Abstract
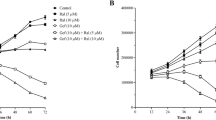
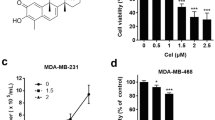
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacking of oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 is a highly malignant disease which results in a poor prognosis and rare treatment options. Despite the use of conventional chemotherapy for TNBC tumours, resistance and short duration responses limit the treatment efficacy. Therefore, a need exists to develop a new chemotherapy for TNBC. The aim of this study was to examine the anti-cancer effects of nafamostat mesilate (NM), a previously known serine protease inhibitor and highly safe drug on breast cancer cells. Here, we showed that NM significantly inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in MDA-MB231 cells, induces G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest, and inhibits the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1). Exposure of MDA-MB231 cells to NM also resulted in decreased transcription factor activities accompanied by the regulated phosphorylation of signalling molecules and a decrease in metalloproteinases, the principal modulators of the extracellular environment during cancer progression. Especially, inhibition of TGFβ-stimulated Smad2 phosphorylation and subsequent metastasis-related gene expression, and downregulation of ERK activity may be pivotal mechanisms underlying inhibitory effects of NM on NM inhibits lung metastasis of breast cancer cells and growth of colonized tumours in mice. Taken together, our data revealed that NM inhibits cell growth and metastasis of TNBC cells and indicated that NM is a multi-targeted drug that could be an adjunct therapy for TNBC treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akizawa T, Koshikawa S, Ota K, Kazama M, Mimura N, Hirasawa Y (1993) Nafamostat mesilate: a regional anticoagulant for hemodialysis in patients at high risk for bleeding. Nephron 64:376–381
Andre F, Zielinski CC (2012) Optimal strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with currently approved agents. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi46–vi51
Bartholomeusz C, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Liu P, Hayashi N, Lluch A, Ferrer-Lozano J, Hortobagyi GN (2012) High ERK protein expression levels correlate with shorter survival in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Oncologist 17:766–774
Benson JR (2004) Role of transforming growth factor beta in breast carcinogenesis. Lancet Oncol 5:229–239
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, Esterni B, Hermitte F, Viens P, Birnbaum D (2008) How basal are triple-negative breast cancers? Int J Cancer 123:236–240
Bose S, Chandran S, Mirocha JM, Bose N (2006) The Akt pathway in human breast cancer: a tissue-array-based analysis. Mod Pathol 19:238–245
Boyle P (2012) Triple-negative breast cancer: epidemiological considerations and recommendations. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi7–vi12
Brandi G, Tavolari S, De Rosa F, Di Girolamo S, Agostini V, Barbera MA, Frega G, Biasco G (2012) Antitumoral efficacy of the protease inhibitor gabexate mesilate in colon cancer cells harbouring KRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations. PLoS ONE 7:e41347
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, Ollila DW, Sartor CI, Graham ML, Perou CM (2007) The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 13:2329–2334
Cho EY, Choi SC, Lee SH, Ahn JY, Im LR, Kim JH, Xin M, Kwon SU, Kim DK, Lee YM (2011) Nafamostat mesilate attenuates colonic inflammation and mast cell infiltration in the experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 11:412–417
Crown J, O’shaughnessy J, Gullo G (2012) Emerging targeted therapies in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi56–vi65
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P, Narod SA (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 13:4429–4434
Egeblad M, Werb Z (2002) New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:161–174
Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 363:1938–1948
Fujii S, Hitomi Y (1981) New synthetic inhibitors of C1r, C1 esterase, thrombin, plasmin, kallikrein and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta 661:342–345
Fujiwara Y, Furukawa K, Haruki K, Shimada Y, Iida T, Shiba H, Uwagawa T, Ohashi T, Yanaga K (2011) Nafamostat mesilate can prevent adhesion, invasion and peritoneal dissemination of pancreatic cancer thorough nuclear factor kappa-B inhibition. J Hepatobil Pancreat Sci 18:731–739
Furukawa K, Iida T, Shiba H, Fujiwara Y, Uwagawa T, Shimada Y, Misawa T, Ohashi T, Yanaga K (2010) Anti-tumor effect by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation using nafamostat mesilate for pancreatic cancer in a mouse model. Oncol Rep 24:843–850
Furukawa K, Uwagawa T, Iwase R, Haruki K, Fujiwara Y, Gocho T, Shiba H, Misawa T, Yanaga K (2012) Prognostic factors of unresectable pancreatic cancer treated with nafamostat mesilate combined with gemcitabine chemotherapy. Anticancer Res 32:5121–5126
Gajria D, Chandarlapaty S (2011) HER2-amplified breast cancer: mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance and novel targeted therapies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 11:263–275
Giltnane JM, Balko JM (2014) Rationale for targeting the Ras/MAPK pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Discov Med 17:275–283
Gocho T, Uwagawa T, Furukawa K, Haruki K, Fujiwara Y, Iwase R, Misawa T, Ohashi T, Yanaga K (2013) Combination chemotherapy of serine protease inhibitor nafamostat mesilate with oxaliplatin targeting NF-kappaB activation for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 333:89–95
Hahn SA, Schutte M, Shamsul Hoque ATM, Moskaluk CA, Da Costa LT, Rozenblum E, Weinstein CL, Fischer A, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH, Kern SE (1996) DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science 271:350–353
Hartman ZC, Poage GM, Den Hollander P, Tsimelzon A, Hill J, Panupinthu N, Zhang Y, Mazumdar A, Hilsenbeck SG, Mills GB, Brown PH (2013) Growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells relies upon coordinate autocrine expression of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8. Cancer Res 73:3470–3480
Hortobagyi GN (2005) Trastuzumab in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:1734–1736
