Abstract
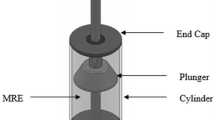
During boring process, tool vibration is a major concern due to its overhanging length, which results in high cutting force, poor surface finish, and increase in tool wear. To suppress tool vibration and improve cutting performance, a novel technique in rheological fluid was designed and developed. In this work, a magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) was developed, and parameters, such as piston location, current intensity, and coil winding direction, were considered. Cutting experiments were conducted to obtain a set of parameters that can efficiently control vibration during boring of hardened AISI 4340 steel. Taguchi method was used to optimize the cutting condition, and findings show that the cutting tool embedded with the MRE reduced tool vibration and effectively increased cutting performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Quintana and J. Ciurana, Chatter in machining processes: A review, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 51 (2011) 363–376.
P. S. Paul, A. S. Varadarajan, X. A. Vasanth and G. Lawrance, Effect of magnetic field on damping ability of magnetorheological damper during hard turning, Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 14 (2014) 433–443.
P. S. Paul, A. S. Varadarajan and S. Mohanasundaram, Effect of magnetorheological fluid on tool wear during hard turning with minimal fluid application, Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 15 (2015) 124–132.
P. S. Paul, J. A. Iasanth, X. A. Vasanth and A. S. Varadarajan, Effect of nanoparticles on the performance of magnetorheological fluid damper during hard turning process, Friction, 3(4) (2015) 333–343.
K. M. Popp, M. Kroger, W. Li, X. Zhang and P. B. Kosasih, MRE properties under shear and squeeze modes and applications, Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 21 (2010) 1471–1477.
J. D. Carlson and M. R. Jolly, MR fluid, foam and elastomer devices, Mechatronics, 10 (2000) 555–569.
L. Chen, X. L. Gong and W. H. Li, Microstructures and viscoelastic properties of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers, Smart Materials and Structures, 16 (2007) 2645–2650.
M. Kallio, The Elastic and Damping Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers, VTT Publications 565, Finland (2005).
J. Wu, X. Gong, Y. Fan and H. Xia, Anisotropic polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer prepared through in situ polycondensation under a magnetic field, Smart Materials and Structures, 19(10) (2010) 105007.
G. V. Stepanov, S. S. Abramchuk, D. A. Grishin, L. V. Nikitin, E. Y. Kramarenko and A. R. Khokhlov, Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers, Polymer, 48(2) (2007) 488–495.
J. L. Leblanc, Rubber-filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds, Progress in Polymer Science, 27(4) (2002) 627–687.
S. Aguib, A. Nour, T. Djedid, G. Bossis and N. Chikh, Forced transverse vibration of composite sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer core, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 30(1) (2016) 15–24.
A. Bendell, J. Disney and W. A. Pridmore, Taguchi Methods: Applications in World Industry, IFS Publications, UK (1989).
X. Zhang and W. Li, Research and applications of MR elastomers, Recent Patents on Mechanical Engineering, 1(3) (2008) 161–166.
A. Saini, S. Dhiman, R. Sharma and S. Setia, Experimental estimation and optimization of process parameters under minimum quantity lubrication and dry turning of AISI-4340 with different carbide inserts, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 28(6) (2014) 2307–2318.
P. S. Paul and A. S. Varadarajan, A multi-sensor fusion model based on an artificial neural network to predict tool wear during hard turning, Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 226(5) (2012) 853–860.
G. Lawrance, P. Sam Paul, A. S. Varadarajan, A. Paul Praveen and X. Ajay Vasanth, Attenuation of vibration in boring tool using spring controlled impact damper, International Journal of Interactive Design and Manufacture, 11 (2017) 903–915.
R. H. Lochner and J. E. Matar, Design for Quality - An Introduction to the Best of Taguchi and Western Methods of Statistical Experimental Design, Chapman and Hall, New York (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Gyuhae Park
G. Lawrance received his Bachelor and Master degrees in Mechanical Engineering in 2010 and 2012, respectively, from Karunya Deemed University, India. He is an Assistant Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department of the Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, India. His research interests include finite element analysis and vibrations.
P. Sam Paul received his Bachelor degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1999 from Manonmonium Sundaranar University and Master degree in CAD in 2001 from Madras University, India. He obtained his Ph.D. degree in Mechanical Engineering at Karunya Deemed University. He joined Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences as a lecturer during 2001 and currently is a Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department of Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences. His research interests include vibration and finite element analysis. He has published papers in numerous refereed international journals and conferences for his highest level of achievement.
X. Ajay Vasanth received his Bachelor degree in Mechanical Engineering in 2011 from SASTRA Deemed University and Master degree in Mechanical Engineering in 2013 from Karunya Deemed University. He is an Assistant Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department of Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, India. His research interests include finite element analysis, vibrations, and control engineering.
A. S. Varadarajan is a Principal of the M.E.S College of Engineering, Kerala, India. He received his M.Tech. and Ph.D. from the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. He is the recipient of the AIMTDR best research work award in 2001, production engineer division gold medal of Institution of Engineers in 2002, and the M.M. Ghani award for the best college teacher offered by the Government of Kerala, India, in 2004. He is working in the area of green manufacturing with a special focus on cutting fluid minimization during machining. Moreover, he has guided three doctoral research programs under Karunya Deemed University and is currently guiding another three doctoral research programs.
E. Daniel received his Bachelor degree in Aerospace Engineering in 2015 and Master degree in Advanced Manufacturing Technology in 2017 from Karunya Deemed University, India. He is an Assistant Professor in Mechanical Engineering Department of the Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawrance, G., Paul, P.S., Vasanth, X.A. et al. Influence of magnetorheological elastomer on tool vibration and cutting performance during boring of hardened AISI4340 steel. J Mech Sci Technol 33, 1555–1561 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0307-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0307-0