Abstract
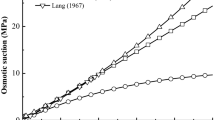
Bentonite is usually selected as the buffering barrier material for high-level nuclear waste repository due to its characteristics of high expansibility and low permeability, yet the swelling properties are influenced by the saline solution existing in the fissures of surrounding rocks. Quantifying the effects of saline solution concentration on the swelling property of compacted bentonite is significant for assessing the security of engineering barrier used to dispose high-level radioactive waste. In this study, the modified effective stress incorporating with osmotic suction generated from saline solution is proposed to depict the volume changes for bentonite in saline solution with different concentrations by a unique equation. The osmotic suctions are calculated with the simplified Debye-Hückel equation and the results are validated by comparing with the experimental data in other literatures. The published experimental data prove the uniform relationship between the volume change and the modified effective stress in saline solution with different concentrations. Therefore, the quantitative predictions of volume change of bentonite in saline solution with different concentrations are presented using the modified effective stress concept.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alawaji, H. A. (1999). “Swell and compressibility characteristics of sand-bentonite mixtures inundated with liquids.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 411–430, DOI: 10.1016/S0169-1317(99)00033-2.
Anvir, D. and Jaroniec, M. (1989). “An isotherm equation for adsorption on fractal surface of heterogeneous porous materials.” Langmuir, Vol. 5, No. 6, pp. 1431–1433, DOI: 10.1021/la00090a032.
Apelblat, A., Dov, M., Wisniak, J., and Zabicky, J. (1995). “The vapour pressure of water over saturated aqueous solutions of malic, tartaric, and citric acids, at temperatures from 288 K to 323 K.” The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 35–41, DOI: 10.1006/jcht.1995.0004.
Barbour, S. and Fredlund, D. G. (1989). “Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils.” Can. Geotech. J., Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 551–562, DOI: 10.1139/t89-068.
Calvello, M., Lasco, M., Vassallo, R., and Di Miao, C. (2005). “Compressibility and residual shear strength of smectitic clays: influence of pore aqueous solutions and organic solvents.” Rivista Italiana Di Geotechnica, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 33–46.
Celies, R., Cornejo, J., and Hermosin, M. C. (1996). “Surface fractal dimensions of synthetic clay-hydrous iron oxide associations from nitrogen adsorption isotherms and mercury porosimetry.” Clay Miner, Vol. 31, No. 3, pp. 55–363, DOI: 10.1180/claymin.1996.031.3.06.
Chen, C. C. and Evans, L. B. A. (1986). “A local composition model for the excess Gibbs energy of aqueous electrolyte systems.” AIChE J., Vol. 32, No. 3, pp. 444–454, DOI: 10.1002/aic.690320311.
Clarke, E. C. W. and Glew, D. N. (1985). “Evaluation of thermodynamic function for aqueous sodium chloride from equilibrium and calorimetric measurements below 154°C.” Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, Vol. 18, No. 1, pp. 489–610, DOI: 10.1063/1.555824.
De Bruyn, C., Collins, C., and Williams, A. (1957). “The specific surface, water affinity and expansive potential of clays.” Clay Minerals, Vol. 3, No. 17, pp. 120–128, DOI: 10.1180/claymin.1957.003.17.02.
Di Maio, C., Santoil, L., and Schiavone, P. (2004). “Volume change behavior of clays: the influence of mineral composition, pore fluid composition and stress state.” Mech. Mater, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 435–451, DOI: 10.1016/S0167-6636(03)00070-X.
Dutta, J. and Mishra, A. K. (2016). “Consolidation behaviour of bentonites in the presence of salt solutions.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 120, No. 8, pp. 61–69, DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.12.001.
Fernández, D. P., Goodwin, A. R. H., Lemmon, E. W., Levelt Sengers, J. M. H., and Williams, R. C. (1997). “A formulation for the Static Permittivity of Water and Steam at Temperature from 238K to 873K at Pressures up to 1200 MPa, Including Derivatives and Debye-Hückel Coefficients.” Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 1125–1166, DOI: 10.1063/1.555997.
Goldberg, R. N. and Nuttall, R. L. (1978). “Evaluated activity and osmotic coefficients for aqueous solutions: The alkaline earth metal halides.” J. Phys. Chem., Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 263–310, DOI: 10.1063/1.555569.
Gray, M. N., Cheung, S. C. H., and Dixon, D. A. (1984). “The influence of sand content on swelling pressure and structure developed in statically compacted Na-bentonite.” Whiteshell Nuclear Research Establishment, Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd., Vol. 782, Pinawa, Manitoba, pp. 1–24.
Hamer, W. J. and Wu, Y. C. (1972). “Osmotic coefficient and mean activity coefficients of univalent electrolytes in water at 25°C.” Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 1047–1099, DOI: 10.1063/1.3253108.
Mesri, G. and Olson, R. E. (1971). “Consolidation Characteristic of Montmorillonite.” Géotechnique, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 341–352, DOI: 10.1680/geot.1971.21.4.341.
Miller, D. J. and Nelson, J. D. (2006). “Osmotic suction in unsaturated soil mechanics.” Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Unsaturated Soil, AZ, USA, pp. 1382–1343.
