Abstract
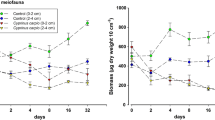
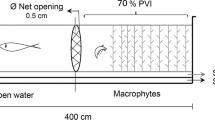
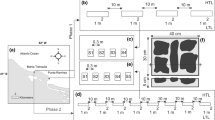
Among the predators, fish are prevalent in intertidal soft-bottom zones, and many create substantial interruptions in the sediment surface through their feeding, thus affecting the movement of fluids in the sediment-water interface and therefore the rates of deposition and local erosion. This study was designed to determine whether or not Micropogonias furnieri—an ecologically significant benthophagic southwestern Atlantic Ocean predator—modified erosion and/or sedimentation processes in salt marshes. The results indicated that this species exhibited a preference for areas without vegetation cover at the time of feeding since a greater abundance of pits was found in those environments. Moreover, the volume analysis of the pits in the two areas indicated that the size of the fish that had foraged in the sediment was significantly larger in the nonvegetated areas. The results of the M. furnieri-exclusion experiment indicated that the presence of this sciaenid neither resulted in a decrease in benthic organisms in the nonvegetated areas nor affected the vertical distribution of the infauna. When M. furnieri was excluded, the sediment exhibited higher critical-shearing and frictional-velocity values than in areas where M. furnieri had access and therefore was less likely to be eroded. The data from these experiments enabled us to conclude that the foraging action of M. furnieri modified the stability of the sediment as a result of the predatory pressure that the fish exerted on the organisms inhabiting the salt marshes, thus resulting in the generation of elliptical depressions. That modification of the sediment stability was evidenced in two principal ways: (i) a negative effect on the microphytobenthic organisms that decreased the concentration of extracellular polymeric substances in the sediment and (ii) an increased roughness of the bottom and increased percentage of sand in the particle composition of the sediment, where the fish had foraged.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson, A., and M. Denny. 1997. Settlement of marine organisms in flow. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 28: 317–339.
Billheimer, L.E., and B.C. Coull. 1988. Bioturbation and recolonization of meiobenthos into juvenile spot (Pisces) feeding pits. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 27: 335–340.
Botto, F., G. Palomo, O. Iribarne, and M.M. Martínez. 2000. The effect of Southwestern Atlantic burrowing crabs on habitat use and foraging activity of migratory shorebirds. Estuaries 23: 208–215.
Cacchione, D.A., and D.E. Drake. 1982. Measurements of storm-generated bottom stresses on the continental shelf. Journal of Geophysical Research. 87: 1952–1960.
Chesson, P. 2000. Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 31: 343–366.
Chestnut, D.E. 1983. Feeding habits of juvenile spot, Leiostomus xanthurus (Lacepede) in North Inlet estuary. Thesis. Columbia: University of South Carolina.
Coull, B.C., M.A. Palmer, and P.E. Myers. 1989. Controls on the vertical distribution of meiobenthos in mud: field and flume studies with juvenile fish. Marine Ecology Progress Series 55: 133–139.
Daborn, G.R., C.L. Amor, M.C. Berlinsky, G. Drapeau, R.W. Faas, J. Grant, B. Long, D.M. Paterson, G.M.E. Perillo, and M.C. Piccolo. 1993. An ecological “cascade” effect: Migratory birds affect stability of intertidal sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 225–231.
Dade, W.B., J.D. Davis, P.D. Nichols, A.R.M. Nowell, D. Thistle, M. Trexler, and D.C. White. 1990. Effects of bacterial exopolymer adhesion on the entrainment of sand. Geomicrobiology Journal 8: 1–16.
De Brouwer, J.F.C., S. Bjelic, E.M.G.T. De Deckere, and L.J. Stal. 2000. Interaction between biology and sedimentology in a mudflat (Biezelingse Ham, Westerschelde, the Netherlands). Continental Shelf Research 20: 1159–1178.
De Groot, S.J. 1971. On the interrelationships between morphology of the alimentary tract, food and feeding behaviour in flatfishes (Pisces: Pleuronectiformes). Netherlands J. Sea Res. 5: 121–196.
Decho, A.W. 2000. Microbial biofilms in intertidal systems: an overview. Continental Shelf Research 20: 1257–1273.
Dittmann, S. 1996. Effects of macrobenthic burrows on infaunal communities in tropical tidal flats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 134: 119–130.
Dubois, M., K.A. Gilles, J.K. Hamilton, P.A. Rebers, and F. Smith. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry 28: 350–356.
