. 15, 163–166.
Pier, G.B. and Madin, S.H. 1976. Streptococcus iniae sp. nov., a betahemolytic streptococcus isolated from an Amazon freshwater dolphin, Inia geoffrensis. Int. J. Syst. Microbiol. 26, 545–553.
Rim, J.H., Lee, Y., Hong, S.K., Park, Y., Kim, M., D’Souza, R., Park, E.S., Yong, D., and Lee, K. 2015. Insufficient discriminatory power of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry dendrograms to determine the clonality of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from an intensive care unit. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 535027.
Seng, P., Drancourt, M., Gouriet, F., La Scola, B., Fournier, P.E., Rolain, J.M., and Raoult, D. 2009. Ongoing revolution in bacteriology: routine identification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin. Infect. Dis. 49, 543–551.
Seng, P., Rolain, J.M., Fournier, P.E., La Scola, B., Drancourt, M., and Raoult, D. 2010. MALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry applications in clinical microbiology. Future Microbiol. 5, 1733–1754.
Shin, G., Palaksha, K., Yang, H., Shin, Y., Kim, Y., Lee, E., Kim, H., Kim, Y., Oh, M., and Yoshida, T. 2006. Discrimination of streptococcosis agents in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish. Pathol. 26, 68.
Wang, J., Zhou, N., Xu, B., Hao, H., Kang, L., Zheng, Y., Jiang, Y., and Jiang, H. 2012. Identification and cluster analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. PLoS One 7, e47152.
Weinstein, M.R., Litt, M., Kertesz, D.A., Wyper, P., Rose, D., Coulter, M., McGeer, A., Facklam, R., Ostach, C., and Willey, B.M. 1997. Invasive infections due to a fish pathogen, Streptococcus iniae. S. iniae study group. N. Engl. J. Med. 337, 589–594.
Zou, L., Wang, J., Huang, B., Xie, M., and Li, A. 2011. MtsB, a hydrophobic membrane protein of Streptococcus iniae, is an effective subunit vaccine candidate. Vaccine 29, 391–394.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.W., Nho, S.W., Im, S.P. et al. Rapid MALDI biotyper-based identification and cluster analysis of Streptococcus iniae . J Microbiol. 55, 260–266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-6472-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-6472-x