Mohammed, T. Z. M. and Jaber, J. S. (2000). “Measurement and correlation of osmotic coefficients and evaluation of vapor pressure for solutions of CaCl2 and Ca(NO3)2 in ethanol at 298K.” Fluid Phase Equilibria, Vol. 172, No. 2, pp. 221–235, DOI: 10.1016/S0378-3812(00)00372-1.
Mollins, L. H., Stewart, D. I., and Cousens, T. W. (1996). “Predicting the properties of bentonite-sand mixtures.” Clay Miner., Vol. 31, No. 2, pp. 243–252, DOI: 10.1180/claymin.1996.031.2.10.
Pfeifer, P., Obert, M., and Cole, M. W. (1989). “Fractal BET and FHH theories of adsorption: A comparative study.” Proceeding of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Science, Vol. 423, No. 1864, pp. 169–188, DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1989.0049.
Pitzer, K. S. and Kim, J. J. (1974). “Thermodynamics of electrolytes. iv. activity and osmotic coefficients for mixed electrolytes.” Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 96, No. 18, pp. 5701–5707, DOI: 10.1021/ja00825a004.
Pitzer, K. S. and Mayorga, G. (1973). “Thermodynamics of electrolytes. II. Activity and osmotic coefficients for strong electrolytes with one or both ions univalent.” The Journal of Physical Chemistry, Vol. 77, No. 19, pp. 2300–2308, DOI: 10.1142/9789812795960_0058.
Pitzer, K. S. and Mayorga, G. (1974). “Thermodynamics of electrolytes. III. Activity and osmotic coefficients for 2–2 electrolytes.” Journal of Solution Chemistry, Vol. 3, No. 7, pp. 534–546, DOI: 10.1007/BF00648138.
Pusch, R. and Yong, R. (2003). “Water saturation and retention of hydrophilic clay buffer microstructural aspects.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 23, pp. 61–68, DOI: 10.1016/S0169-1317(03)00087-5.
Rao, S. M. and Thyagaraj, T. (2007). “Swell-compression behavior of compacted clays under chemical gradients.” Can. Geotech. J, Vol. 44, No. 5, pp. 520–532, DOI: 10.1139/T07-002.
SKB (2004). Interim process report for the safety assessment SR-Can, Report 04–33, Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co. Stockholm, Sweden.
Sposito, G., Holtzclaw, K. M., Charlet, L., Jouany, C., and Page, A. L. (1983). “Sodium-calcium and sodium-magnesium exchange on Wyoming bentonite in perchlorate and chloride background ionic media.” Soil Sci. Soc. of America J., Vol. 47, No. 1, pp. 51–56, DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700010010x.
Studds, P. G., Stewart, D. I., and Cousens, T. W. (1998). “The effects of salt solutions on the properties of bentonite-sand mixtures.” Clay Miner., Vol. 33, No. 4, pp. 651–661, DOI: 10.1180/claymin.1998.033.4.12.
Su, K. and Patrick, L. (2006). “Andra’s feasibility study on deep geological disposal of high-level long-lived radioactive waste.” Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 25, No. 4, pp. 813–824.
Tripathy, S., Bag, R., and Thomas, H. R. (2013). “Effect of Stern-layer on the compressibility behaviour of bentonites.” Acta Geotech., Vol. 9, pp.1097-1109, DOI: 10.1007/s11440-013-0222-y.
Verwey, E. J. W. (1948). “Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids.” J. Phys. Chem., Vol. 51, No. 3, pp. 631–636.
Wijmans, J. G. and Baker, R. W. (1995). “The solution-diffusion model: a review.” J. Memb. Sci., Vol. 107, No. 1, pp. 1–21, DOI: 10.1016/0376-7388(95)00102-I.
Xiang, G. S., Jiang, H., and Xu, Y. F. (2015). “Fractal calculation method for swelling deformation of compacted bentonite.” Rook and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 36, No. 4, pp. 1009–1014, DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.04.014.
Xiang, G. S., Xu, Y. F., and Xie, S. H. (2016). “Effects on bentonite microstructure by salt solution.” Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), Vol. 46, Sup, pp. 230–234, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2016.S1.040.
Xu, Y. F., Matsuoka, H., and Sun, D. A. (2003). “Swelling characteristics of fractal textured bentonite and its mixtures.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 197–209, DOI: 10.1016/S0169-1317(02)00159-X.
Xu, Y. F., Xiang, G. S., Jiang, H., Chen, T., and Chu, F. F. (2014). “Role of osmotic suction in volume change of clays in salt solution.” Appl. Clay Sci., Vol. 101, No. 45, pp. 354–361, DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.09.006.
Ye, W. M., Zhang, F., Chen, B., Chen, Y. G., Wang, Q., and Cui, Y. J. (2014). “Effects of salt solutions on the hydro-mechanical behavior of compacted GMZ01 bentonite.” Environ. Earth. Sci., Vol. 72, No. 7, pp. 2621–2630, DOI: 10.1007/s12665-014-3169-x.
Yong, R. N. and Mohamed, A. M. O. (1992). “A study of particle interaction energies in wetting of unsaturated expansive clays.” Can. Geotech. J., Vol. 29, No. 6, pp. 1060–1070, DOI: 10.1139/t92-123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, C. & Xu, Y. Representation of Volume Change for Bentonite in Saline Solution based on Modified Effective Stress. KSCE J Civ Eng 23, 2065–2073 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0789-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0789-4