Abstract
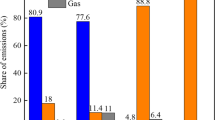
Polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) was blended in diesel at volume ratios of 0 %, 10 %, 20 %, and 30 % (denoted as P0, P10, P20, and P30). The experimental study was carried on an unmodified YD480Q diesel engine. An engine exhaust particle sizer was introduced to analyze the particulate matter (PM) concentration and particle size distribution of diesel engine emission. The evaporation-oxidation characteristics of the PODE/diesel blends and the effect of the fuel blends on the oxidative activity of PM were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis and Arrhenius theorem. The results showed that blending PODE in diesel improved the evaporation-oxidation characteristics of the fuel and decreased the apparent activation energy of the fuel blends. PODE played a positive role in reducing PM emissions. The particle total number concentration of P30 decreased 28.29 ~ 66.60 % and the particle total volume density decreased 54.16 ~ 80.06 % compared to diesel. The particle size distribution shifted to a smaller particle size as the PODE blending ratio was increased. The mass fraction of the volatile substances (VS) increased and the mass fraction of the dry soot (DS) decreased by employing PODE as a diesel additive. Also, the oxidation activity of VS increased as the PODE blending ratio was increased. The oxidation activity of DS climbed to the peak when the PODE blending ratio was 20 % and then decreased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Qudais, M., Haddad, O. and Qudaisat, M. (2000). The effect of alcohol fumigation on diesel engine performance and emissions. Energy Conversion and Management, 414, 389–399.
Ahn, K. (2014). The role of air pollutants in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 1345, 993–999.
Burger, J., Siegert, M., Ströfer, E. and Hasse, H. (2010). Poly(oxymethylene) dimethyl ethers as components of tailored diesel fuel: Properties, synthesis and purification concepts. Fuel, 8911, 3315–3319.
Burtscher, H. (2005). Physical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Science, 367, 896–932.
Chen, Z. H., Li, Z. J., Jiao, P. H., Gao, L. B., Zhang, W. F. and Liu, L. (2011). Micro-reaction kinetics calculation for reducing diesel NOx and PM by adsorber-reduction catalyst. Trans. Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 427, 10–15.
Churchill, G. V. and Srinivasan, C. A. (2017). Experimental investigations on combustion and emission characteristics of biodiesel blends in CI engine. Int. Research J. Engineering and Technology, 0401, 1523–1529.
Ciajolo, A., D’Anna, A., Barbella, R., Tregrossi, A. and Violi, A. (1996). The effect of temperature on soot inception in premixed ethylene flames. Symp. (Int.) Combustion, 262, 2327–2333.
Gao, J. B., Ma, C. C., Tian, G. H., Chen, J. Y., Xing, S. K. and Huang, L. Y. (2018). Oxidation activity restoration of diesel particulate matter by aging in air. Energy & Fuels, 322, 2450–2457.
Guo, Y., He, M. G., Zhong, Q. and Zhang, Y. (2009). Mass diffusion coefficients of oxygenated fuel additives in air. Energy, 3410, 1560–1564.
Hao, B. (2014). Effect of Fuel Identity on the Exhaust Particles from Diesel Engine. Ph. D. Dissertation. Tianjin University. Tianjin, China.
Hu, Z. Y., Yang, Q., Tan, P. Q. and Lou, D. M. (2013). Ultrafine particle number emission and size distribution of an on-used common rail diesel engine fueled with Shanghai IV diesel. J. Tongji Univ: Nat. Sci. Ed, 4111, 1721–1725.
Jiao, W., Xu, C. C., Liu, Y., Guo, L., Li, J. and Liu, W. L. (2014). Research advances in diesel-alcohol blends. Acta Physica Sinica -Chinese Edition, 305, 945–956.
Karin, P., Boonsakda, J., Siricholathum, K., Saenkhumvong, E., Charoenphonphanich, C. and Hanamura, K. (2016). Morphology and oxidation kinetics of ci engine’s biodiesel particulate matters on cordierite diesel particulate filters using TGA. Int. J. Automotive Technology, 181, 31–40.
Kweon, C. B., Foster, D. E., Schauer, J. J. and Okada, S. (2002). Detailed chemical composition and particle size assessment of diesel engine exhaust. SAE Paper No. 2002-01-2670.
Laidler, K. J. (1984). The development of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chemical Education, 616, 494–498.
Liu, H. Y., Wang, Z., Wang, J. X., He, X., Zheng, Y. Y., Tang, Q. and Wang, J. F. (2015). Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE3-4)/ diesel blends. Energy, 88, 793–800.
Liu, H. Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, J. X. and Shuai, S. J. (2017a). Study on combustion and emission characteristics of Polyoxymethylene Dimethyl Ethers/diesel blends in light-duty and heavy-duty diesel engines. Applied Energy, 185Part 2, 1393–1402.
Liu, J. L., Wang, H., Li, Y., Zheng, Z. Q., Xue, Z. Z., Shang, H. Y. and Yao, M. F. (2016). Effects of diesel/PODE (polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers) blends on combustion and emission characteristics in a heavy duty diesel engine. Fuel, 177, 206–216.
Liu, J. H., Sun, P., Huang, H., Meng, J. and Yao, X. H. (2017b). Experimental investigation on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a commonrail diesel engine fueled with polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers-diesel blends. Applied Energy, 202, 527–536.
Mei, D. Q., Zhao, X., Wang, S. L., Yuan, Y. N. and Sun, P. (2013). Thermogravimetric characteristics analysis of particulate matter of emission of divided diesel. Trans. Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2916, 50–56.
