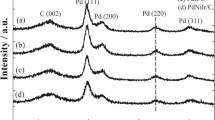
Abstract
A novel carbon-supported cyanogel (C@cyanogel)-derived strategy is used to synthesize an intermetallic Pd3Fe/C compound of the desired ordered Pd3Fe phase with a small particle size. The novelty of this work lies in using carbon-supported K2PdIICl4/K4FeII(CN)6 cyanogel as a reaction precursor, generated through the substitution of two chloride ligands by the nitrogen ends of the cyanide ligands on the metal center. The inherent nature of cyanogels can effectively suppress the movement of Pd0 and Fe0 nuclei in the crystal, benefiting the formation of the intermetallic, which is otherwise challenging via traditional synthesis techniques. The ordered Pd3Fe/C catalyst exhibits excellent catalytic activity and good cycle stability for the formic acid oxidation (FAO) reaction relative to the properties of disordered Pd3Fe/C and commercial Pd/C catalysts, demonstrating that the ordered Pd3Fe/C is a promising replacement for commercial Pd-based catalysts. The outstanding performance can be ascribed to the full isolation of active sites in the ordered Pd3Fe structure and the modified electronic structure of the active components. This work provides an effective and novel route to obtain Pd-based intermetallic compounds with potential applications in a wide range of electrocatalysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, M. M.; Zhang, R. Z.; Chen, W. Graphene-supported nanoelectrocatalysts for fuel cells: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5117–5160.
Peng, Z. M.; Yang, H. PtAu bimetallic heteronanostructures made by post-synthesis modification of Pt-on-Au nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 406–415.
Klinkova, A.; De Luna, P.; Sargent, E. H.; Kumacheva, E.; Cherepanov, P. V. Enhanced electrocatalytic performance of palladium nanoparticles with high energy surfaces in formic acid oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11582–11585.
Chang, J. F.; Feng, L. G.; Liu, C. P.; Xing, W.; Hu, X. L. An effective Pd-Ni2P/C anode catalyst for direct formic acid fuel cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 122–126.
Xu, H.; Ding, L. X.; Feng, J. X.; Li, G. R. Pt/Ni(OH)2-NiOOH/Pd multi-walled hollow nanorod arrays as superior electrocatalysts for formic acid electrooxidation. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6991–6998.
Bin, D.; Yang, B. B.; Ren, F. F.; Zhang, K.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. K. Facile synthesis of PdNi nanowire networks supported on reduced graphene oxide with enhanced catalytic performance for formic acid oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14001–14006.
Jiang, X.; Fu, G. T.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. Y.; Sun, D. M.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y. W. Ultrathin AgPt alloy nanowires as a high-performance electrocatalyst for formic acid oxidation. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 499–510.
Luan, C. L.; Zhou, Q. X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Dai, X. P.; Huang, X. L.; Zhang, X. A general strategy assisted with dual reductants and dual protecting agents for preparing Pt-based alloys with high-index facets and excellent electrocatalytic performance. Small 2017, 13, 1702617.
Liu, D.; Xie, M. L.; Wang, C. M.; Liao, L. W.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J.; Huang, H.; Long, R.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y. J. Pd-Ag alloy hollow nanostructures with interatomic charge polarization for enhanced electrocatalytic formic acid oxidation. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1590–1599.
Ho, S. F.; Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Guo, S. J.; He, K.; Su, D.; Liu, S.; Metin, Ö.; Sun, S. H. A facile route to monodisperse MPd (M = Co or Cu) alloy nanoparticles and their catalysis for electrooxidation of formic acid. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6970–6973.
Yu, X. W.; Pickup, P. G. Recent advances in direct formic acid fuel cells (DFAFC). J. Power Sources 2008, 182, 124–132.
Mahmood, A.; Saleem, F.; Lin, H. F.; Ni, B.; Wang, X. Crystallinity-induced shape evolution of Pt-Ag nanosheets from branched nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10547–10550.
Qin, Y. C.; Zhang, X.; Dai, X. P.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. S.; Shi, Q. X.; Gao, D. W.; Wang, H.; Yu, N. F. et al. Graphene oxide-assisted synthesis of Pt-Co alloy nanocrystals with high-index facets and enhanced electrocatalytic properties. Small 2016, 12, 524–533.
Wang, X. X.; Yang, J. D.; Yin, H. J.; Song, R.; Tang, Z. Y. "Raisin bun"-like nanocomposites of palladium clusters and porphyrin for superior formic acid oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2728–2732.