Ellis, M.J., and B.C. Coull. 1989. Fish predation on meiobenthos: field experiments with juvenile spot Leiostomus xanthurus Lacepede. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 130: 19–32.
Esselink, P., and L. Zwarts. 1989. Seasonal trend in burrow depth and tidal variation in feeding activity of Nereis diversicolor. Marine Ecology Progress Series 56: 243–254.
Fitzhugh, G.R., and W. Fleeger. 1985. Goby (Pisces: Gobiidae) interactions with meiofauna and small macrofauna. Bulletin of Marine Science 36: 436–444.
Fleeger, J.W., G. Tita, K.R. Carman, R.N. Millward, E.B. Moser, R.J. Portier, and R.P. Gambrell. 2006. Does bioturbation by a benthic fish modify the effects of sediment contamination on saltmarsh benthic microalgae and meiofauna? J. Exp. Mar. Biol and Ecol. 330: 180–194.
Friend, P.L., C.H. Lucas, and S.K. Rossington. 2005. Day-night variation of cohesive sediment stability. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 64: 407–418.
Grafals-Soto, R., and K. Nordstrom. 2009. Sand fences in the coastal zone: intended and unintended effects. Environmental Management 44 (3): 420–429.
Hall, S.J. 1994. Physical disturbance and marine communities: life in unconsolidated sediments. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review. 32: 179–239.
Heck, K.L., and J.F. Valentine. 2007. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuar. Coast. 30: 371–381.
Hiddink, J.G., R. Ter Hofstede, and W.J. Wolff. 2002. Predation of intertidal infauna on juveniles of the bivalve Macoma balthica. Journal of Sea Research 47: 141–159.
Hilton, C., S.J. Walde, and M.L. Leonard. 2002. Intense episodic predation by shorebirds may influence life history strategy of an intertidal amphipod. Oikos 99: 368–376.
Howard, J.D., T.V. Mayou, and R.W. Heard. 1977. Biogenic sedimentary structures formed by rays. J. Sed. Petrol. 47: 339–346.
Hozbor, N.M., and S.B. Garcia dela Rosa. 2000. Alimentación de juveniles de corvina rubia (Micropogonias furnieri) en la Laguna de Mar Chiquita. Frente Marítimo 18: 59–70.
Ieno, E., and R. Bastida. 1998. Spatial and temporal patterns in coastal macrobenthos of Samborombon Bay, Argentina: a case study of very low diversity. Estuaries 21 (4): 690–699.
Johnson, K.R., Neison, C.H., and Barber Jr., J.H. 1983. Assessment of gray whale feeding grounds and seafloor interaction in the northeastern Bering Sea. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 83–727, 112 p.
Johnson, K.R., and C.H. Nelson. 1984. Side-scan sonar assessment of gray whale feeding in the Bering Sea. Science 225: 1150–1152.
Lei, Y., K. Stumm, N. Volkenborn, U.G. Berninger, and S.A. Wickham. 2010. Impact of Arenicola marina (Polychaeta) on the microbial assemblages and meiobenthos in a marine intertidal flat. Marine Biology 157: 1271–1282.
Little, C. 2000. The biology of soft shores and estuaries. USA: Oxford University Press.
Lorenzen, C.J. 1967. Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. and Oc. 12: 343–346.
Lucas, C.H., J. Widdows, and L. Hall. 2003. Relating spatial and temporal variability in sediment chlorophyll a and carbohydrate distribution with erodibility of a tidal flat. Estuaries 26 (4): 885–893.
Lundkvist, M.M., P.L. Gruea, B. Friend, and M.R. Flindt. 2007. The relative contributions of physical and microbiological factors to cohesive sediment stability. Continental Shelf Research. 27: 1143–1152.
Luo, J., Y. Ye, and X. Yin. 2015. Bioaccumulation and dietary exposure of the red-crowned cranes (Grus japonensis) to arsenic in Zhalong wetland, Northeastern China. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management. 18(1): 121-129
Martin, J.P. 2002. Aspectos biológicos y ecológicos de los poliquetos de ambientes mixohalinos de la Provincia de Buenos Aires. Tesis Doctoral. Argentina: Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, 314 pp.
Martinetto, P., O. Iribarne, and G. Palomo. 2005. Effect of fish predation on intertidal benthic fauna is modified by crab bioturbation. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 318: 71–84.
Mendoza-Carranza, M., and J.P. Vieira. 2007. Whitemouth croaker Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, 1823) feeding strategies across four southern Brazilian estuaries. Aquatic Ecology 42 (1): 83–93.
