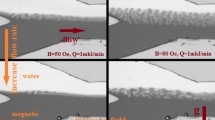
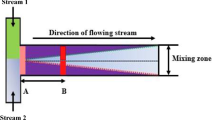
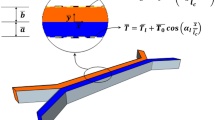
Abstract
Microfluidic devices are widely used in microbiology, fine organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, biomedicine, etc. Most applications require rapid mixing of the fluids that pass through the microfluidic chip. Continuous-flow microreactors used in flow chemistry have a characteristic channel size that is small enough, compared to standard laboratory size in fluid mechanics but large enough to render the diffusion mixing mechanism ineffective. In this work, we study, experimentally and theoretically, the efficiency of using various mechanisms of natural convection for the mixing of fluids entering the microfluidic chip. Solutions typically differ in buoyancy and diffusion rates of solutes, making them sensitive to gravity-dependent instabilities such as Rayleigh-Taylor convection, double diffusion, and diffusion layer convection. We consider a Y-shaped microreactor, which is, on the one hand, the simple scheme of mixing and, on the other hand, a typical element of a microfluidic network. We assume that two miscible solutions independently enter through different tubes into a common channel, where they come into contact and begin to mix. For simplicity, we do not consider chemical reactions in this paper. For each type of instability, we numerically estimated the characteristic channel length, after which complete mixing of the solutions occurs. The numerical simulations are performed in the framework of the 3D model. Finally, we compare the experimental data and numerical results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available at the web address: https://disk.yandex.ru/d/o-AN5z1TQV7OPA.
References
Arias, S., Montlaur, A.: Influence of contact angle boundary condition on CFD simulation of T-junction. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30(4), 435–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9605-x
Arias, S., Montlaur, A.: Numerical and experimental study of the squeezing-to-dripping transition in a T-junction. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32(4), 687–697 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-020-09794-z
Bau, H.H., Zhong, J., Yi, M.: A minute magneto hydro dynamic (MHD) mixer. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 79(2–3), 207–215 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(01)00851-6
Baumann, M., Baxendale, I.R.: The synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) using continuous flow chemistry. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 11(1), 1194–1219 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.11.134
Boyko, E., Rubin, S., Gat, A.D., Bercovici, M.: Flow patterning in hele-shaw configurations using non-uniform electro-osmotic slip. Phys. Fluids 27(10), 102001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4931637
Boyko, E., Bercovici, M., Gat, A.D.: Flow of power-law liquids in a hele-shaw cell driven by non-uniform electro-osmotic slip in the case of strong depletion. J. Fluid Mech. 807, 235–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.622
Bratsun, D., De Wit, A.: Control of chemoconvective structures in a slab reactor. Tech. Phys. 53(2), 146–153 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784208020023
Bratsun, D., Siraev, R.: Controlling mass transfer in a continuous-flow microreactor with a variable wall relief. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 113, 104522 (2020a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104522
Bratsun, D., Siraev, R.:Switching modes of mixing due to an adjustable gap in a continuous-flow microreactor. In: Actuators, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute 9, 2 (2020b). https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010002
Bratsun, D., Shi, Y., Eckert, K., De Wit, A.: Control of chemo-hydrodynamic pattern formation by external localized cooling. EPL (Europhysics Letters) 69(5), 746–752 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2004-10417-9
Bratsun, D., Krasnyakov, I., Zyuzgin, A.: Delay-induced oscillations in a thermal convection loop under negative feedback control with noise. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 47, 109–126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.11.015
Bratsun, D., Kostarev, K., Mizev, A., Aland, S., Mokbel, M., Schwarzenberger, K., Eckert, K.:Adaptive micromixer based on the solutocapillary marangoni effect in a continuous-flow microreactor. Micromachines 9(11), 600 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110600
Bratsun, D., Mizev, A., Mosheva, E.: Extended classification of the buoyancy-driven flows induced by a neutralization reaction in miscible fluids. Part 2. Theoretical study. J. Fluid Mech. 916, A23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.202
