Abstract
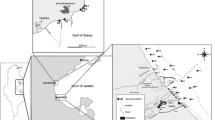
This study investigates and compares the seasonal variations during winter and summer of living benthic foraminiferal assemblages in the Saquarema Lagoon System (SLS) located in a tropical coastal region of SE Brazil. The physicochemical parameters in the SLS presented strong differences between both seasons; however, they remained quite homogeneous in winter and exhibited great oscillations in summer. In the study area, 29 and 19 living foraminiferal species were identified in summer and winter, respectively. Ammonia tepida was the dominant species in both seasons followed by Ammonia parkinsoniana and Cribroelphidium excavatum. The detrended correspondence analysis showed that in the SLS: the calcareous species, such as Adelosina carinatastriata, Bulimina patagonica, and Miliolinella antartica were mostly influenced by high dissolved oxygen contents and low temperature, whereas the agglutinated foraminiferal species were indicators of the most confined lagoonal areas, under the lowest pH and salinity values. The results of this work evidence that the seasonal variation in the SLS might play a more important role in the benthic foraminiferal assemblages’ distribution than the anthropogenic impacts and shows the importance of seasonal studies for coastal biomonitoring programs.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
28 October 2019
In the original article, João Marcelo Ballalai was inadvertently omitted as an author of this article. The author list is correct as reflected here.
References
Agardy, T., Alder, J. 2005. Coastal systems. In Ecosystems and human well-being: current state and trends. Volume 1. Findings of the Condition and Trends Working Group of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, vol 1, eds. Hassan R et al., 513–549. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Series.
Alve, E. 1995. Benthic foraminiferal responses to estuarine pollution: a review. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 25 (3): 190–203.
Alve, E., and F. Olsgard. 1999. Benthic foraminiferal colonization in experiments with copper contaminated sediments. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 29 (3): 186–195.
Alves, A.R. 2003. Modelagem numérica como ferramenta de gestão ambiental: aplicação ao sistema lagunar de Saquarema—RJ. (Dissertação de mestrado). Niterói: Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciência Ambiental, UFF 102p.
Alves Martins, M.V., N. Zaaboub, L. Aleya, F. Frontalini, E. Pereira, P. Miranda, M. Mane, F. Rocha, L. Laut, and M. El Bour. 2015. Environmental quality assessment of Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia) using living foraminifera assemblages and a multiproxy approach. PLoS One 10 (9): e0137250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137250.
Belart, P., V. Laut, I.M.M.M. Clemente, D. Raposo, M.V.A. Martins, F. Frontalini, M.L. Lorini, R. Fortes, and L. Laut. 2017. Living benthic foraminifera from the Saquarema lagoonal system (Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil). Check List 13 (2): 2062. https://doi.org/10.15560/13.2.2062.
Belart, P., I. Clemente, D. Raposo, R. Habib, E.K. Volino, A. Villar, M.V.A. Martins, L.F. Fontana, M.L. Lorini, G. Panigai, F. Frontalini, M.S.L. Figueiredo, S.C. Vasconcelos, and L. Laut. 2018. Living and dead foraminifera as bioindicators in Saquarema Lagoon System, Brazil. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research 46 (5): 1055–1072. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol46-issue5-fulltext-18.
Berkeley, A., C.T. Perry, S.G. Smithers, B.P. Horton, and A.B. Cundy. 2009. Foraminiferal biofacies across mangrove mudflat environments at Cocoa Creek, North Queensland, Australia. Marine Geology 263 (1-4): 64–86.
Bhalla, S.N., and R. Nigam. 1986. Recent foraminifera from polluted marine environment of Velsao Beach, South Goa. India Revue Paleobiologia 5: 43–46.
Bhattacharjee, D., B.C. Choudhury, K. Sivakumar, C. Sharma, S. John, S. Behera, S. Behera, and P. Bhadury. 2013. Benthic foraminifer assemblages in turtle congregation sites along the north-east coast of India. Journal of the Marine Biological Association UK 93 (04): 877–887.
Boltovskoy, E., G. Giussani, S. Watanabe, and R.C. Wright. Atlas of benthic shelf foraminifera of the Southwest Atlantic. Vol. 1980, 154. Netherlands: Springer.