Molina, L.M. 2013. El rol de la biota en los procesos de estabilización—desestabilización de sedimentos estuariales. UNS: Doctoral thesis.
Molina, L.M., M.S. Valiñas, P.D. Pratolongo, R. Elias, and G.M.E. Perillo. 2009. First record of the sea anemone Diadumene lineata (Verrill 1871) associated to Spartina alterniflora roots and stems in marshes at the Bahia Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Biological Invasions 11: 409–416.
Nelson, C.H., K.R. Johnson, and J.H. Barber. 1987. Gray Whale and Walrus Feeding Excavation on the Bering Shelf, Alaska. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 57: 419–430.
Norton, S.F., and Cook, A. E. 1999. Predation by fishes in intertidal. En: Horn, M. H., Martin, K. L. M., y Chotkowski, M. A. (Eds.), Intertidal fishes: Life in two worlds, Academic Press, USA. pp. 223–263.
Nowell, A.R.M., and P.A. Jumars. 1984. Flow environments of aquatic benthos. AnnualReview of Ecology and Systematics 15: 303–328.
Olsson, D., F. Forni, G. Saona, J. Verocai, and W. Norbis. 2013. Temporal feeding habits of the whitemouth croaker Micropogonias furnieri in a shallow coastal lagoon (southwestern Atlantic Ocean, Uruguay). Ciencias Marinas 39 (3): 265–276.
Palomo, G., F. Botto, D. Navarro, M. Escapa, and O. Iribarne. 2003. The predator-prey interaction between migratory shorebirds and the polychaete Laeonereis acuta is modified by burrowing crabs. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 290: 211–228.
Paterson, D., T.J. Tolhurst, J.A. Kelly, C. Honeywill, E.M.G.T. De Deckere, V. Huet, S.A. Shayler, K.S. Black, J. De Brouwer, and I. Davidson. 2000. Variations in sediment properties, Skeffling mudflat, Humber Estuary, UK. Continental Shelf Research 20: 1373–1396.
Perillo, G.M.E., D.R. Minkoff, and M.C. Piccolo. 2005. Novel mechanism of stream formation in coastal wetlands by crab–fish–groundwater interaction. Geo-Marine Letters. 25 (4): 214–220.
Perillo, G.M.E., Piccolo, M.C., Parodi, E., and R.H. Freije. 2000. The Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. In Coastal marine ecosystem of Latin America. Ecological studies, vol 14, ed. Seeliger U, y Kjerfv B. (s). 205–215. Springer.
Piccolo, M.C., and G.M.E. Perillo. 1990. Physical characteristics of the Bahia Blanca estuary (Argentina). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 31: 303–317.
Pratolongo, P.D., G.M.E. Perillo, and M.C. Piccolo. 2010. Combined effects of waves and marsh plants on mud deposition events at a mudflat-saltmarsh edge. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Sciences. 87: 207–212.
Quijón, P., and Jaramillo, E. 1996. Seasonal vertical distribution of the intertidal macroinfauna in an estuary of south-central Chile. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science :653–663.
Reise, K. 1979. Moderate predation on meiofauna by the macrobenthos of the Wadden Sea. Helgolander wiss. Meeresunters. 32: 453–465.
Risk, M.J., and H.D. Craig. 1976. Flatfish feeding traces in the Minas Basin. I. Sed. Pet. 46: 411–413.
Sardiña, P., and A. Lopez Cazorla. 2005. Ontogenetic and seasonal changes in the diet of the whitemouth croaker, Micropogonias furnieri (Pisces: Sciaenidae), in South-western Atlantic waters. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 85: 405–413.
Seitz, R.D., R.N. Lipcius, A.H. Hines, and D.B. Eggleston. 2001. Density-dependent predation, habitat variation and the persistence of the marine bivalve prey. Ecology 82: 2435–2451.
Self, R.F.L., A.R.M. Nowell, and P.A. Jumars. 1989. Factors controlling critical shears for deposition and erosion of individual grains. Marine Geology 86: 181–199.
Sewell, M. 1996. Detection of the impact of predation by migratory shorebirds: an experimental test in the Fraser River Estuary, British Columbia (Canada). Marine Ecology Progress Series 144 (18): 23–40.
Sheskin, D.J. 2004. Handbook of Parametric and Nonparametric Statistical Procedures. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: Chapman y Hall.
Shirley, T.C. 1990. Ecology of Priapulus caudatus Lamarck, 1816 (Priapulida) in an Alaskan subarctic ecosystem. Bull. Mar. Science. 47: 149–158.
