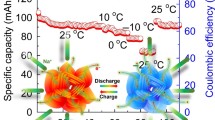
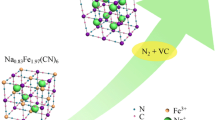
Abstract
Low-cost room-temperature sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are expected to promote the development of stationary energy storage applications. However, due to the large size of Na+, most Na+ host structures resembling their Li+ counterparts show sluggish ion mobility and destructive volume changes during Na ion (de)intercalation, resulting in unsatisfactory rate and cycling performances. Herein, we report a new type of sodium iron phosphate (Na0.71Fe1.07PO4), which exhibits an extremely small volume change (~ 1%) during desodiation. When applied as a cathode material for SIBs, this new phosphate delivers a capacity of 78 mA·h·g−1 even at a high rate of 50 C and maintains its capacity over 5,000 cycles at 20 C. In situ synchrotron characterization disclosed a highly reversible solid-solution mechanism during charging/discharging. The findings are believed to contribute to the development of high-performance batteries based on Earth-abundant elements.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larcher, D.; Tarascon, J. M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29.
Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Ding, Z.; Lee, M. H.; Lim, K.; Yoon, G.; Kang, K. Recent progress in electrode materials for sodiumion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600943.
Yabuuchi, N.; Kubota, K.; Dahbi, M.; Komaba, S. Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11636–11682.
Pan, H. L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L. Q. Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2338–2360.
Berthelot, R.; Carlier, D.; Delmas, C. Electrochemical investigation of the P2-NaxCoO2 phase diagram. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 74–80.
Komaba, S.; Takei, C.; Nakayama, T.; Ogata, A.; Yabuuchi, N. Electrochemical intercalation activity of layered NaCrO2 vs. LiCrO2. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 355–358.
Yabuuchi, N.; Kajiyama, M.; Iwatate, J.; Nishikawa, H.; Hitomi, S.; Okuyama, R.; Usui, R.; Yamada, Y.; Komaba, S. P2-type Nax[Fe1/2Mn1/2]O2 made from earth-abundant elements for rechargeable Na batteries. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 512–517.
Wang, Y. S.; Yu, X. Q.; Xu, S. Y.; Bai, J. M.; Xiao, R. J.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Yang, X.-Q.; Chen, L. Q.; Huang, X. J. A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2365.
Oh, S.-M.; Myung, S.-T.; Hassoun, J.; Scrosati, B.; Sun, Y.-K. Reversible NaFePO4 electrode for sodium secondary batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 22, 149–152.
Kim, H.; Shakoor, R. A.; Park, C.; Lim, S. Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Jo, Y. N.; Cho, W.; Miyasaka, K.; Kahraman, R.; Jung, Y. et al. Na2FeP2O7 as a promising iron-based pyrophosphate cathode for sodium rechargeable batteries: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1147–1155.
Jian, Z. L.; Zhao, L.; Pan, H. L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, L. Q. Carbon coated Na3V2(PO4)3 as novel electrode material for sodium ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 14, 86–89.
Padhi, A. K.; Nanjundaswamy, K. S.; Goodenough, J. B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1188–1194.
Kang, B.; Ceder, G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nature 2009, 458, 190–193.
Lee, M. J.; Lho, E.; Bai, P.; Chae, S.; Li, J.; Cho, J. Lowtemperature carbon coating of nanosized Li1.015Al0.06Mn1.925O4 and high-density electrode for high-power Li-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 3744–3751.
Fang, Y. J.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, L. F.; Ai, X. P.; Yang, H. X.; Cao, Y. L. High-performance olivine NaFePO4 microsphere cathode synthesized by aqueous electrochemical displacement method for sodium ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17977–17984.
Han, M. H.; Gonzalo, E.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Rojo, T. Structural evolution and electrochemistry of monoclinic NaNiO2 upon the first cycling process. J. Power Sources 2014, 258, 266–271.
Ait Salah, A.; Jozwiak, P.; Zaghib, K.; Garbarczyk, J.; Gendron, F.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C. M. FTIR features of lithium-iron phosphates as electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Spectrochim. Acta A 2006, 65, 1007–1013.
Guo, Y. G.; Hu, J. S.; Wan, L. J. Nanostructured materials for electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2878–2887.