Sun, H. Y.; Guo, X.; Ye, W.; Kou, S. F.; Yang, J. Charge transfer accelerates galvanic replacement for PtAgAu nanotubes with enhanced catalytic activity. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1173–1181.
Ha, S.; Larsen, R.; Masel, R. I. Performance characterization of Pd/C nanocatalyst for direct formic acid fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2005, 144, 28–34.
Mazumder, V.; Chi, M. F.; Mankin, M. N.; Liu, Y.; Metin, Ö.; Sun, D. H.; More, K. L.; Sun, S. H. A facile synthesis of MPd (M = Co, Cu) nanoparticles and their catalysis for formic acid oxidation. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1102–1106.
Huang, X. Q.; Tang, S. H.; Mu, X. L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, G. X.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Ruan, F. X.; Yang, Z. L.; Zheng, N. F. Freestanding palladium nanosheets with plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 28–32.
Iyyamperumal, R.; Zhang, L.; Henkelman, G.; Crooks, R. M. Efficient electrocatalytic oxidation of formic acid using Au@Pt dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5521–5524.
Jiang, K.; Zhang, H. X.; Zou, S. Z.; Cai, W. B. Electrocatalysis of formic acid on palladium and platinum surfaces: From fundamental mechanisms to fuel cell applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20360–20376.
Fu, G. T.; Xia, B. Y.; Ma, R. G.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y. W.; Lee, J. M. Trimetallic PtAgCu@PtCu core@shell concave nanooctahedrons with enhanced activity for formic acid oxidation reaction. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 824–832.
Yan, X. X.; Hu, X. J.; Fu, G. T.; Xu, L.; Lee, J. M.; Tang, Y. W. Facile synthesis of porous Pd3Pt half-shells with rich "active sites" as efficient catalysts for formic acid oxidation. Small, in press, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201703940.
Xu, H.; Zhang, K.; Yan, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Q.; Li, S. M.; Gu, Z. L.; Du, Y. K.; Yang, P. Ultra-uniform PdBi nanodots with high activity towards formic acid oxidation. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 27–35.
Matin, M. A.; Jang, J. H.; Kwon, Y. U. PdM nanoparticles (M = Ni, Co, Fe, Mn) with high activity and stability in formic acid oxidation synthesized by sonochemical reactions. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 356–363.
Du, C. Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, W. G.; Yin, G. P.; Shi, P. F. Electrodeposited PdNi2 alloy with novelly enhanced catalytic activity for electrooxidation of formic acid. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 843–846.
Lu, Q. Q.; Wang, H. J.; Eid, K.; Alothman, Z. A.; Malgras, V.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wang, L. Synthesis of hollow platinum-palladium nanospheres with a dendritic shell as efficient electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 1939–1944.
Chen, D.; Sun, P. C.; Liu, H.; Yang, J. Bimetallic Cu-Pd alloy multipods and their highly electrocatalytic performance for formic acid oxidation and oxygen reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4421–4429.
Saleem, F.; Ni, B.; Yong, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, X. Ultra-small tetrametallic Pt-Pd-Rh-Ag nanoframes with tunable behavior for direct formic acid/methanol oxidation. Small 2016, 12, 5261–5268.
Mao, J. J.; Liu, Y. X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Bimetallic Pd-Cu nanocrystals and their tunable catalytic properties. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4588–4591.
McMillan, R. A.; Howard, J.; Zaluzec, N. J.; Kagawa, H. K.; Mogul, R.; Li, Y. F.; Paavola, C. D.; Trent, J. D. A self-assembling protein template for constrained synthesis and patterning of nanoparticle arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2800–2801.
Chai, J.; Li, F. H.; Hu, Y. W.; Zhang, Q. X.; Han, D. X.; Niu, L. Hollow flower-like aupd alloy nanoparticles: One step synthesis, self-assembly on ionic liquid-functionalized graphene, and electrooxidation of formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17922–17929.
Tominaka, S.; Momma, T.; Osaka, T. Electrodeposited Pd-Co catalyst for direct methanol fuel cell electrodes: Preparation and characterization. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4679–4686.
Zhang, Z. H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Z.; Kou, T. Y.; Zhao, C. C. Ultrafine nanoporous Cu-Pd alloys with superior catalytic activities towards electro-oxidation of methanol and ethanol in alkaline media. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11820–11828.
Rong, H. P.; Mao, J. J.; Xin, P. Y.; He, D. S.; Chen, Y. J.; Wang, D. S.; Niu, Z. Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. D. Kinetically controlling surface structure to construct defect-rich intermetallic nanocrystals: Effective and stable catalysts. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2540–2546.
