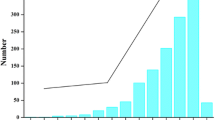
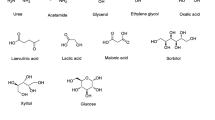
Abstract
Perfect solvents in biocatalysis have to fulfill a large number of requirements, such as high enzyme activity and stability, and high substrate solubility. Deep eutectic solvents (DES) have recently been evaluated as new solvents in different biocatalytic reactions. They can provide improvements in substrate supply, conversion and stability. The best results were obtained when the DES is formed by the substrates of an enzymatic reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Pätzold M, Siebenhaller S, Kara S et al. (2019) Deep eutectic solvents as efficient solvents in biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.03.007
Abbott AP, Capper G, Davies DL et al. (2003) Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem Commun (Camb) 1:70–71
Gorke JT, Srienc F, Kazlauskas RJ (2008) Hydrolase-catalyzed biotransformations in deep eutectic solvents. Chem Commun (Camb) 10:1235–1237
Liu P, Hao J-W, Mo L-P et al. (2015) Recent advances in the application of deep eutectic solvents as sustainable media as well as catalysts in organic reactions. RSC Adv 5:48675–48704
Pena-Pereira F, Namiesnik J (2014) Ionic liquids and deep eutectic mixtures: sustainable solvents for extraction processes. ChemSusChem 7:1784–1800
Choi YH, van Spronsen J, Dai Y et al. (2011) Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol 156:1701–1705
Paiva A, Craveiro R, Aroso I et al. (2014) Natural deep eutectic solvents — solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1063–1071
Zhao H, Zhang C, Crittle TD (2013) Choline-based deep eutectic solvents for enzymatic preparation of biodiesel from soybean oil. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85–86:243–247
Sheldon RA (2005) Green solvents for sustainable organic synthesis: state of the art. Green Chem 7:267–278
Siebenhaller S, Muhle-Goll C, Luy B et al. (2016) Sustainable enzymatic synthesis of glycolipids in a deep eutectic solvent system. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 133:S281–S287
Milker S, Pätzold M, Bloh JZ et al. (2019) Comparison of deep eutectic solvents and solvent-free reaction conditions for aldol production. Mol Catal 466:70–74
Hümmer M, Kara S, Liese A et al. (2018) Synthesis of (-)-menthol fatty acid esters in and from (-)-menthol and fatty acids — novel concept for lipase catalyzed esterification based on eutectic solvents. Mol Catal 458:67–72
Pätzold M, Weimer A, Liese A et al. (2019) Optimization of solvent-free enzymatic esterification in eutectic substrate reaction mixture. Biotechnol Rep 22:e00333
Ni Y, Holtmann D, Hollmann F et al. (2014) How green is biocatalysis? To calculate is to know. ChemCatChem 6:930–943
Francisco M, van den Bruinhorst A, Kroon MC (2013) Low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs): a new generation of designer solvents. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:3074–3085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Danksagung
Wir danken dem Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung für die freundliche Unterstützung der Forschungsarbeiten im Rahmen des Projektes „NIESEL — Niedrig schmelzende eutektische Solventien als Lösungsmittel für die Biokatalyse“ (Förderkennzeichen 031B0014C).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pätzold, M., Holtmann, D. Eutektische Lösungsmittel in der Biokatalyse. Biospektrum 25, 458–460 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-019-1074-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-019-1074-2