Bratsun, D.A., Krasnyakov, I.V., Zyuzgin, A.V.: Active control of thermal convection in a rectangular loop by changing its spatial orientation. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30(1), 43–52 (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-017-9573-6
Bratsun, D.A., Oschepkov, V.O., Mosheva, E.A., Siraev, R.R.: The effect of concentration-dependent diffusion on double-diffusive instability. Phys. Fluids 34(034), 112 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0079850
Brodskii, A., Levich, V.: Chemical reactor theory for homogeneous-heterogeneous processes in continuous flow reactors. Teor Osn Khim Tekhnol 1, 147–157 (1967)
Cai, G., Xue, L., Zhang, H., Lin, J.: A review on micromixers. Micromachines 8(9), 274 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8090274
Filipponi, P., Ostacolo, C., Novellino, E., Pellicciari, R., Gioiello, A.: Continuous flow synthesis of thieno[2,3-c]isoquinolin-5(4h)-one scaffold: A valuable source of parp-1 inhibitors. Org. Process Res. Dev. 18(11), 1345–1353 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/op500074h
Gershuni, G., Lyubimov, D.: Thermal Vibrational Convection. Willey, New York (1998)
Gershuni, G.Z., Zhukhovitsky, E.M.: On the convectional instability of a two-component mixture in a gravity field. J Appl Math Mech 27(2), 301–308 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-8928(63)90012-1
Han, W., Chen, X.: Effect of geometry configuration on the merged droplet formation in a double T-junction. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31(6), 855–864 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09720-y
Hao, G., Li, L., Wu, L., Yao, F.: Electric-field-controlled droplet sorting in a bifurcating channel. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 34(2), 1–17 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-022-09944-5
Hessel, V., Löwe, H., Schönfeld, F.: Micromixers-a review on passive and active mixing principles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(8–9), 2479–2501 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.11.033
Huang, Y., Yang, Q., Zhao, J., Miao, J., Shen, X., Fu, W., Wu, Q., Guo, Y.: Experimental study on flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of ammonia in microchannels. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32(3), 477–492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-020-09786-z
Ingel’, L.K.: Double-diffusive density flows. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 46, 41–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433810010068
Levenspiel, O.: Chemical Reaction Engineering. John Wiley & Sons, New York (1999)
Levich, V., Brodskii, A., Pismen, L.: A contribution to theory of branching homogeneous chain reaction in a flow. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 176, 371–373 (1967)
Martin, A.D., Siamaki, A.R., Belecki, K., Gupton, B.F.: A flow-based synthesis of telmisartan. Journal of Flow Chemistry 5(3), 145–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1556/JFC-D-15-00002
Minakov, A., Rudyak, V., Gavrilov, A., Dekterev, A.: On optimization of mixing process of liquids in microchannels. Journal of Siberian Federal University Mathematics and Physics 3(2), 146–156 (2010)
Mizev, A., Mosheva, E., Bratsun, D.: Extended classification of the buoyancy-driven flows induced by a neutralization reaction in miscible fluids. Part 1. Experimental study. J. Fluid Mech. 916, A22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.201
Newman, S.G., Jensen, K.F.: The role of flow in green chemistry and engineering. Green Chem. 15(6), 1456–1472 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC40374B
Nguyen, N.T.: Micromixers: Fundamentals, Design and Fabrication. William Andrew (2011)
Nguyen, T., Kim, M.C., Park, J.S., Lee, N.E.: An effective passive microfluidic mixer utilizing chaotic advection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 132(1), 172–181 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.01.022
Nieves-Remacha, M.J., Kulkarni, A.A., Jensen, K.F.: Hydrodynamics of liquid–liquid dispersion in an advanced-flow reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(50), 16251–16262 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie301821k
Nimafar, M.: Study and development of new passive micromixers based on split and recombination principle. PhD. Dissertation in Mechanic Politecnico Di Torino (2013)
Nimafar, M., Viktorov, V., Martinelli, M.: Experimental comparative mixing performance of passive micromixers with H-shaped sub-channels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 76, 37–44 (2012a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2012.03.036
