Abstract
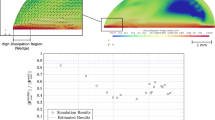
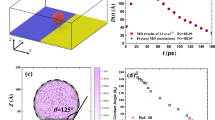
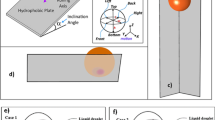
To find out the mechanism of droplet movement on the composite wedge-shaped surface with multi wettability gradients and simulated gravitational field in a micro view, the model of droplet movement was built and studied by molecular dynamics. It was found that the droplet would move faster and farther with greater vertex angle on hydrophobic surface than on hydrophilic surface until the whole droplet reached the strong wettability surface. Applied force was used to simulate gravitational field. An inflection point was appeared in the average velocity curve. The average velocity increased first and then decreased with greater applied force. The simulation results of relationship between average velocity and applied force corresponded well with nonlinear fitting curve, indicating the reasonable and reliable of simulation results. With the increase of applied force, the droplet became more flat. However, the effect of wettability gradient to shrink the spread area played a major role in the early to make the droplet narrower and then the combined effect of wettability gradient to enlarge the spread area and applied force had a major impact in the later to make the droplet spread more.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiadis, A., Kassinos, S.: Molecular simulation of water in carbon nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 108, 5014 (2008)
Bai, H., Tian, X.L., Zheng, Y.M., Ju, J., Zhao, Y., Jiang, L.: Direction controlled driving of tiny water drops on bioinspired artificial spider silks. Adv. Mater. 22, 5521–5525 (2010)
Cieplak, M., Koplik, J., Banavar, J.R.: Nanoscale fluid flows in the vicinity of patterned surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 114502 (2006)
Chaudhury, M.K., Whitesides, G.M.: How to make water run uphill. Science 256, 1539–1541 (1992)
Chen, Y., Wang, L., Xue, Y., Jiang, L., Zheng, Y.: Bioinspired tilt-angle fabricated structure gradient fibers: micro-drops fast transport in a long-distance. Sci. Rep., 3 (2013)
Chen, X., Ding, Z.J., Liu, R.: Spreading of annular droplets on a horizontal fiber. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 143–153 (2018)
Chou, I.H., Benford, M., Beier, H.T., Cote, G.L.: Nanofluidic biosensing for beta-amyloid detection using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 8, 1729–1735 (2008)
Daniel, S., Chaudhury, M.K., Chen, J.C.: Past drop movements resulting from the phase change on a gradient surface. Science 291, 633–636 (2001)
Daniel, S., Chaudhury, M.K., De Gennes, P.G.: Vibration-actuated drop motion on surfaces for batch microfluidic processes. Langmuir 21, 4240–4248 (2005)
De Coninck, J., Blake, T.D.: Wetting and molecular dynamics simulations of simple liquids. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 38, 1 (2008)
Deng, S., Shang, W., Feng, S., Zhu, S., Xing, Y., Li, D., Hou, Y., Zheng, Y.: Controlled droplet transport to target on a high adhesion surface with multi-gradients. Sci. Rep., 7 (2017a)
Deng, S.Y., Shang, W.F., Feng, S.L., Zhu, S.P., Xing, Y., Li, D., Hou, Y.P., Zheng, Y.M.: Controlled droplet transport to target on a high adhesion surface with multi-gradients. Sci. Rep-UK, 45687 (2017b)
Furuta, T., Sakai, M., Isobe, T., Matsushita, S., Nakajima, A.: Sliding of water droplets on hydrophobic surfaces with various hydrophilic region sizes. Langmuir 27, 7307–7313 (2011)
Greenspan, H.P.: Motion of a small viscous droplet that wets a surface. J. Fluid Mech. 84, 125–143 (1978)
Guo, L., Tang, G.H.: Experimental study on directional motion of a single droplet on cactus spines. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 84, 198–202 (2015)
Ghosh, A., Ganguly, R., Schutzius, T.M., Megaridis, C.M.: Wettability patterning for high-rate, pumpless fluid transport on open, non-planar microfluidic platforms. Lab Chip 14, 1538–1550 (2014)
Grunze, M.: Surface science - driven liquids. Science 283, 41–42 (1999)
Halverson, J.D., Maldarelli, C., Couzis, A., Koplik, J.: A molecular dynamics study of the motion of a nanodroplet of pure liquid on a wetting gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 129, 164708 (2008)
Hoover, W.G.: Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 31, 1695 (1985)
Ito, Y., Heydari, M., Hashimoto, A., Konno, T., Hirasawa, A., Hori, S., Kurita, K., Nakajima, A.: The movement of a water droplet on a gradient surface prepared by photodegradation. Langmuir 23, 1845–1850 (2007)
Ju, J., Bai, H., Zheng, Y., Zhao, T., Fang, R., Jiang, L.: A multi-structural and multi-functional integrated fog collection system in cactus. Nat. Commun. 3, 1247 (2012)
Ju, J., Xiao, K., Yao, X., Bai, H., Jiang, L.: Bioinspired conical copper wire with gradient wettability for continuous and efficient fog collection. Adv. Mater. 25, 5937–5942 (2013)
Koishi, T., Yasuoka, K., Fujikawa, S., Ebisuzaki, T., Zeng, X.C.: Coexistence and transition between Cassie and Wenzel state on pillared hydrophobic surface. PNAS 106, 8435–8440 (2009)
