Abstract
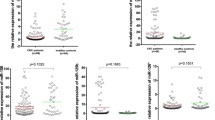
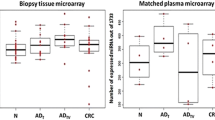
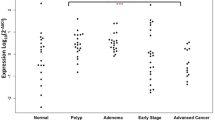
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been found to play a critical role in colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. MiRNA-specific high-throughput arrays became available to detect promising miRNA expression alterations even in biological fluids, such as plasma samples, where miRNAs are stable. The purpose of this study was to identify circulating miRNAs showing altered expression between normal colonic (N), tubular adenoma (ADT), tubulovillous adenoma (ADTV) and colorectal cancer (CRC) matched plasma and tissue samples. Sixteen peripheral plasma and matched tissue biopsy samples (N n = 4; ADT n = 4; ADTV n = 4; CRC n = 4) were selected, and total RNA including miRNA fraction was isolated. MiRNAs from plasma samples were extracted using QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit (Qiagen). Matched tissue-plasma miRNA microarray experiments were conducted by GeneChip® miRNA 3.0 Array (Affymetrix). RT-qPCR (microRNA Ready-to-use PCR Human Panel I + II; Exiqon) was used for validation. Characteristic miRNA expression alterations were observed in comparison of AD and CRC groups (miR-149*, miR-3196, miR-4687) in plasma samples. In the N vs. CRC comparison, significant overexpression of miR-612, miR-1296, miR-933, miR-937 and miR-1207 was detected by RT-PCR (p < 0.05). Similar expression pattern of these miRNAs were observed using microarray in tissue pairs, as well. Although miRNAs were also found in circulatory system in a lower concentration compared to tissues, expression patterns slightly overlapped between tissue and plasma samples. Detected circulating miRNA alterations may originate not only from the primer tumor but from other cell types including immune cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20107
Patai AV, Valcz G, Hollosi P, Kalmar A, Peterfia B, Patai A, Wichmann B, Spisak S, Bartak BK, Leiszter K, Toth K, Sipos F, Kovalszky I, Peter Z, Miheller P, Tulassay Z, Molnar B (2015) Comprehensive DNA methylation analysis reveals a common ten-gene methylation signature in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. PLoS One 10(8):e0133836. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133836
Yan L, Zhao W, Yu H, Wang Y, Liu Y, Xie C (2016) A comprehensive meta-analysis of MicroRNAs for predicting colorectal cancer. Medicine 95(9):e2738. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002738
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(4):259–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1840
Nagy ZB, Wichmann B, Kalmar A, Galamb O, Bartak BK, Spisak S, Tulassay Z, Molnar B (2017) Colorectal adenoma and carcinoma specific miRNA profiles in biopsy and their expression in plasma specimens. Clin Epigenetics 9:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0305-3
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10513–10518. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Yuan T, Huang X, Woodcock M, Du M, Dittmar R, Wang Y, Tsai S, Kohli M, Boardman L, Patel T, Wang L (2016) Plasma extracellular RNA profiles in healthy and cancer patients. Sci Rep 6:19413. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19413
Tufekci KU, Oner MG, Genc S, Genc K (2010) MicroRNAs and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune Dis 2011:807426. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/807426
Ge Q, Shen Y, Tian F, Lu J, Bai Y, Lu Z (2015) Profiling circulating microRNAs in maternal serum and plasma. Mol Med Rep 12(3):3323–3330. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3879
Leidinger P, Galata V, Backes C, Stahler C, Rheinheimer S, Huwer H, Meese E, Keller A (2015) Longitudinal study on circulating miRNAs in patients after lung cancer resection. Oncotarget 6(18):16674–16685. 10.18632/oncotarget.4322
Ma R, Jiang T, Kang X (2012) Circulating microRNAs in cancer: origin, function and application. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-31-38
Pathak S, Meng WJ, Nandy SK, Ping J, Bisgin A, Helmfors L, Waldmann P, Sun XF (2015) Radiation and SN38 treatments modulate the expression of microRNAs, cytokines and chemokines in colon cancer cells in a p53-directed manner. Oncotarget 6(42):44758–44780. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5815
Tambyah PA, Sepramaniam S, Mohamed Ali J, Chai SC, Swaminathan P, Armugam A, Jeyaseelan K (2013) microRNAs in circulation are altered in response to influenza a virus infection in humans. PLoS One 8(10):e76811. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076811
Zhou N, Zhou Y, Tang Y, Yu W (2016) MiR-519 inhibits gastric cancer cell activity through regulation of HuR expression. Journal of Central South University Medical Sciences 41(1):19–23. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2016.01.003
Sheng L, He P, Yang X, Zhou M, Feng Q (2015) miR-612 negatively regulates colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting AKT2. Cell Death Dis 6:e1808. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.184
Bhajun R, Guyon L, Pitaval A, Sulpice E, Combe S, Obeid P, Haguet V, Ghorbel I, Lajaunie C, Gidrol X (2015) A statistically inferred microRNA network identifies breast cancer target miR-940 as an actin cytoskeleton regulator. Sci Rep 5:8336. https://doi.org/10.1038/Srep08336
