Abstract
Although plant cell cultures produce low yields of recombinant proteins compared to other production systems, a dramatic increase of the heterologous protein production in transgenic rice cells was achieved with the alpha-amylase isozyme 3D (RAmy3D) promoter system. However, this expression system has inherent limitations in that gene expression is initiated by sucrose/glucose deprivation, concurrently triggering starvation-derived autophagy and rapid cell death. Decreased viability and culture longevity subsequently prevent further increment of production. In this study, we introduced autophagy inducers and inhibitors in the rrhGAA-producing transgenic rice cell cultures in order to explore their effects on production controlled by the RAmy3D promoter. The autophagy inducers rapamycin and CCI-779 increased autophagosome and autolysosome while concanamycin A1 and bafilomycin A successfully decreased autolysosome. Interestingly, autophagy inhibitors improved viability, DCW loss, and rrhGAA production, while autophagy inducers deteriorated these profiles compared to the control. As the production conditions under the death phase may facilitate protein degradation, and subsequently exacerbate functional activity, the size variant distribution and enzyme activity of the purified rrhGAAs were evaluated. However, no significant difference in rrhGAA degradation as well as GAA activity was observed compared to the control condition, thus indicating that the autophagy regulation is an efficient approach to increase protein yield in rice cell culture system for rrhGAA production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philippidis, A. (2017) The Top 15 Best-Selling Drugs of 2016, Prospect of Price Curbs May Dent Future Results for Blockbusters. In: Editor (ed.) (eds.). Book Title. Publisher, City.
Santos, R. B., R. Abranches, R. Fischer, M. Sack, and T. Holland (2016) Putting the spotlight back on plant suspension cultures. Front Plant Sci. 7: 297.
Yao, J., Y. Weng, A. Dickey, and K. Y. Wang (2015) Plants as factories for human pharmaceuticals: applications and challenges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16: 28549–28565.
Xu, J. and N. Zhang (2014) On the way to commercializing plant cell culture platform for biopharmaceuticals: present status and prospect. Pharm Bioprocess 2: 499–518.
Lee, S. J., C. I. Park, M. Y. Park, H. S. Jung, W. S. Ryu, S. M. Lim, H. K. Tan, T. H. Kwon, M. S. Yang, and D. I. Kim (2007) Production and characterization of human CTLA4Ig expressed in transgenic rice cell suspension cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 51: 293–302.
Shin, Y. J., Y. J. Chong, M. S. Yang, and T. H. Kwon (2011) Production of recombinant human granulocyte macrophagecolony stimulating factor in rice cell suspension culture with a human-like N-glycan structure. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9: 1109–1119.
Torres, E., C. Vaquero, L. Nicholson, M. Sack, E. Stoger, J. Drossard, P. Christou, R. Fischer, and Y. Perrin (1999) Rice cell culture as an alternative production system for functional diagnostic and therapeutic antibodies. Transgenic Res. 8: 441–449.
Kim, N. S., H. Y. Yu, N. D. Chung, T. H. Kwon, and M. S. Yang (2014) High-level production of recombinant trypsin in transgenic rice cell culture through utilization of an alternative carbon source and recycling system. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 63: 21–27.
Huang, L. F., C. C. Tan, J. F. Yeh, H. Y. Liu, Y. K. Liu, S. L. Ho, and C. A. Lu (2015) Efficient secretion of recombinant proteins from rice suspension-cultured cells modulated by the choice of signal peptide. PLoS One 10: e0140812.
Liu, Y. K., Y. T. Li, C. F. Lu, and L. F. Huang (2015) Enhancement of recombinant human serum albumin in transgenic rice cell culture system by cultivation strategy. N Biotechnol. 32: 328–334.
Baek, E., S. M. Noh, and G. M. Lee (2017) Anti-apoptosis engineering for improved protein production from CHO cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 1603: 71–85.
Kim, Y. J., E. Baek, J. S. Lee, and G. M. Lee (2013) Autophagy and its implication in Chinese hamster ovary cell culture. Biotechnol. Lett. 35: 1753–1763.
Hwang, S. O. and G. M. Lee (2008) Autophagy and apoptosis in Chinese hamster ovary cell culture. Autophagy 4: 70–72.
Baek, E., C. L. Kim, M. G. Kim, J. S. Lee, and G. M. Lee (2016) Chemical inhibition of autophagy: Examining its potential to increase the specific productivity of recombinant CHO cell lines. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 113: 1953–1961.
Voitsekhovskaja, O. V., A. Schiermeyer, and S. Reumann (2014) Plant peroxisomes are degraded by starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in tobacco BY-2 suspension-cultured cells. Front Plant Sci. 5: 629.
Wang, W., M. Xu, G. Wang, and G. Galili (2016) Autophagy: An important biological process that protects plants from stressful environments. Front Plant Sci. 7: 2030.