Bomfim, C.S., C.G. Vilela, and D.C. Guedes. 2010. Benthic foraminifera in surface sediments in the Maricá Lagoon, Rio de Janeiro State. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências 33 (1): 09–19. https://revistas.ufrj.br/index.php/aigeo/article/view/6799/5396. Accessed 17 Apr 2018.
Borja, A., A. Basset, S. Bricker, J. Dauvin, M. Elliot, T. Harrison, J. Marques, S. Weisberg, and R. West. 2012. Classifying ecological quality and integrity of estuaries. In Treatise on estuarine and coastal science, ed. E. Wolanski and D. McLusky, vol. 1, 125–162. Cambridge: Academic Press.
Bruno, R.L.M. 2013. Reconstrução paleoambiental nas lagunas de Maricá e Saquarema, RJ, com base em foraminíferos. Tese de Doutorado. Pós-Graduação em Geologia, Departamento de Paleontologia e Estratigrafia, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, 180p.
Carmouze JP (1994) O metabolismo dos ecossistemas aquáticos—fundamentos teóricos, métodos de estudo e análises químicas: editora. FAPESP. 254 p.
Castro, B.M., and L.B. Miranda. 1998. Physical oceanography of the western Atlantic continental shelf located between 4° N and 34° S. In The sea, ed. A.R. Robinson and K.H. Brink, 209–251. New York: Wiley.
Clemente, I.M.M.M., F.S. Silva, L.L.M. Laut, F. Frontalini, V.L. Costa, and R.M.A. Conceição. 2015. Biochemical composition and foraminiferal content of sediments for determining bottom sector environments in Guanabara Bay (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Journal of Coastal Research 315: 1190–1204. https://doi.org/10.2112/jcoastres-d-14-00104.1.
Culver, S.J., and M.A. Buzas. 1995. The effects of anthropogenic habitat disturbance, habitat destruction, and global warming on shallow marine benthic foraminifera. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 25 (3): 204–211.
De Stigter, H.C., W. Boer, P. de Jesus Mendes, C.C. Jesus, L. Thomsen, G.D. van den Bergh, and T.C.E. van Weering. 2007. Recent sediment transport and deposition in Nazaré canyon, Portuguese continental margin. Marine Geology 246: 144–164.
Debenay, J.P., B.B. Eichler, W. Duleba, C. Bonetti, and P. Eichler-Coelho. 1998. Water stratification in coastal lagoons: its influence on foraminiferal assemblages in two Brazilian lagoons. Marine Micropaleontology 35 (1-2): 67–89.
Debenay, J.P., E. Geslin, B.B. Eichler, W. Duleba, F. Sylvestre, and P. Eichler. 2001. Foraminifera assemblages in a hypersaline lagoon: the Lagoon of Araruama (RJ), Brazil. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 31 (2): 133–155.
Debenay, J.P., D. Guiral, and M. Parra. 2004. Behaviour and taphonomic loss in foraminiferal assemblages of mangrove swamps of French Guiana. Marine Geology 208 (2-4): 295–314.
Debenay, J.P., B. Millet, and M.O. Angelidis. 2005. Relationships between foraminiferal assemblages and hydrodynamics in the gulf of Kalloni, Greece. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 35 (4): 327–343.
Debenay, J.P., C. Marchand, N. Molnar, A. Aschenbroich, and T. Meziane. 2015. Foraminiferal assemblages as bioindicators to assess potential pollution in mangroves used as a natural biofilter for shrimp farm effluents (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 93 (1–2): 103–120.
Delavy, F.P., A.G. Figueiredo Jr., M.V.A. Martins, R. Rodrigues, E. Pereira, M.A.R.C. Brito, M.C.M. Fonseca, L.L.M. Laut, S. Bergamaschi, P. Miranda, and M.A.C. Rodrigues. 2016. High-resolution acoustic mapping of gas charged sediments and living benthic foraminifera assemblages from the NE region of the Guanabara Bay (RJ, Brazil). Journal of Sedimentary Environments 1 (3): 367–392. https://doi.org/10.12957/jse.2016.26281.
