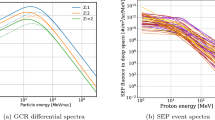
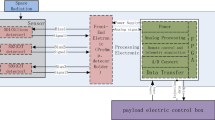
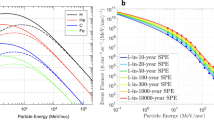
Abstract
Highly energized particles deliver ionizing radiation of galactic cosmic rays as well as solar particle events is a severe risk to the crews in long-term space missions. Two ground-based heavy ion experiment platforms simulating radiation environment of outer space have been established at the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences. One task of the Department of Space Radiobiology is to manage the platforms and provide support to the experimental studies carried out on the platforms. The other one is to conduct basic studies on space radiobiology to establish accurate risk assessment models of space radiation and develop efficient countermeasures for the long-term exploration in deep space.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cucinotta FA, Durante M (2006) Cancer risk from exposure to galactic cosmic rays: implications for space exploration by human beings. Lancet Oncol 7:431–435
Cucinotta FA, Hu S, Schwadron NA, Kozarev K, Townsend LW, Kim MHY (2010) Space radiation risk limits and Earth-Moon-Mars environmental models. Space Weather 8(12)
Ding N, Pei H, He J, Furusawa Y, Hirayama R, Liu C, Matsumoto Y, Li H, Hu W, Li Y, Wang J, Wang T, Zhou G (2013) Simulated studies on the biological effects of space radiation on quiescent human fibroblasts. Adv Space Res 52:1314–1319
Durante M, Cucinotta FA (2008) Heavy ion carcinogenesis and human space exploration. Cancer 8:465–472
Durante M, Cucinotta FA (2011) Physical basis of radiation protection in space travel [J]. Rev Mod Phys 83(4):1245
Hei TK, Zhou H, Ivanov VN, Hong M, Lieberman HB, Brenner DJ, Amundson SA, Geard CR (2008) Mechanism of radiation-induced bystander effects: a unifying model. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:943–950
Hellweg CE, Kham CB (2007) Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts’ risk from space radiation. Naturwissenschaften 94:517–526
Ishikawa H, Ohno T, Kato S, Wakatsuki M, Iwakawa M, Ohta T et al (2012) Status of ion sources at National Institute of Radiological Sciences. Rev Sci Instrum 83(2):02A332
Kim MY, Angelis GD, Cucinante FA (2011) Probabilistic assessment of radiation risk for astronauts in space missions. Acta Astron 68:747–759
Lloyd SA, Bandstra ER, Willey JS, Riffle SE, Tirado-Lee L, Nelson GA et al (2012) Effect of proton irradiation followed by hindlimb unloading on bone in mature mice: a model of long-duration spaceflight. Bone 51(4):756–764
Lowenstein DI (2000) BNL accelerator-based radiobiology facilities. Brookhaven National Lab., Upton, NY (US)
Shay JW, Cucinotta FA, Sulzman FM (2011) From mice and men to earth and space: joint NASA-NCI workshop on lung cancer risk resulting from space and terrestrial radiation. Cancer Res 71:6926–6932
Wang F, Bing Z, Zhang Y, Ao B, Zhang S, Ye C, He J, Ding N, Ye W, Xiong J, Sun J, Furusawa Y, Zhou G, Yang L (2013a) Quantitative proteomic analysis for radiation-induced cell cycle suspension in 92-1 melanoma cell line. J Radiat Res 1–14
Wang J, He J, Su F, Ding N, Hu W, Yao B, Wang W, Zhou G (2013b) Repression of ATR pathway by miR-185 enhances radiation-induced apoptosis and proliferation inhibition. Cell Death Disease 4:e699
Wei BW (1989) Results from Lanzhou K450 heavy ion cyclotron. In: Proceedings of 1989 Particle Accelerators Conference, IEEE
Wei BW (1993) HIRFL heavy ion cooler-storage ring proposal. In: Proceedings of the Fifth China–Japan Joint Symposium on Accelerators for Nuclear Science and Their Applications, Osaka, Japan, pp 162
Williams JR (1999) Predicting cancer rates in astronauts from animal carcinogenesis studies and cellular markers. Mutat Res 430:255–269
Xia JW, Rao YN, Yuan YJ, Wei BW (1996) HIRFL-CSR plan. In: Proceedings of the Sixth China–Japan Joint Symposium on Accelerators for Nuclear Science and Their Applications, Chengdu, China, pp 24
Xia JW, Wang YF, Rao YN, Yuan YJ, Song MT, Zhang WZ, Watanabe S (1998) HIRFL STATUS and HIRFL-CSR project in Lanzhou. In: Proceedings of the First Asian Particle Accelerators Conference, KEK, Japan, pp 342
Xia JW, Zhan WL, Wei BW et al (2002) The heavy ion cooler-storage-ring project (HIRFL-CSR) at Lanzhou. NIM(A) 488(1):11–25
Ye C, Zhang X, Wan J, Chang L, Bing Z, Zhang S, Li J, He J, Wang J, Zhou G (2013) Long-term G2-arrested cells exposed to ionizing radiation undergo cellular senescence via slipping into the G1 phase. Cell Cycle 12(9):1424–1432
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, No. 2010CB834201), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDA01040411), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China awarded to Guangming Zhou (No. 31070763) and Jufang Wang (No. U1232125 & 31270895).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Liu, T., Li, H. et al. Ground-based platforms for space radiation research at the Institute of Modern Physics. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 25 (Suppl 1), 13–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-013-0262-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-013-0262-0