Koishi, T., Yasuoka, K., Fujikawa, S., Zeng, X.C.: Measurement of contact-angle hysteresis for droplets on nanopillared surface and in the Cassie and Wenzel states: a molecular dynamics simulation study. ACS Nano 5, 6834–6842 (2011)
Kostoglou, M., Karapantsios, T.D., Buffone, C., Glushchuk, A., Iorio, C.: A theoretical study of steady state and transient condensation on axisymmetric fins under combined capillary and gravitational forces. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 559–567 (2016)
Kou, J.L., Mei, M.F., Lu, H.J., Wu, F.M., Fan, J.T.: Unidirectional motion of a water nanodroplet subjected to a surface energy gradient. Phys. Rev. E 85, 056301 (2012)
Lei, Y.C., Chen, Z.Q., Shi, J.: Analysis of condensation heat transfer performance in curved triangle microchannels based on the volume of fluid method. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 433–443 (2017)
Li, P.P., Chen, Z.Q., Shi, J.: Numerical study on the effects of gravity and surface tension on condensation process in square minichannel. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 19–24 (2018)
Li, K., Ju, J., Xue, Z., Ma, J., Feng, L., Gao, S., Jiang, L.: Structured cone arrays for continuous and effective collection of micron-sized oil droplets from water. Nat. Commun. 4, 2276 (2013)
Lundgren, M., Neil, L.A., Terence, C.: Modeling of wetting: a study of nanowetting at rough and heterogeneous surfaces. Langmuir 23, 1187–1194 (2007)
Lv, C.J., Chen, C., Chuang, Y.C., Tseng, F.G., Yin, Y.J., Grey, F., Zheng, Q.S.: Substrate curvature gradient drives rapid droplet motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 026101 (2014)
Martin, B., Hervé, C., Youen, V., Stéphane, D.: Electrically charged droplets in microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 229–239 (2017)
Paradisanos, I., Fotakis, C., Anastasiadis, S.H., Stratakis, E.: Gradient induced liquid motion on laser structured black Si surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 111603 (2015)
Plimpton, S.: Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 117(1), 1–19 (1995)
Price, S.L., Stone, A.J., Alderton, M.: Explicit formulae for the electrostatic energy, forces and torques between a pair of molecules of arbitrary symmetry. Mol. Phys. 52(7), 987–1001 (1984)
Tan, X., Zhu, Y., Shi, T., Tang, Z., Liao, G.: Patterned gradient surface for spontaneous droplet transportation and water collection: simulation and experiment. J. Micromech. Microeng. 26, 115009 (2016)
Tian, X., Chen, Y., Zheng, Y., Bai, H., Jiang, L.: Controlling water capture of bioinspired fibers with hump structures. Adv. Mater. 23, 5486–5491 (2011)
Wang, F.C., Yang, F., Zhao, Y.P.: Size effect on the coalescence-induced self-propelled droplet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 053112 (2011)
Wang, T., Li, W., Liu, L., Chen, H.X., Wang, Y.F., Zhang, J., Yan, Y.G.: The mechanism for the motion of nanoscale water droplet induced by wetting gradient: a molecular dynamic study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 105, 39–46 (2015)
Xu, T., Lin, Y., Zhang, M., Shi, W., Zheng, Y.: High-efficiency fog collector: water unidirectional transport on heterogeneous rough conical wires. ACS Nano 10, 10681–10688 (2016)
Yen, T.H.: Wetting characteristics of nanoscale water droplet on silicon substrates with effects of surface morphology. Mol. Simulat. 37, 766–778 (2011)
Yong, X., Zhang, L.T.: Nanoscale wetting on groove-patterned surfaces. Langmuir 25, 5045–5053 (2009)
You, I., Lee, T.G., Nam, Y.S., Lee, H.: Fabrication of a micro-omnifluidic Device by omniphilic/omniphobic patterning on nanostructured surfaces. ACS Nano 8, 9016–9024 (2014)
Zhang, L.G., Shi, J., Xu, B., Chen, Z.Q.: Experimental study on distribution characteristics of condensate droplets under ultrasonic vibration. Microgravity Sci. Technol., 1–10 (2018)
Zhang, J., Han, Y.: Shape-gradient composite surfaces: water droplets move uphill. Langmuir 23, 6136–6141 (2007a)
Zhang, J.L., Han, Y.C.: Shape-gradient composite surfaces: water droplets move uphill. Langmuir 23, 6136–3414 (2007b)
Zhang, K., Wang, F.H., Zhao, X.: The self-propelled movement of the water nanodroplet in different surface wettability gradients: a contact angle view. Comput. Mater. Sci. 124, 190–194 (2016)
Zheng, Y., Bai, H., Huang, Z., Tian, X., Nie, F.Q., Zhao, Y., Jiang, L.: Directional water collection on wetted spider silk. Nature 463, 640 (2010)
Zou, Z.Z., Luo, X.H., Yu, Q.: Droplet image super resolution based on sparse representation and kernel regression. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 321–329 (2018)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China’s Manned Space Program [grant number TZ-1] and Scientific Research Foundation of Graduate School of Southeast University [grant number YBJJ1602].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Chen, Z. Droplet Movement on a Composite Wedge-Shaped Surface with Multi-Gradients and Different Gravitational Field by Molecular Dynamics. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 571–579 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9641-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9641-6