Dias, P.P.B.B., M.V.A. Martins, I.M.M.M. Clemente, T.G. Carelli, F.S. Silva, L.F. Fontana, M.L. Lorini, G. Panigai, R. Habib, J.G. Mendonça-Filho, and L.L.M. Laut. 2017. Assessment of the trophic state of Saquarema Lagoonal System, Rio de Janeiro (Brazil). Journal of Sedimentary Environments 2 (1): 49–64.
Duleba, W. 2004. Foraminíferos e tecamebas como bioindicadores da circulação hirodinâmica do estuário do rio Verde e do lago Itacolomi. In Estação Ecológica Juréria-Itatins. Ambiente físico, flora e fauna, ed. O.A.V. Marques and W. Duleba, 86–103. Ribeirão Preto: Holus.
Duros, P., F.J. Jorissen, F. Cesbron, S. Zaragosi, S. Schmidt, E. Metzger, and C. Fontanier. 2014. Benthic foraminiferal thanatocoenoses from the Cap-Ferret Canyon area (NE Atlantic): a complex interplay between hydro-sedimentary and biological processes. Deep-Sea Research Part II 104: 145–163.
Esteves, F.A. 1998. Lagoas costeiras: origem, funcionamento e possibilidades de manejo. In Ecologia das lagoas costeiras do Parque Nacional da Restinga de Jurubatiba e do Município de Macaé (RJ), ed. F.A. Esteves, 63–87. Rio de Janeiro: NUPEM/UFRJ.
Fatela, F., and R. Taborda. 2002. Confidence limits of species proportions in microfossil assemblages. Marine Micropaleontology 45 (2): 169–174.
Folk, R. L., W. C. Ward. 1957. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Research 27 (1):3–26.
Frontalini, F., and R. Coccioni. 2008. Benthic foraminifera for heavy metal pollution monitoring: a case study from the central Adriatic Sea coast of Italy. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 76 (2): 404–417.
Frontalini, F., C. Buosi, S. Da Pelo, R. Coccioni, A. Cherchi, and C. Bucci. 2009. Benthic foraminifera as bio-indicators of trace element pollution in the heavily contaminated Santa Gilla lagoon (Cagliari, Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin 58 (6): 858–877.
Gehrels, W.R., and S.W.G. Newman. 2004. Salt-marsh foraminifera in Ho Bugt, western Denmark, and their use as sea-level indicators. Dan Journal of Geography 104 (1): 97–106.
Ghosh, A., S. Saha, P.K. Saraswati, S. Banerjee, and S. Burley. 2009. Intertidal foraminifera in the macro-tidal estuaries of the Gulf of Cambay: implications for interpreting sea level change in palaeo-estuaries. Marine and Petroleum Geology 26 (8): 1592–1599.
Guerra, L.V., F. Savergnini, F.S. Silva, M.C. Bernardes, and M.A.C. Crapez. 2011. Biochemical and microbiological tools for the evaluation of environmental quality of a coastal lagoon system in southern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology 71 (2): 461–468.
Hayward, B.W., Cedhagen, T., Kaminski, M., Gross, O. 2016. World Foraminifera database. http://www.marinespecies.org/foraminifera.
Hayward, B.W., H.R. Grenfell, C.M. Reid, and K.A. Hayward. 1999. Recent New Zealand shallow-water benthic foraminifera: taxonomy, ecologic distribution, biogeography, and use in paleoenvironmental assessment. Lower Hutt: New Zealand Geological Survey: GNS Science Monograph 21.
Horton, B.P., and J.W. Murray. 2007. The roles of elevation and salinity as primary controls on living foraminiferal distributions: Cowpen Marsh, Tees estuary, UK. Marine Micropaleontology 63 (3-4): 169–186.
Horton, B.P., J.E. Whittaker, K.H. Thompson, M.I.J. Hardbattle, A. Kemp, S.A. Woodrofee, and M.R. Wright. 2005. The development of a modern foraminiferal data set for sea-level reconstructions, Wakatobi Marine National Park, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 35 (1): 1–14.
IBGE, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 2004. Censo Demográfico. Rio de Janeiro: Agregado por setor censitário dos resultados do universo do Rio de Janeiro.