Iwaki M, Ino Y, Motoyoshi A, Ozeki M, Sato T, Kurumi M, Aoyama T (1986) Pharmacological studies of FUT-175, nafamostat mesilate. V. Effects on the pancreatic enzymes and experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 41:155–162
Jakowlew SB (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:435–457
Johnston SR, Maclennan KA, Sacks NP, Salter J, Smith IE, Dowsett M (1994) Modulation of Bcl-2 and Ki-67 expression in oestrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer by tamoxifen. Eur J Cancer 30a:1663–1669
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Investig 112:1776–1784
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Investig 119:1420–1428
Kassam F, Enright K, Dent R, Dranitsaris G, Myers J, Flynn C, Fralick M, Kumar R, Clemons M (2009) Survival outcomes for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: implications for clinical practice and trial design. Clin Breast Cancer 9:29–33
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 141:52–67
Kimura T, Fuchimoto S, Iwagaki H, Hizuta A, Orita K (1992) Inhibitory effect of nafamostat mesilate on metastasis into the livers of mice and on invasion of the extracellular matrix by cancer cells. J Int Med Res 20:343–352
Lee HO, Sheen YY (1997) Estrogen modulation of human breast cancer cell growth. Arch Pharm Res 20:566–571
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B, Green M, Cristofanilli M, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2008) Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:1275–1281
Lu YX, Ju HQ, Wang F, Chen LZ, Wu QN, Sheng H, Mo HY, Pan ZZ, Xie D, Kang TB, Chen G, Yun JP, Zeng ZL, Xu RH (2016) Inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway by nafamostat mesilate suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Lett 380:87–97
Lv ZD, Kong B, Li JG, Qu HL, Wang XG, Cao WH, Liu XY, Wang Y, Yang ZC, Xu HM, Wang HB (2013) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 enhances the invasiveness of breast cancer cells by inducing a Smad2-dependent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep 29:219–225
Mukherjee D, Zhao J (2013) The Role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in breast cancer metastasis. Am J Cancer Res 3:46–57
Naber HP, Wiercinska E, Pardali E, Van Laar T, Nirmala E, Sundqvist A, Van Dam H, Van Der Horst G, Van Der Pluijm G, Heckmann B, Danen EH, Ten Dijke P (2012) BMP-7 inhibits TGF-beta-induced invasion of breast cancer cells through inhibition of integrin beta(3) expression. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 35:19–28
Nakatsuka M, Asagiri K, Noguchi S, Habara T, Kudo T (2000) Nafamostat mesilate, a serine protease inhibitor, suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide synthesis and apoptosis in cultured human trophoblasts. Life Sci 67:1243–1250
Noguchi S, Nakatsuka M, Konishi H, Kamada Y, Chekir C, Kudo T (2003) Nafamostat mesilate suppresses NF-kappaB activation and NO overproduction in LPS-treated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 3:1335–1344
Okamoto T, Mizoguchi S, Terasaki H, Morioka T (1994) Safety of high-dose of nafamostat mesilate: toxicological study in beagles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:639–644
Padua D, Massague J (2009) Roles of TGF[beta] in metastasis. Cell Res 19:89–102
Parkin DM, Fernandez LM (2006) Use of statistics to assess the global burden of breast cancer. Breast J 12(Suppl 1):S70–S80
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, Van De Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Prat A, Baselga J (2008) The role of hormonal therapy in the management of hormonal-receptor-positive breast cancer with co-expression of HER2. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:531–542
Singh JK, Simoes BM, Howell SJ, Farnie G, Clarke RB (2013) Recent advances reveal IL-8 signaling as a potential key to targeting breast cancer stem cells. Breast Cancer Res 15:210
Slamon D, Clark G, Wong S, Levin W, Ullrich A, Mcguire W (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–182
Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S (2005) The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med 9:59–71
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lonning PE, Brown PO, Borresen-Dale AL, Botstein D (2003) Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8418–8423
Stingl J, Caldas C (2007) Molecular heterogeneity of breast carcinomas and the cancer stem cell hypothesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7:791–799
Tang CH, Lu DY, Yang RS, Tsai HY, Kao MC, Fu WM, Chen YF (2007) Leptin-induced IL-6 production is mediated by leptin receptor, insulin receptor substrate-1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, NF-kappaB, and p300 pathway in microglia. J Immunol 179:1292–1302
Thiagalingam S, Lengauer C, Leach FS, Schutte M, Hahn SA, Overhauser J, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Hamilton SR, Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1996) Evaluation of candidate tumour suppressor genes on chromosome 18 in colorectal cancers. Nat Genet 13:343–346
Uchima Y, Sawada T, Nishihara T, Maeda K, Ohira M, Hirakawa K (2004) Inhibition and mechanism of action of a protease inhibitor in human pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 29:123–131
Uwagawa T, Li Z, Chang Z, Xia Q, Peng B, Sclabas GM, Ishiyama S, Hung MC, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL, Chiao PJ (2007) Mechanisms of synthetic serine protease inhibitor (FUT-175)-mediated cell death. Cancer 109:2142–2153
Uwagawa T, Misawa T, Tsutsui N, Ito R, Gocho T, Hirohara S, Sadaoka S, Yanaga K (2013) Phase II study of gemcitabine in combination with regional arterial infusion of nafamostat mesilate for advanced pancreatic cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 36:44–48
Woolf DK, Padhani AR, Makris A (2015) Assessing response to treatment of bone metastases from breast cancer: what should be the standard of care? Ann Oncol 26:1048–1057
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (MSIP; No. NRF-2016R1A2B1010036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mander, S., You, DJ., Park, S. et al. Nafamostat mesilate negatively regulates the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 41, 229–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0996-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0996-9