Sinha, S.N., A.K. Gupta, and M.M. Oberai. 1982. Laminar separating flow over backsteps and cavities: Part II: Cavities. AIAAJ 20: 370–375.
Smith, D.L., and B.C. Coull. 1987. Juvenile spot (Pisces) and grass shrimp predation on meiobenthos in muddy and sandy substrata. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 105: 123–136.
Stal, L., and J. De Brouwer. 2003. Biofilm formation by benthic diatoms and their influence on the stabilization of intertidal mudflats. Forschungszentrum Terramare Berichte. 12 (12): 109–111.
Stephen, A.C. 1941. The echiniudae, sipunculidae and priapulidae collected by the ships of the discovery committee during the years 1926 to 1937. Discovery Rep 21: 235–260.
Thiel, H., O. Pfannkuche, G. Schriever, K. Lochte, A.J. Gooday, C.H. Hemleben, R.F.C. Mantoura, C.M. Turley, J.W. Patching, and F. Riemann. 1989. Phytodetritus on the deep-sea floor in a central oceanic region of the North-east Atlantic. Biological Oceanography 6: 203–239.
Thistle, D. 1981. Natural physical disturbances and communities of marine soft bottoms. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 6: 223–228.
Thrush, S.F. 1991. Spatial patterns in soft-bottom communities. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 6 (3): 75–79.
Thrush, S.F., J.E. Hewitt, M. Gibbs, C. Lundquist, and Y.A. Norkko. 2006. Functional Role of Large Organisms in Intertidal Communities: Community Effects and Ecosystem Function. Ecosystems 9: 1029–1040.
Thrush, S.F., J.E. Hewitt, and A. Norkko. 2003. Catastrophic sedimentation on estuarine sandflats: recovery of macrobenthic communities is influenced by a variety of environmental factors. Ecological Applications 13: 1433–1455.
Thrush, S.F., R.D. Pridmore, J.E. Hewitt, and V.J. Cummings. 1994. The importance of predators on a sandflat: interplay between seasonal changes in prey densities and predator effects. Marine Ecology Progress Series 107: 211–222
Tolhurst, T.J., K.S. Black, S.A. Shayler, S. Mather, I. Black, K. Baker, and D.M. Paterson. 1999. Measuring the in situ Erosion Shear Stress of Intertidal Sediments with the Cohesive Strength Meter (CSM). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 49: 281–294.
Underwood, G.J.C., and D.M. Paterson. 1993. Seasonal changes in diatom biomass, sediment stability and biogenic stabilization in the Severn Estuary. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK. 73: 871–887.
Underwood, G.J.C., D.M. Paterson, and R.J. Parkes. 1995. The measurement of microbial carbohydrate exopolymers from intertidal sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1243–1253.
Valiñas, M.S., L.M. Molina, M. Addino, D. Montemayor, E.M. Acha, and O. Iribarne. 2012. Biotic and abiotic factors affect SW Atlantic saltmarsh use by juvenile fishes. Journal of Sea Research. 68: 49–56.
Varzaly, A.M. 1978. Some features of low- speed flow over a rectangular cavity. Engineer thesis. CA: Stanford Univ., 189 pp.
Wilson, W.H. 1991. Competition and predation in marine soft-sediment communities. Annual Reviews in Ecology and Systematics. 21: 221–241.
Wong, M.C., C.H. Peterson, and M.F. Piehler. 2011. Evaluating estuarine habitats using secondary production as a proxy for food web support. Marine Ecology Progress Series 440: 11–25.
Yager, P.L., A.R.M. Nowell, and P.A. Jumars. 1993. Enhanced deposition to pits: a local food source for benthos. Journal of Marine Research 51: 209–236.
Yallop, M.L., D.M. Paterson, and P. Wellsbury. 2000. Interrelationships between rates of microbial production, microbial biomass, and sediment stability in biofilms of intertidal sediments. Microbial Ecology 39: 116–127.
Zar, J.H. 1999. Biostatistical analysis. Englewood Cliff: Prentice-Hall.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Donald F. Haggerty, a retired academic career investigator and native English speaker, who edited the final version of the manuscript. This project was supported in part by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Técnica (ANPCYT). L. Molina was supported by a scholarship from CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by James L. Pinckney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, L.M., Valiñas, M.S., Pratolongo, P.D. et al. Effect of “Whitemouth Croaker” (Micropogonias furnieri, Pisces) on the Stability of the Sediment of Salt Marshes—an Issue To Be Resolved. Estuaries and Coasts 40, 1795–1807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0237-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0237-y