Imhoff, K., and R. Klaus. 1985. Manual de Tratamento de Águas Residuárias. ed. Edgar Blucher. São Paulo.
Intituto Nacional de Meteorologia (INMET). 2017. avaible on http://www.inmet.gov.br/portal/index.php?r=estacoes/estacoesAutomaticas. Accessed Jan 2017.
Jorissen, F.J., and I. Wittling. 1999. Ecological evidence from live–dead comparisons of benthic foraminiferal faunas off Cape Blanc (Northwest Africa). Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology 149 (1-4): 151–170.
Kjerfve, B. 1994. Coastal lagoon processes, 1–8. Amsterdan: Elselvier Science 576 p.
Knoppers, B., and B. Kjerfve. 1999. Coastal lagoons of southeastern Brazil: physical and biogeochemical characteristics. In Estuaries of South America, ed. G.M.E. Perillo, M.C. Piccolo, and M.P. Quivira, 35–66. Berlin: Springer.
Lacerda, L.D., and G.O. Gonçalves. 2001. Mercury distribution and speciation in waters of the coastal lagoons of Rio de Janeiro, SE Brazil. Marine Chemistry 76 (1–2): 47–58.
Laut, L.L.M., F.S. Silva, C. Bonetti, A.G. Figueiredo Jr., and M.A.C. Crapez. 2007. Foraminíferos e atividade bacteriana aplicados no diagnóstico ambiental do estuário do rio Itacorubí, Florianópolis. Revista Brasileira de Geociencias 37 (3): 565–578.
Laut, L.L.M., F.S. Silva, J.R.A.G. Figueiredo, and V. Laut. 2011. Assembleias de foraminíferos e tecamebas associadas a análises sedimentológicas e microbiológicas no delta do rio Paraíba do Sul, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Pesquisa em Geociências 38 (3): 251–267.
Laut, L.L.M., F.S. Silva, M.V.A. Martins, M.A.C. Rodrigues, J.O. Mendonça, I.M.M.M. Clemente, V.M. Laut, and L.G. Mentzigen. 2012. Foraminíferos do Complexo Sepetiba/Guaratiba. In Baía de Sepetiba, estado da arte, ed. M.A.C. Rodrigues, S.D. Pereira, and S.B. Santos, 115–148. Rio de Janeiro: Editora Corbã.
Laut, L.L.M., I.A. Cabral, M.A.C. Rodrigues, F.S. Sobrinho, M.V.A. Martins, T. Boski, A.I. Gomes, J.M. Alverinho Dias, L.F. Fontana, V.M. Laut, and J.G. Mendonca-Filho. 2014. Compartimentos Ambientais do Estuário do Rio Arade, Sul de Portugal, com base na distribuição e ecologia de foraminíferos. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências (UFRJ Impresso) 37 (2): 60–74.
Laut, L.L.M., F.S. Silva, M.V.A. Martins, M.A.C. Crapez, L.F. Fontana, S.B.V. Carvalhal-Gomes, and R.C.C.L. Souza. 2016. Foraminifera, thecamoebians, and bacterial activity in polluted intertropical and subtropical Brazilian estuarine systems. Journal of Coastal Research 317: 56–69.
Laut, L., I. Clemente, M.V.A. Martins, F. Frontalini, D. Raposo, P. Belart, R. Habib, R. Fortes, and M.L. Lorini. 2017. Foraminíferos e tecamebas bentônicos do estuário do Rio Godineau, Golfo de Paria, Ilha de Trinidad. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências (UFRJ IMPRESSO) 40: 118–143.
Loeblich, A.R., and H. Tappan. 1988. Foraminiferal genera and their classification. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company 970 pp.
Martins, V., and V. Gomes. 2004. Foraminíferos da margem conti-nental NW Ibérica: sistemática e ecologia. 4th ed. Aveiro: Universidade de Aveiro 331 pp.
