Abstract
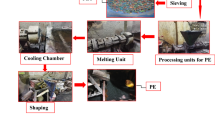
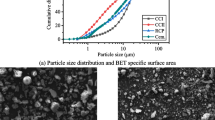
The aim of the research is to achieve the strength development performance of high-volume slag concrete or zero-cement concrete with 0.45 of W/B by incorporating of recycled aggregates as a cost-effective alkali activator. Based on the blast-furnace slag (BFS) based cement, like an alkali activated slag (AAS), recycled aggregates were replaced by natural aggregates and were used as an alkali activator for BFS. For compressive strength improvement in concrete, different replacement ratios of ordinary Portland cement ranged from zero to 50%, recycled fine aggregates (RFA) and recycled coarse aggregates (RCA) ranged from zero to 100% were varied. The test results indicated that recycled aggregates could be used as an alkali activator for BFS, and they were also able to help achieve about 90% of compressive strength of the concrete with natural aggregate depending on its optimum proportion with BFS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aïtcin P, Mindess S (2011) Sustainability of concrete. Spon Press, New York, NY, USA
Al-kheetan MJ, Rahman MM, Chamberlain DA (2017) Influence of early water exposure on modified cementitious coating. Construction and Building Materials 141:64–71, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.159
Al-kheetan MJ, Rahman MM, Chamberlain DA (2018) A novel approach of introducing crystalline protection material and curing agent in fresh concrete for enhancing hydrophobicity. Construction and Building Materials 160:644–652, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.11.108
Awoyera P, Adesina A (2019a) A critical review on application of alkali activated slag as a sustainable composite binder. Case Studies in Construction Materials 11:e00268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2019.e00268
Awoyera P, Adesina A (2019b) Durability properties of alkali activated slag composites: Short overview. Silicon 1–10, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00199-1
Awoyera P, Adesina A, Sivakrishna A, Gobinath R, Kumar KR, Srinivas A (2019a) Alkali activated binders: Challenges and opportunities. Materials today: Proceedings 1–4, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.199
Bentz D, Peltz M, Duran-Herrera A, Valdez P, Juarez C (2010) Thermal properties of high-volume fly ash mortars and concretes. Journal of Building Physics 34(3):263–275, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1744259110376613
Berry EE, Hemmings RT, Zhang MH (1994) Hydration in high-volume fly ash concrete binders. Fuel and Energy Abstracts 36(3):190, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6701(95)80360-2
Chen W, Brouwers HJH (2007a) The hydration of slag, part 1: Reaction models for alkali-activated slag. Journal of Materials Science 42(2): 428–443, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0873-2
Chen W, Brouwers HJH (2007b) The hydration of slag, part 2: Reaction models for blended cement. Journal of Materials Science 42(2): 444–464, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0874-1
Duxson P, Fernández-Jiménez A, Provis JL, Lukey GC, Palomo A, Deventer JSJ (2006) Geopolymer technology: The current state of Hie art. Journal of Materials Science 42(9):2917–2933, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0637-z
Duxson P, Provis JL, Lukey GC, Mallicoat SW, Kriven WM, van Deventer JSJ (2005) Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 269(1–3):47–58, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.06.060
Evangelista L, de Brito J (2007) Mechanical behaviour of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Cement and Concrete Composites 29(5):3970401, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.12.004
Juenger MCG, Winnefeld F, Provis JL, Ideker JH (2011) Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cement and Concrete Research 41(12):1232–1243, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.11.012
Li G (2004) Properties of high-volume fly ash concrete incorporating nano-SiO2. Cement and Concrete Research 34(6):1043–1049, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.11.013
Malhotra VM, Mehta PK (2002) High-performance, high-volume fly ash concrete: Materials, mixture proportioning, properties, construction practice, and case histories. Supplementary Cementing Materials for Sustainable Development Inc., Ottawa, Canada
Mindess S, Young J, Darwin D (2002) Concrete. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA
Otsuki N, Miyazato S, Yodsudjai W (2003) Influence of recycled aggregate on interfacial transition zone, strength, chloride penetration and carbonation of concrete. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 15(5):443–451, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2003)15:5(443)
Padmini A, Ramamurthy K, Mathews M (2009) Influence of parent concrete on the properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Construction and Building Materials 23(2):829–836, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.03.006
Poon C, Kou S, Lam L (2002) Use of recycled aggregates in molded concrete bricks and blocks. Construction and Building Materials 16(5):281–289, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00019-3
Poon C, Shui Z, Lam L (2004) Effect of microstructure of ITZ on compressive strength of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates. Construction and Building Materials 18(6):461–468, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.03.005
Poon C, Shui Z, Lam L, Fok H, Kou S (2004) Influence of moisture states of natural and recycled aggregates on the slump and compressive strength of concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 34(1):31–36, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(03)00186-8
Purdon A (1940) The action of alkalis on blast-furnace slag. Journal of the Society of Chemical Industry 59(9):191–202
Rakshvir M, Barai SV (2006) Studies on recycled aggregates-based concrete. Waste Management & Research 24(3):225–233, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X06064820
Ram P, Dam VT, Meijer J, Smith K (2011) Sustainable recycled materials for concrete pavements. RC-1550, Michigan Department of Transportation Office of Research & Best Practices, Lansing, MI, USA
Sim J, Park C, Park SJ, Kim YJ (2006) Characterization of compressive strength and elastic modulus of recycled aggregate concrete with respect to replacement ratios. Journal of Korean Society of Civil Engineers 26(1A):213–218 (in Korean)
Sisomphon K, Franke L (2007) Carbonation rates of concretes containing high volume of pozzolanic materials. Cement and Concrete Research 37(12):1647–1653, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.08.014
Wang S-D, Scrivener KL (1995) Hydration products of alkali activated slag cement. Cement and Concrete Research 25(3):561–571, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(95)00045-E
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, D., Kim, JH., Han, M. et al. Use of Recycled Aggregate as Alkali Activator to Enhance Strength Development in High-Volume Blast-Furnace Slag Concrete. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 902–912 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1329-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1329-y