Nimafar, M, Viktorov, V., Martinelli, M.: Experimental investigation of split and recombination micromixer in confront with basic T-and O-type micromixers. Int. J. Mech. Appl. 2(5), 61–69 (2012b). https://doi.org/10.5923/j.mechanics.20120205.02
Noro, S., Kokunai, K., Shigeta, M., Izawa, S., Fukunishi, Y.: Mixing enhancement and interface characteristics in a small-scale channel. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 3(8), 1020–1030 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1299/jfst.3.1020
Ohkawa, K., Nakamoto, T., Izuka, Y., Hirata, Y., Inoue, Y.: Flow and mixing characteristics of σ-type plate static mixer with splitting and inverse recombination. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 86(12), 1447–1453 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2008.09.004
Pellegatti, L., Sedelmeier, J.: Synthesis of vildagliptin utilizing continuous flow and batch technologies. Org. Process Res. Dev. 19(4), 551–554 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00058
Raja, S., Satyanarayan, M., Umesh, G., Hegde, G.: Numerical investigations on alternate droplet formation in microfluidic devices. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 33(6), 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-021-09917-0
Reschetilowski, W.: Microreactors in preparative chemistry: practical aspects in bioprocessing, nanotechnology, catalysis and more. John Wiley & Sons (2013)
Singer, J., Bau, H.H.: Active control of convection. Phys. Fluids A 3(12), 2859–2865 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.857831
Siraev, R., Ilyushin, P., Bratsun, D.: Mixing control in a continuous-flow microreactor using electro-osmotic flow. Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena 16, 49 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1051/mmnp/2021043
Stern, M.E.: The “salt-fountain” and thermohaline convection. Tellus 12(2), 172–175 (1960). https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusa.v12i2.9378
Stern, M.E., Turner, J.S.: Salt fingers and convecting layers. Deep-Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 16(5), 497–511 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-7471(69)90038-2
Stroock, A.D., Dertinger, S.K.W., Ajdari, A., Mezić, I., Stone, H.A., Whitesides, G.M.: Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295(5555), 647–651 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066238
Tian, W.C., Finehout, E.: Microfluidics for Biological Applications, vol. 16. Springer Science & Business Media (2009)
Tian, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, S.: Numerical study on bilateral koch fractal baffles micromixer. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31(6), 833–843 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09713-x
Tsai, J.H., Lin, L.: Active microfluidic mixer and gas bubble filter driven by thermal bubble micropump. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 97, 665–671 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-4247(02)00031-6
Turner, J.S.: Double-diffusive phenomena. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 6(1), 37–54 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fl.06.010174.000345
Viktorov, V., Mahmud, M.R., Visconte, C.: Comparative analysis of passive micromixers at a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Micromachines 6(8), 1166–1179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi6081166
Wegner, J., Ceylan, S., Kirschning, A.: Ten key issues in modern flow chemistry. Chem. Commun. 47(16), 4583–4592 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC05060A
Wyant, J.C.: Use of an AC heterodyne lateral shear interferometer with real-time wavefront correction systems. Appl Opt 14(11), 2622–2626 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.14.002622
Funding
This study was funded by Perm National Research Polytechnic University in the framework of the federal academic leadership program “Priority 2030”. Also, E.M. wishes to thank the Scholarship of RF President for young scientists (no. SP-2408.2021.1) and the Ministry of Science and High Education of Russia (theme no. 121031700169-1) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: The Effect of Gravity on Non-equilibrium Processes in Fluids
Guest Editors: Tatyana Lyubimova, Valentina Shevtsova
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bratsun, D.A., Siraev, R.R., Pismen, L.M. et al. Mixing Enhancement By Gravity-dependent Convection in a Y-shaped Continuous-flow Microreactor. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 34, 90 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-022-09994-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-022-09994-9