Martins, M.V.A., F. Frontalini, K.M. Tramonte, R.C.L. Figueira, P. Miranda, C. Sequeira, S. Fernández-Fernández, J.A. Dias, C. Yamashita, L.L.M. Laut, F. Sobrinho, M.A. Rodrigues, C. Bernardes, R. Nagai, S.S.M. Sousa, M. Mahiques, B. Rubio, A. Bernabeu, D. Rey, and F. Rocha. 2013. Assessment of the health quality of Ria de Aveiro (Portugal): heavy metals and benthic foraminifera. Marine Pollution Bulletin 70 (1–2): 18–33.
Martins, M.V.A., A. Soares-Gomes, C. Yamashita, A.F.S. Pinto, F. Frontalini, C. Sequeira, L.L.M. Laut, P. Belart, N. Zaaboub, P. Miranda, S.H.M. Sousa, F. Figueira, A.L. Pena, D.L. Terroso, and F. Rocha. 2016. Similarity between the dead and living foraminiferal assemblages of the NE sector of Guanabara Bay (Brazil). Journal of Sedimentary Environments 1 (4): 411–431. https://doi.org/10.12957/jse.2016.26875.
Meyer-Reil, L.A., and M. Koster. 2000. Eutrophication of marine waters: effects on benthic microbial communities. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41 (1-6): 255–263.
Murray J (1991) Ecology and palaeoecology of benthic foraminifera. 1. Wiley, 397.
Murray, J. 2006. Ecology and applications of benthic foraminifera, 426. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nogueira, F.F., Costa, I.A., and Pereira, E. 2015. Análise de parâmetros físico-químicos da água e do uso e ocupação do solo na sub-bacia do Córrego da Água Branca no município de Nerópolis—Goiás.
Oliveira, L., R. Nascimento, L. Krau, and A. Miranda. 1955. Observações biogeográficas e hidrobiológias sobre a lagoa de Maricá. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 53 (2,3,4): 171–227.
Orabi, O.H., A.A. El-Badry, and A.M. Badr-El Din. 2017. Benthic foraminifera for heavy metal pollution monitoring: a case study from Burullus Lagoon of Egypt. Marine Pollution Bulletin 121 (1–2): 411–417.
Pedrozo, C.S. 2000. Avaliação da qualidade ambiental das lagoas da Planície Costeira do Rio Grande do Sul com ênfase na comunidade zooplanctônica. Tese (Doutorado Ecologia e Recursos Naturais). São Carlos: UFSCar 241 p.
Prado, P., C. Ibáñez, N. Caiola, and E. Reyes. 2013. Evaluation of seasonal variability in the food-web properties of coastal lagoons subjected to contrasting salinity gradientes using network analyses. Elselvier Science 265: 180–193.
Ramanantsoa, J.D., M. Krug, P. Penven, M. Rouault, and J. Gula. 2018. Coastal upwelling south of Madagascar: temporal and spatial variability. Journal of Marine Systems 178: 29–37.
Raposo, D., V. Laut, I. Clemente, M.V.A. Martins, F. Frontalini, F. Silva, M.L. Lorini, R. Fortes, and L. Laut. 2016. Recent benthic foraminifera from the Itaipu Lagoon, Rio de Janeiro (southeastern Brazil). Check List 12 (5): 1959. https://doi.org/10.15560/12.5.1959.
Raposo, D., I. Clemente, M. Figueiredo, A. Vilar, M.L. Lorini, F. Frontalini, M.V.A. Martins, P. Belart, L. Fontana, R. Habib, and L. Laut. 2018. Benthic foraminiferal and organic matter compounds as proxies of environmental quality in a tropical coastal lagoon: the Itaipu lagoon (Brazil). Marine Pollution Bulletin 129: 114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.018.
Ruiz, F.M., M.L. González, J.G. Pendón, M. Abad, M. Olías, and J.M. Muñoz. 2005. Correlation between foraminifera and sedimentary environments in recent estuaries of Southwestern Spain: applications to Holocene reconstructions. Quaternary International 140: 21–36.
Samir, A.M. 2000. The response of benthic foraminifera and ostracods to various pollution sources: a study from two lagoons in Egypt. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 30 (2): 83–98.