Michaeli, S., G. Galili, P. Genschik, A. R. Fernie, and T. Avin-Wittenberg (2016) Autophagy in plants—what’s new on the menu? Trends Plant Sci. 21: 134–144.
Bassham, D. C. (2007) Plant autophagy—more than a starvation response. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10: 587–593.
Yoshimoto, K. (2012) Beginning to understand autophagy, an intracellular self-degradation system in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 53: 1355–1365.
Lee, J. S., and G. M. Lee (2012) Rapamycin treatment inhibits CHO cell death in a serum-free suspension culture by autophagy induction. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109: 3093–3102.
Li, S., Y. Liang, M. Wu, X. Wang, H. Fu, Y. Chen, and Z. Wang (2013) The novel mTOR inhibitor CCI-779 (temsirolimus) induces antiproliferative effects through inhibition of mTOR in Bel-7402 liver cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13: 30.
Shacka, J. J., B. J. Klocke, and K. A. Roth (2006) Autophagy, bafilomycin and cell death: the “a-B-cs” of plecomacrolide-induced neuroprotection. Autophagy 2: 228–230.
Yano, K., T. Yanagisawa, K. Mukae, Y. Niwa, Y. Inoue, and Y. Moriyasu (2015) Dissection of autophagy in tobacco BY-2 cells under sucrose starvation conditions using the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor concanamycin A and the autophagy-related protein Atg8. Plant Signal Behav. 10: e1082699.
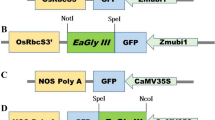
Jung, J.-W., N.-X. Huy, H.-B. Kim, N.-S. Kim, D. Van Giap, and M.-S. Yang (2017) Production of recombinant human acid α-glucosidase with high-mannose glycans in gnt1 rice for the treatment of Pompe disease. Journal of Biotechnology 249: 42–50.
Kwon, J.-Y., S.-H. Jeong, J.-W. Choi, Y.-Y. Pak, and D.-I. Kim (2013) Assessment of long-term cryopreservation for production of hCTLA4Ig in transgenic rice cell suspension cultures. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 53: 216–222.
McVie-Wylie, A. J., K. L. Lee, H. Qiu, X. Jin, H. Do, R. Gotschall, B. L. Thurberg, C. Rogers, N. Raben, M. O’Callaghan, W. Canfield, L. Andrews, J. M. McPherson, and R. J. Mattaliano (2008) Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of different recombinant acid alpha-glucosidase preparations evaluated for the treatment of Pompe disease. Mol. Genet Metab. 94: 448–455.
Li, F., N. Vijayasankaran, A. Y. Shen, R. Kiss, and A. Amanullah (2010) Cell culture processes for monoclonal antibody production. MAbs 2: 466–479.
Mizushima, N. (2007) Autophagy: process and function. Genes Dev. 21: 2861–2873.
Glick, D., S. Barth, and K. F. Macleod (2010) Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Pathol. 221: 3–12.
Yang, Y. P., L. F. Hu, H. F. Zheng, C. J. Mao, W. D. Hu, K. P. Xiong, F. Wang, and C. F. Liu (2013) Application and interpretation of current autophagy inhibitors and activators. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 34: 625–635.
Yang, Y., M. Qin, P. Bao, W. Xu, and J. Xu (2017) Secretory carrier membrane protein 5 is an autophagy inhibitor that promotes the secretion of alpha-synuclein via exosome. PLoS One 12: e0180892.
Liu, Y., M. Schiff, K. Czymmek, Z. Talloczy, B. Levine, and S. P. Dinesh-Kumar (2005) Autophagy regulates programmed cell death during the plant innate immune response. Cell 121: 567–577.
Han, Y. K., T. K. Ha, S. J. Lee, J. S. Lee, and G. M. Lee (2011) Autophagy and apoptosis of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells during fed-batch culture: effect of nutrient supplementation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 108: 2182–2192.
Zhao, J., B. Zhai, S. P. Gygi, and A. L. Goldberg (2015) mTOR inhibition activates overall protein degradation by the ubiquitin proteasome system as well as by autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112: 15790–15797.
Jardon, M. A., B. Sattha, K. Braasch, A. O. Leung, H. C. F. Côté, M. Butler, S. M. Gorski, and J. M. Piret (2012) Inhibition of glutamine-dependent autophagy increases t-PA production in CHO Cell fed-batch processes. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 109: 1228–1238.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Biomedical Research Council of A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), Singapore, and the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, No. PJ01334605), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J.K., Choi, HY., Park, HR. et al. Inhibition of Autolysosome Formation Improves rrhGAA Production Driven by RAmy3D Promoter in Transgenic Rice Cell Culture. Biotechnol Bioproc E 24, 568–578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0005-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0005-x