Abstract
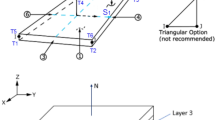
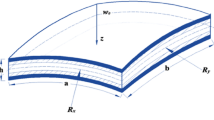
We present a finite element model of laminated composite cylindrical shells with piezoelectric layers by using layerwise theory. The formulation, which is based on Reddy’s layerwise displacement theory, involves the coupling between mechanical deformations and electric displacements. The full layerwise theory is used to represent the total displacement field and electric potential, and then a finite element model has been formulated based on the developed mechanics by employing Hamilton’s principle and variational method. This layerwise finite element model can give an accurate description of displacement field at the ply level and can model complex boundary conditions. Numerical example of a simply-supported laminated piezoelectric composite shell for static response and free vibration analysis was implemented to evaluate the efficiency and accuracy of the present method. Numerical results obtained with the present method are in excellent agreement with other similar solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. R. Fuller, S. J. Elliott and P. A. Nelson, Active control of vibration, Physics Today, 50 (50) (1997) 313–326.
D. A. Rade and V. Steffen Jr., Introduction to smart materials and structures. Dynamics of smart systems and structures, Springer International Publishing (2016).
A. L. Araujo and C. A. M. Soares, Smart structures and materials, Springer International Publishing (2017).
E. Crawley and E. Anderson, Detailed models of piezoceramic actuation of beams, J. of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1 (1) (1990) 4–25.
D. H. Robbins and J. N. Reddy, Analysis of piezoelectrically actuated beams using a layer-wise displacement theory, Computers and Structures, 41 (2) (1991) 265–279.
C. K. Lee, Theory of laminated piezoelectric plates for the design of distributed sensors/actuators. Parts I, II, J. of the Acoustical Society of America, 87 (3) (1990) 1144–1158.
B. T. Wang and C. A. Rogers, Laminate plate theory for spatially distributed induced strain actuators, J. of Composite Materials, 25 (4) (1991) 433–452.
R. C. Batra, X. Q. Liang and J. S. Yang, The vibration of a simply supported rectangular elastic plate due to piezoelectric actuators, International J. of Solids and Structures, 33 (11) (1996) 1597–1618.
S. Brooks and P. Heyliger, Static behavior of piezoelectric laminates with distributed and patched actuators, J. of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 5 (5) (1994) 635–646.
P. Heyliger and S. Brooks, Free vibration of piezoelectric laminates in cylindrical bending, International J. of Solids and Structures, 32 (20) (1995) 2945–2960.
M. Cengiz Dökmeci, Theory of vibrations of coated, thermopiezoelectric laminae, J. of Mathematical Physics, 60 (1) (1976) 109–126.
R. Gholami and R. Ansari, A unified nonlocal nonlinear higher-order shear deformable plate model for postbuckling analysis of piezoelectric-piezomagnetic rectangular nanoplates with various edge supports, Composite Structures, 166 (2017) 202–218.
R. Gholami, R. Ansari and Y. Gholami, Nonlocal largeamplitude vibration of embedded higher-order shear deformable multiferroic composite rectangular nanoplates with different edge conditions, J. of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures (2017).
D. S. Drumheller and A. Kalnins, Dynamic shell theory for ferroelectric ceramics, J. of the Acoustical Society of America, 46 (46) (1970) 1343–1353.
H. S. Paul and M. Venkatesan, Vibrations of a hollow circular cylinder of piezoelectric ceramics, J. of the Acoustical Society of America, 82 (82) (1987) 952–956.
N. T. Adelman and Y. Stavsky, Vibrations of radially polarized composite piezoceramic cylinders and disks, J. of Sound and Vibration, 43 (1) (1975) 37–44.
H. S. Tzou and J. P. Zhong, A linear theory of piezoelastic shell vibrations, J. of Sound and Vibration, 175 (1) (1994) 77–88.
P. C. Dumir, G. P. Dube and S. Kapuria, Exact piezoelastic solution of simply-supported orthotropic circular cylindrical panel in cylindrical bending, International J. of Solids and Structures, 34 (6) (1997) 685–702.
C. Q. Chen, Y. P. Shen and X. M. Wang, Exact solution of orthotropic cylindrical shell with piezoelectric layers under cylindrical bending, International J. of Solids and Structures, 33 (30) (1996) 4481–4494.