Liu, Y. X.; Liu, X. W.; Feng, Q. C.; He, D. S.; Zhang, L. B.; Lian, C.; Shen, R.; Zhao, G. F.; Ji, Y. J.; Wang, D. S. et al. Intermetallic NixMy (M = Ga and Sn) nanocrystals: A non-precious metal catalyst for semi-hydrogenation of alkynes. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4747–4754.
Cui, Z. M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, M. T.; DiSalvo, F. J. High-performance Pd3Pb intermetallic catalyst for electrochemical oxygen reduction. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2560–2566.
Shi, Q. R.; Zhu, C. Z.; Bi, C. X.; Xia, H. B.; Engelhard, M. H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. H. Intermetallic Pd3Pb nanowire networks boost ethanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions with significantly improved methanol tolerance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 23952–23959.
Du, X. X.; He, Y.; Wang, X. X.; Wang, J. N. Fine-grained and fully ordered intermetallic PtFe catalysts with largely enhanced catalytic activity and durability. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2623–2632.
Gunji, T.; Noh, S. H.; Tanabe, T.; Han, B.; Nien, C. Y.; Ohsaka, T.; Matsumoto, F. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of carbon-supported ordered intermetallic palladium-lead (Pd3Pb) nanoparticles toward electrooxidation of formic acid. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2906–2913.
Li, X.; An, L.; Wang, X. Y.; Li, F.; Zou, R. Q.; Xia, D. G. Supported sub-5nm Pt-Fe intermetallic compounds for electrocatalytic application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6047–6052.
Cui, Z. M.; Li, L. J.; Manthiram, A.; Goodenough, J. B. Enhanced cycling stability of hybrid Li-air batteries enabled by ordered Pd3Fe intermetallic electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7278–7281.
Kuttiyiel, K. A.; Sasaki, K.; Su, D.; Wu, L. J.; Zhu, Y. M.; Adzic, R. R. Gold-promoted structurally ordered intermetallic palladium cobalt nanoparticles for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5185.
Zhang, G. J.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L. P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y. M.; Tang, Y. W.; Lu, T. H. Synthesis and electrocatalytic properties of palladium network nanostructures. ChemPlusChem 2012, 77, 936–940.
Liu, H. M.; Li, J. H.; Wang, L. J.; Tang, Y. W.; Xia, B. Y.; Chen, Y. Trimetallic PtRhNi alloy nanoassemblies as highly active electrocatalyst for ethanol electrooxidation. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3324–3332.
Fu, G. T.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. F.; Wu, J. Y.; Xu, L.; Sun, D. M.; Zhang, J. B.; Tang, Y. W.; Chen, P. Spinel MnCo2O4 nanoparticles cross-linked with two-dimensional porous carbon nanosheets as a high-efficiency oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2110–2122.
Fu, G. T.; Liu, H. M.; You, N. K.; Wu, J. Y.; Sun, D. M.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y. W.; Chen, Y. Dendritic platinum-copper bimetallic nanoassemblies with tunable composition and structure: Arginine- driven self-assembly and enhanced electrocatalytic activity. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 755–765.
Hammer, B.; Morikawa, Y.; Nørskov, J. K. CO chemisorption at metal surfaces and overlayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 2141–2144.
Wang, Y. C.; Chen, J. W.; Zhou, F. L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X. Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, G.; Wang, R. L. Dealloyed platinum-copper with isolated Pt atom surface: Facile synthesis and promoted dehydrogenation pathway of formic acid electro-oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 799, 78–83.
Kristian, N.; Yan, Y. S.; Wang, X. Highly efficient submonolayer Pt-decorated Au nano-catalysts for formic acid oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2008, 353–355.
Cui, Z. M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, W. D.; Zhao, M. T.; DiSalvo, F. J. Structurally ordered Pt3Cr as oxygen reduction electrocatalyst: Ordering control and origin of enhanced stability. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7538–7545.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21503111, 21576139, and 21376122), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20171473), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 16KJB150020) and Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. Y607k51001). The authors are also grateful for the supports from National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Biomedical Functional Materials and a project sponsored by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2018_2051_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Facile synthesis based on novel carbon-supported cyanogel of structurally ordered Pd3Fe/C as electrocatalyst for formic acid oxidation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Fu, G., Li, J. et al. Facile synthesis based on novel carbon-supported cyanogel of structurally ordered Pd3Fe/C as electrocatalyst for formic acid oxidation. Nano Res. 11, 4686–4696 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2051-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2051-7