Abstract
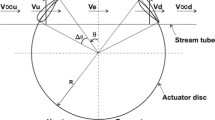
This research focuses on design and calculations for the horizontal axis wind turbine to fulfill energy demands at small scales in Pakistan. This is the design to produce about 5 kilowatts of electricity to share the load of average home appliances. Area chosen for this research is Pasni, Balochistan in Pakistan to build the wind turbine for electricity. Design values are approximated by appropriate formulas of wind energy design. In current research, turbine blade profile is designed by blade element momentum (BEM) theory. Warlock wind turbine calculator is used to verify the design parameters like wind speed, tip speed ratio (TSR) and efficiency factor. Effects of wind speed, wind power, TSR, pitch angle, blade tip angle, number of blades, blade design and tower height on power coefficient are analyzed in this research. Maximum power coefficient is achieved at a designed velocity of 6m/s. Design analysis is also performed on simulation software ANSYS Fluent. It is observed that designed velocity parameter of this research is very suitable for the turbine blade, so blade designing is perfect according to wind speed range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BASIR R, AZIZ N, AHMAD S S, et al. Satellite remote sensing for identification of solar potential sites in Pakistan [J]. International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2013, 2(2): 200–209.
ASIF M. Sustainable energy options for Pakistan [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13: 903–909.
ABBAS T, BAZMI A A, BHUTTO A W, et al. Greener energy: Issues and challenges for Pakistan solar energy prospective [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 31: 258–269.
GHAFFAR M A. The energy supply situation in the rural sector of Pakistan and the potential of renewable energy technologies [J]. Renewable Energy, 1995, 6(8): 941–976.
MAALAWI K Y, BADRM A. A practical approach for selecting optimum wind rotors [J]. Renewable Energy, 2003, 28: 803–822.
YURDUSEV M A, ATA R, CETIN N S. Assessment of optimum tip speed ratio in wind turbines using artificial neural networks [J]. Energy, 2006, 31: 2153–2161.
WOLSINK M. Wind power and the NIMBY-myth: Institutional capacity and the limited significance of public support [J]. Renewable Energy, 2000, 21: 49–64.
HABALI S M, SALEH I A. Local design, testing and manufacturing of small mixed airfoil wind turbine blades of glass fiber reinforced plastics. Part I. Design of the blade and root [J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2000, 41: 249–280.
REICHE D, BECHNERGER M. Policy differences in the promotion of renewable energies in the EU member states [J]. Energy Policy, 2004, 32: 39–52.
BRØNDSTEAD P, HOLMES J W, SØRENSEN B F. Wind rotor blade materials technology [J]. European Sustainable Energy Review, 2008, 2: 36–41.
STOL K A, ZHAO W X, WRIGHT A D. Individual blade pitch control for the controls advanced research turbine (CART) [J]. Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, 2006, 128: 498–505.
SHEIKH M A. Energy and renewable energy scenario of Pakistan [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010, 14: 354–363.
ABBASI S A, ABBASI N. The likely adverse environmental impacts of renewable energy sources [J]. Applied Energy, 2000, 65: 121–144.
BARLAS T K, VAN KUIK G A M. Review of state of the art in smart rotor control research for wind turbines [J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2010, 46: 1–27.
BARR S, GILG A. Sustainable lifestyles: Framing environmental action in and around the home [J]. Geoforum, 2006, 37(6): 906–920.
MUSIAL W. Offshore wind electricity: A viable energy option for the coastal United States [J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2007, 41(3): 32–43.
POLINDER H, VAN DER PIJL F F A, DE VILDER G J, et al. Comparison of direct-drive and geared generator concepts for wind turbines [J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2006, 21: 725–733.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, Z., Abbas, S., Butt, Z. et al. Design and Parametric Investigation of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 23, 345–351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-018-1949-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-018-1949-2