Schönfeld, J., E. Alve, E. Geslin, F. Jorissen, S. Korsun, S. Spezzaferri, S. Abramovich, A. Almogi-Labin, E.A. du Chatelet, C. Barras, L. Bergamin, E. Bicchi, V. Bouchet, A. Cearreta, L. Di Bella, N. Dijkstra, S.T. Disaro, L. Ferraro, F. Frontalini, G. Gennari, E. Golikova, K. Haynert, S. Hess, K. Husum, V. Martins, M. McGann, S. Oron, E. Romano, S.M. Sousa, and A. Tsujimoto. 2012. The FOBIMO (FOraminiferal BIo-MOnitoring) initiative—towards a standardised protocol for soft-bottom benthic foraminiferal monitoring studies. Marine Micropaleontology 94–95: 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marmicro.2012.06.001.
Sen, A., and P. Bhadury. 2016. Exploring the seasonal dynamics within the benthic foraminiferal biocoenosis in a tropical monsoon-influenced coastal lagoon. Aquatic Biology 25 (121–138): 2016–2138. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00658.
Sharifi, A.R., I.W. Croudace, and R.L. Austin. 1991. Benthic foraminiferids as pollution indicators in Southampton Water, southern England, UK. Journal of Micropalaeontology 10 (1): 109–113.
Silva, F.S., J.A.P. Bitencourt, F. Savergnini, L.V. Guerra, J.A. Baptista-Neto, and M.A.C. Crapez. 2011. Bioavailability of organic matter in the superficial sediment of Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências—UFRJ 34 (1): 52–63.
Smayda, T.J. 1983. The phytoplankton of estuaries. In Estuaries and enclosed sea, ed. B.H. Ketchum, 65–102. Amsterdan: Elsevier Scientific Publishing.
Souza, N.S., W.J. Souza, and J.M.S. Cardoso. 2017. Caracterização hidrológica e influência da cobertura do solo nos parâmetros de vazão do Rio das Fêmeas. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental 22 (3): 453–462.
Teodoro, A.C., W. Duleba, S. Gubitoso, S.M. Prada, C.C. Lamparelli, and J.E. Bevilacqua. 2010. Analysis of foraminifera assemblages and sediment geochemical properties to characterise the environment near Araçá and Saco da Capela domestic sewage submarine outfalls of São Sebastião Channel, São Paulo State, Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60 (4): 536–553.
Valentin, J.L., L.A. Dalmo, and A.J. Salvador. 1987. Hydrobiology in the Cabo Frio (Brazil) upwelling: two-dimensional structure and variability during a wind cycle. Continental Shelf Research 7 (1): 77–88.
Vilela, C.G., D.S. Batista, J.A. Baptista-Neto, M. Crapez, and J.J. Mcallister. 2004. Benthic Foraminifera distribution in high polluted sediments from Niterói Harbor (Guanabara Bay), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences 76 (1): 161–171.
Vilela, C.G., D.S. Batista, J.A. Baptista Neto, and R.O. Ghiselli. 2011. Benthic foraminifera distribution in a tourist lagoon in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: A response to anthropogenic impacts. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62 (10): 2055–2074.
Yanko, V., J. Kronfeld, and A. Flexer. 1994. Response of benthic foraminifera to various pollutions sources: implications for monitoring. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 24 (1): 1–17.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development—CNPq (grant: Universal 445830/2014-0). Pierre Belart and Débora Raposo received scholarships from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Level Personnel (CAPES). Renan Habib received scholarship from CNPq.
This research was supported by the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development—CNPq (grant: Universal 445839/2014-0). This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. The author Pierre Belart received a grant from CAPES (Finance Code 001). The authors Maria Virginia A. Martins and Lazaro Laut received a scientific productivity grand from CNPq (reference numbers: 301588/2016-3 and 301870/2016-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for sampling have been followed, and no specific permissions were required for these locations/activities. The field studies (and the provided specific locations by GPS coordinates) did not involve endangered or protected species and areas or particular spaces.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Marianne Holmer
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(XLSX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belart, P., Habib, R., Raposo, D. et al. Seasonal Dynamics of Benthic Foraminiferal Biocoenosis in the Tropical Saquarema Lagoonal System (Brazil). Estuaries and Coasts 42, 822–841 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-018-00514-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-018-00514-w