C. Q. Chen and Y. P. Shen, Three-dimensional analysis for the free vibration of finite-length orthotropic piezoelectric circular cylindrical shells, J. of Vibration and Acoustics, 120 (1) (1998) 194–198.
C. Q. Chen and Y. P. Shen, Piezothermoelasticity analysis for a circular cylindrical shell under the state of axisymmetric deformation, International J. of Engineering Science, 34 (14) (1996) 1585–1600.
S. S. Vel and B. P. Baillargeon, Analysis of static deformation, vibration and active damping of cylindrical composite shells with piezoelectric shear actuators, J. of Vibration and Acoustics, 127 (4) (2005) 395–407.
M. S. Choi, T. Kondou and H. J. Choi, Free vibration analysis of axisymmetric shells with various shapes using sylvestertransfer stiffness coefficient method, J. of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29 (7) (2015) 2755–2766.
R. Ansari, T. Pourashraf, R. Gholami and A. Shahabodini, Analytical solution for nonlinear postbuckling of functionally graded carbon nanotube-reinforced composite shells with piezoelectric layers, Composites Part B, 90 (2016) 267–277.
M. C. Ray and J. N. Reddy, Active control of laminated cylindrical shells using piezoelectric fiber reinforced composites, Composites Science and Technology, 65 (7) (2005) 1226–1236.
F. Heidary and M. R. Eslami, Piezo-control of forced vibrations of a thermoelastic composite plate, Composite Structures, 74 (1) (2006) 99–105.
W. Hwang and H. C. Park, Finite element modeling of piezoelectric sensors and actuators, AIAA J., 31 (31) (2015) 930–937.
J. A. Mitchell and J. N. Reddy, A study of embedded piezoelectric layers in composite cylinders, Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 62 (1) (1995) 166–173.
A. R. Daneshmehr and M. Shakeri, Three-dimensional elasticity solution of cross-ply shallow and non-shallow panels with piezoelectric sensors under dynamic load, Composite Structures, 80 (3) (2007) 429–439.
J. H. Han and I. Lee, Analysis of composite plates with piezoelectric actuators for vibration control using layerwise displacement theory, Composites Engineering Part B, 29 (5) (1998) 621–632.
S. A. Kulkarni and K. M. Bajoria, Finite element modeling of smart plates/shells using higher order shear deformation theory, Composite Structures, 62 (1) (2003) 41–50.
P. Heyliger, K. C. Pei and D. Saravanos, Layerwise mechanics and finite element model for laminated piezoelectric shells, AIAA J., 34 (34) (2012) 2353–2360.
R. Ansari and R. Gholami, Nonlocal nonlinear first-order shear deformable beam model for postbuckling analysis of magneto-electro-thermo elastic nanobeams, Scientia Iranica, 20 (6) (2016) 3099–3114.
R. Ansari and R. Gholami, Size-dependent nonlinear vibrations of first-order shear deformable magneto-electro-thermo elastic nanoplates based on the nonlocal elasticity theory, International J. of Applied Mechanics, 8 (4) (2016) 1650053.
R. Ansari and R. Gholami, Size-dependent buckling and postbuckling analyses of first-order shear deformable magneto-electro-thermo elastic nanoplates based on the nonlocal elasticity theory, International J. of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 17 (1) (2016) 1750014.
R. Ansari and R. Gholami, Nonlocal free vibration in the pre-and post-buckled states of magneto-electro-thermo elastic rectangular nanoplates with various edge conditions, Smart Material Structures, 25 (9) (2016) 095033.
D. H. J. Robbins and J. N. Reddy, Modeling of thick composites using a layer-wise theory, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 36 (4) (1993) 655–677.
J. N. Reddy and J. H. Starnes Jr., General buckling of stiffened circular cylindrical shells according to a layerwise theory, Computers and Structures, 49 (4) (1993) 605–616.
J. N. Reddy, Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells: Theory and analysis, CRC Press (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Heung Soo Kim
Wei Li is a Ph.D. student of Aerospace Engineering and Applied Mechanics, Tongji University, China. His research interests include mechanics of plates and shells for composite and smart structures and finite element method.
Hai-jun Shen is a Professor of Aerospace Engineering and Applied Mechanics, Tongji University, China. His research primarily focuses on fracture mechanics and nanomechanics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Shen, H. A layerwise finite element formulation of laminated composite cylindrical shells with piezoelectric layers. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 731–741 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0122-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0122-4