Abstract
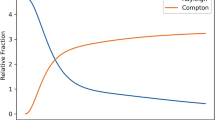
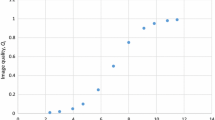
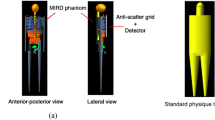
The purpose of this work was to present body size and tube voltage-dependent equations for optimal selection of image acquisition parameters in guiding clinical X-ray imaging. The dose output of X-ray tubes was expressed as a function of the image acquisition parameters of tube voltage (kVp), tube current–exposure time product (mAs), and body size (d). Dose power (n) to kVp was determined to be a linear function of body size in an earlier phantom study. Tube voltage-dependent attenuation coefficients of water were used to determine the kVp effect on the depth dose of X-rays from the body’s entrance surface. The new expression for the dose output of X-ray tubes in patients was then employed for image quality and radiation dose optimization, assuming that image quality is a logistic function of the radiation dose to patients. For constant kVp, the percentage of mAs increase for a 1-cm increase in body size d is dependent on the kVp applied. For constant mAs, the percentage of kVp increase for a 1-cm increase in body size is dependent on both body size d and the kVp applied. For constant body size, the percentage of kVp increase should be a fraction of the percentage of decrease in the mAs, where the fraction is dependent on the body size. The improved body size and tube voltage-dependent governing equations for variations in X-ray imaging parameters should be more accurate in guiding optimal selection of the kVp and mAs image acquisition parameters in medical X-ray imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huda W, Abrahams RB. Radiographic techniques, contrast, and noise in X-ray imaging. AJR. 2015;204:W126–31.
Kalender WA, Wolf K, Suess C. Dose reduction in CT by anatomically adapted tube current modulation. II. Phantom measurements. Med Phy. 1999;26(11):2248–53.
Ching W, Robinson J, McEntee M. Patient-based radiographic exposure factor selection: a systematic review. J Med Rad Sci. 2014;61:176–90.
Van der Plaats GJ. Medical X-ray techniques in diagnostic radiology. London: The Macmillan Press Ltd; 1980.
AAPM task group 116. An exposure indicator for digital radiography. College Park: American association of physicists in medicine; 2009. ISBN 978-1-888340-86-0.
Herrmann TL, Fauber TL, Gill J, Hoffman C, Orth DK, Peterson PA, Prouty RR, Woodward AP, Odle TG. Best practices in digital radiography. Radiol Technol. 2012;84:83–9.
Soderberg M, Gunnarsson M. Automatic exposure control in computed tomography—an evaluation of system from different manufacturers. Acta Radiol. 2010;6:625–34.
Spearman JV, Schoepf UJ, Rottenkolber M, Driesser I, Canstein C, Thierfelder KM, Krazinski AW, De Cecco CN, Meinel FG. Effect of Automated attenuation-based tube voltage selection on radiation dose at CT: an observational study on a global scale. Radiology. 2016;279(1):167–74.
Wambersie A. Radiation quantities and units, dose to the patients, and image quality in computed tomography (CT). European Commission Directorate-General for Research; EUR 23464; 2008. https://www.cordiseuropa.eu/project/rcn/75837_en.html. Accessed 16 Apr 2018.
Zheng X. Attenuation based governing equations for automatic mAs and kVp controls in medical X-ray CT imaging. CT Theory Appl. 2016;25(6):625–32.
Zheng X. Patient size based guiding equations for automatic mAs and kVp selections in general medical X-ray projection radiography. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2017;174(4):545–50.
Zheng X. General equations for optimal selection of diagnostic image acquisition parameters in clinical X-ray imaging. Radiol Phys Technol. 2017;10:415–21.
AAPM task group 204. Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in paediatric and adult body CT examinations. College Park: American association of physicists in medicine; 2011. ISBN 978-1-936366-08-8.
Zheng X, Nardi L, Murray M. Size effect on dose output in phantoms of X-ray tubes in medical X-ray imaging. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017;3:065004.
NIST (n, d) X-ray mass attenuation coefficients—water, liquid. https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/XrayMassCoef/ComTab/water.html. Accessed 26 Sep 2017.
ICRU Radiation dose and image quality assessment in computed tomography. J ICRU 12 (2012) report 87.
Williams MB, Krupinski EA, Strauss KJ, Breeden WK, Rzeszotarski MS. Digital radiography image quality: image acquisition. J Am Coll Radiol. 2007;4:37–88.
Zheng X, Chiang H-W, Li J-H, Chiang H-J, Lin L-H. Personal exposure prescription method reduces dose in radiography. Radiol Technol 2018;89(5) (In press).
Zheng, X. A method and system for automating radiation dose parameters. Australian patent: AU2016902943. 27-07-2016.
European commission. European guideline on quality criteria for diagnostic radiographic images in paediatrics. Luxemburg: Office for official publications of the European communities; 1996. ISBN 92-827-7843-6.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank the Journal Editor for English editorial assistance and my colleague Mr. Andrew Kilgour for critical reading of and comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Research involving human or animal participants
This article does not report any studies involving human participants or animals performed by the author.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not required.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X. Body size and tube voltage-dependent guiding equations for optimal selection of image acquisition parameters in clinical X-ray imaging. Radiol Phys Technol 11, 212–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-018-0457-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-018-0457-2