Bobowicz M, Skrzypski M, Czapiewski P, Marczyk M, Maciejewska A, Jankowski M, Szulgo-Paczkowska A, Zegarski W, Pawlowski R, Polanska J, Biernat W, Jaskiewicz J, Jassem J (2016) Prognostic value of 5-microRNA based signature in T2-T3N0 colon cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 33(8):765–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9810-1
Cakmak HA, Coskunpinar E, Ikitimur B, Barman HA, Karadag B, Tiryakioglu NO, Kahraman K, Vural VA (2015) The prognostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure: preliminary results from a genome-wide expression study. J Cardiovasc Med 16(6):431–437. https://doi.org/10.2459/JCM.0000000000000233
Shan X, Wen W, Zhu D, Yan T, Cheng W, Huang Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, Wang T, Zhu W, Zhu Y, Zhu J (2017) miR 1296-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression. PLoS One 12(1):e0170298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170298
Wei WJ, Wang YL, Li DS, Wang Y, Wang XF, Zhu YX, Pan XD, Wang ZY, Wu Y, Jin L, Wang JC, Ji QH (2015) Association study of single nucleotide polymorphisms in mature microRNAs and the risk of thyroid tumor in a Chinese population. Endocrine 49(2):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0467-8
Dong G, Zhang RF, Xu JJ, Guo YF (2015) Association between microRNA polymorphisms and papillary thyroid cancer susceptibility. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(10):13450–13457
Poliseno L, Haimovic A, Segura MF, Hanniford D, Christos PJ, Darvishian F, Wang J, Shapiro RL, Pavlick AC, Berman RS, Hernando E, Zavadil J, Osman I (2012) Histology-specific microRNA alterations in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 132(7):1860–1868. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.451
Zhang L, Zeng D, Chen Y, Li N, Lv Y, Li Y, Xu X, Xu G (2016) miR-937 contributes to the lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting INPP4B. Life Sci 155:110–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.014
Li Y, Liang M, Zhang Z (2014) Regression analysis of combined gene expression regulation in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS Comput Biol 10(10):e1003908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003908
Slattery ML, Herrick JS, Mullany LE, Valeri N, Stevens J, Caan BJ, Samowitz W, Wolff RK (2015) An evaluation and replication of miRNAs with disease stage and colorectal cancer-specific mortality. Int J Cancer 137(2):428–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29384
Wang W, Sun J, Li F, Li R, Gu Y, Liu C, Yang P, Zhu M, Chen L, Tian W, Zhou H, Mao Y, Zhang L, Jiang J, Wu C, Hua D, Chen W, Lu B, Ju J, Zhang X (2012) A frequent somatic mutation in CD274 3′-UTR leads to protein over-expression in gastric cancer by disrupting miR-570 binding. Hum Mutat 33(3):480–484. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22014
Barsotti AM, Beckerman R, Laptenko O, Huppi K, Caplen NJ, Prives C (2012) p53-dependent induction of PVT1 and miR-1204. J Biol Chem 287(4):2509–2519. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.322875
Ali Sheikh MS, Xia K, Li F, Deng X, Salma U, Deng H, Wei Wei L, Yang TL, Peng J (2015) Circulating miR-765 and miR-149: potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for geriatric coronary artery disease patients. Biomed Res Int 2015:740301. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/740301
Chen YX, Gelfond JAL, McManus LM, Shireman PK (2009) Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 10:407. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-10-407
Wang ZS, Zhong M, Bian YH, Mu YF, Qin SL, Yu MH, Qin J (2016) MicroRNA-187 inhibits tumor growth and invasion by directly targeting CD276 in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7(28):44266–44276. 10.18632/oncotarget.10023
Tsang WP, Ng EK, Ng SS, Jin H, Yu J, Sung JJ, Kwok TT (2010) Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 31(3):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgp181
Song Q, Song J, Wang Q, Ma Y, Sun N, Ma J, Chen Q, Xia G, Huo Y, Yang L, Li B (2016) miR-548d-3p/TP53BP2 axis regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Med 5(2):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.567
Larrea E, Sole C, Manterola L, Goicoechea I, Armesto M, Arestin M, Caffarel MM, Araujo AM, Araiz M, Fernandez-Mercado M, Lawrie CH (2016) New concepts in cancer biomarkers: circulating miRNAs in liquid biopsies. Int J Mol Sci 17(5):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050627
Ji X, Takahashi R, Hiura Y, Hirokawa G, Fukushima Y, Iwai N (2009) Plasma miR-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin Chem 55(11):1944–1949. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2009.125310
Igaz I, Igaz P (2015) Why is microRNA action tissue specific? A putative defense mechanism against growth disorders, tumor development or progression mediated by circulating microRNA? Med Hypotheses 85(5):530–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2015.07.013
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (KMR-12-1-2012-0216 grant) and Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA-K111743) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, Z.B., Barták, B.K., Kalmár, A. et al. Comparison of Circulating miRNAs Expression Alterations in Matched Tissue and Plasma Samples During Colorectal Cancer Progression. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 25, 97–105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0308-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0308-1