Ait-Salah, A.; Dodd, J.; Mauger, A.; Yazami, R.; Gendron, F.; Julien, C. M. Structural and magnetic properties of LiFePO4 and lithium extraction effects. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2006, 632, 1598–1605.
Fang, Y. J.; Xiao, L. F.; Qian, J. F.; Ai, X. P.; Yang, H. X.; Cao, Y. L. Mesoporous amorphous FePO4 nanospheres as high-performance cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3539–3543.
Kim, J.; Seo, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Park, I.; Yoo, J.-K.; Jung, S.-K.; Park, Y.-U.; Goddard, W. A., III; Kang, K. Unexpected discovery of low-cost maricite NaFePO4 as a high-performance electrode for Na-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 540–545.
Zhu, Y. J.; Xu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. H.; Luo, C.; Wang, C. S. Comparison of electrochemical performances of olivine NaFePO4 in sodium-ion batteries and olivine LiFePO4 in lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 780–787.
Liu, C. F.; Neale, Z. G.; Cao, G. Z. Understanding electrochemical potentials of cathode materials in rechargeable batteries. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 109–123.
Jamnik, J.; Maier, J. Nanocrystallinity effects in lithium battery materials: Aspects of nano-ionics. Part IV. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 5215–5220.
Li, C.; Miao, X.; Chu, W.; Wu, P.; Tong, D. G. Hollow amorphous NaFePO4 nanospheres as a high-capacity and high-rate cathode for sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8265–8271.
Langrock, A.; Xu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. H.; Ehrman, S.; Manivannan, A.; Wang, C. S. Carbon coated hollow Na2FePO4F spheres for Na-ion battery cathodes. J. Power Sources 2013, 223, 62–67.
Barpanda, P.; Oyama, G.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Chung, S.-C.; Yamada, A. A 3.8-V earth-abundant sodium battery electrode. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4358.
Qian, J. F.; Zhou, M.; Cao, Y. L.; Ai, X. P.; Yang, H. X. Nanosized Na4Fe(CN)6/C composite as a low-cost and high-rate cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater 2012, 2, 410–414.
Chen, J. E.; Huang, Z. G.; Wang, C. Y.; Porter, S.; Wang, B. F.; Lie, W.; Liu, H. K. Sodium-difluoro(oxalato)borate (NaDFOB): A new electrolyte salt for Na-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9809–9812.
Hu, M.; Wei, J. P.; Xing, L. Y.; Zhou, Z. Effect of lithium difluoro(oxalate)borate (LiDFOB) additive on the performance of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 291–296.
Gauthier, M.; Carney, T. J.; Grimaud, A.; Giordano, L.; Pour, N.; Chang, H.-H.; Fenning, D. P.; Lux, S. F.; Paschos, O.; Bauer, C. et al. Electrode–electrolyte interface in Li-ion batteries: Current understanding and new insights. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4653–4672.
Kim, H.; Park, I.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Park, K.-Y.; Park, Y. U.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Lim, H.-D.; Yoon, W.-S. et al. Understanding the electrochemical mechanism of the new iron-based mixed-phosphate Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) in a Na rechargeable battery. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3614–3622.
Kim, H.; Yoon, G.; Park, I.; Park, K. Y.; Lee, B.; Kim, J.; Park, Y. U.; Jung, S. K.; Lim, H. D.; Ahn, D. et al. Anomalous Jahn-Teller behavior in a manganese-based mixed-phosphate cathode for sodium ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3325–3335.
Gibot, P.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Laffont, L.; Levasseur, S.; Carlach, P.; Hamelet, S.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Masquelier, C. Room-temperature single-phase Li insertion/extraction in nanoscale LixFePO4. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 741–747.
Acknowledgements
Financial Support from Australian Research Council (ARC) through its Discovery Projects (DPs) and Linkage Projects (LPs) is acknowledged. The authors also acknowledge the facilities, and the scientific and technical assistance, of the Australian Microscopy & Microanalysis Research Facility (AMMRF) at the Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis (CMM), The University of Queensland, as well as the beamline at the Australian Synchrotron, part of Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Mochiku, T., Fujii, H. et al. A new sodium iron phosphate as a stable high-rate cathode material for sodium ion batteries. Nano Res. 11, 6197–6205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2139-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2139-0