Murcak, A., Karabektas, M., Ergen, G. and Hasimoglu, C. (2016). Performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fuelled with emulsified biodiesel-diesel fuel blends. Int. J. Automotive Engineering and Technologies, 54, 176–185.
Pellegrini, L., Marchionna, M., Patrini, R., Beatrice, C., Giacomo, N. D. and Guido, C. (2012). Combustion behaviour and emission performance of neat and blended polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers in a lightduty diesel engine. Microelectronic Engineering, 875-8, 778–781.
Pellegrini, L., Marchionna, M., Patrini, R. and Florio, S. (2013). Emission performance of neat and blended polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers in an old light-duty diesel car. SAE Paper No. 2013-01-1035.
Pirjola, L., Rönkkö, T., Saukko, E., Parviainen, H., Malinen, A., Alanen, J. and Saveljeff, H. (2017). Exhaust emissions of non-road mobile machine: Real-world and laboratory studies with diesel and HVO fuels. Fuel, 202, 154–164.
Prashant, G. K., Lata, D. B. and Joshi, P. C. (2016). Investigations on the effect of methanol blend on the combustion parameters of dual fuel diesel engine. Applied Thermal Engineering, 103, 187–194.
Reitz, D. R. (2013). Directions in internal combustion engine research. Combustion and Flame, 160, 1–8.
Richter, H. and Howard, J. B. (2000). Formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their growth to soot-a review of chemical reaction pathways. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 264-6, 565–608.
Rodríguezfernández, J., Oliva, F. and Vázquez, R. A. (2011). Characterization of the diesel soot oxidation process through an optimized thermogravimetric method. Energy & Fuels, 255, 2039–2048.
Roy, M. M., Calder, J., Wang, W., Mangad, A. and Diniz, F. C. M. (2016). Cold start idle emissions from a modern Tier-4 turbo-charged diesel engine fueled with dieselbiodiesel, diesel-biodiesel-ethanol, and diesel-biodieseldiethyl ether blends. Applied Energy, 180, 52–65.
Song, J. H., Alam, M. and Boehman, A. L. (2007). Impact of alternative fuels on soot properties and DPF regeneration. Combustion Science and Technology, 1799, 1991–2037.
Stratakisa, G. A. and Stamatelosa, A. M. (2003). Thermogravimetric analysis of soot emitted by a modern diesel engine run on catalyst-doped fuel. Combustion and Flame, 1321-2, 157–169.
Su, C. M. and Puls, R. W. (1999). Kinetics of trichloroethene reduction by zerovalent iron and tin_ pretreatment effect, apparent activation energy, and intermediate products. Environmental Science & Technology, 331, 163–168.
Sukjit, E., Herreros, J. M., Piaszyk, J., Dearn, K. D. and Tsolakis, A. (2013). Finding synergies in fuels properties for the design of renewable fuels — Hydroxylated biodiesel effects on butanol-diesel blends. Environmental Science & Technology, 477, 3535–3542.
Wang, C. Q., Li, Y. G., Han, D. Y., Li, D. D. and Cao, Z. B. (2015). Research progress of containing oxygen components in oxygenated diesel. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 443, 531–533.
Wang, C. W., Cui, F. F. and Song, Y. (2014). Research situation and development prospect of bidiesel. China Oils and Fats, 395, 44–48.
Wang, J. X., Wu, F. J., Xiao, J. H. and Shuai, S. J. (2009). Oxygenated blend design and its effects on reducing diesel particulate emissions. Fuel, 8810, 2037–2045.
Wang, Y., Raj, A. and Chung, S. H. (2013). A PAH growth mechanism and synergistic effect on PAH formation in counterflow diffusion flames. Combustion and Flame, 1609, 1667–1676.
Weng, J. Q., Shen, Y. G., Zhang, X. L. and Fan, Y. L. (2008). The corrosion wear of biodiesel on diesel engine and its mechanism analysis. Lubrication Engineering, 338, 54–57.
Xia, D., Chen, G. X., Liao, Z. J., Wang, H. M., Wang, X. C. and Du, P. F. (2015). Recearch status and development tendency of ashless diesel additives. Energy Conservation Technologies, 332, 155–158.
Xie, M., Ma, Z. J., Wang, Q. H., Liu, J. C. and Liu, S. H. (2017). Investigation of engine combustion and emission performance fuelled with neat PODE and PODE/diesel blend. J. Xi’an Jiaotong University, 513, 32–37, 140.
Yang, H., Xinghu, L. I., Mingfei, M. U. and Xuehao, L. I. (2015). Experiments on the performances and emissions of diesel engine fuelled with diesel/polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers blends. J. Automotive Safety and Energy, 63, 280–285.
Zhang, W. G., Wei, X. D., Lin, D. and Zhu, Y. J. (2016). Experimental study on the influence of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) on ultrafne particle emission of a compression ignition engine. J. Automotive Safety and Energy, 73, 330–336.
Zhang, Z. H. and Balasubramanian, R. (2015). Effects of oxygenated fuel blends on carbonaceous particulate composition and particle size distributions from a stationary diesel engine. Fuel, 141, 1–8.
Zielinska, B., Sagebiel, J., Rogers, C. F., Kelly, K. E., Wagner, D. A., Lighty, J. S., Sarofim, A. F. and Palmer, G. (2004). Phase and size distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in diesel and gasoline vehicle emissions. Environmental Science & Technology, 389, 2557–2567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Cai, Y., Shi, Y. et al. Effect of Polyoxymethylene Dimethyl Ethers/Diesel Blends on Fuel Properties and Particulate Matter Oxidation Activity of A Light-Duty Diesel Engine. Int.J Automot. Technol. 20, 277–288 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-019-0027-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-019-0027-6