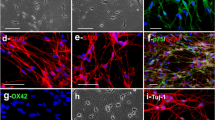
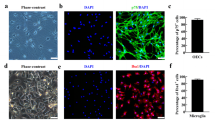
Abstract
Olfactory ensheathing glia (OEG) play an important role in regulating the regeneration of an injured nervous system. However, chronic inflammation damage reduces the viability of OEG via poorly understood mechanisms. We aimed to investigate the pathological responses of OEG in response to LPS-mediated inflammation stress in vitro. The results indicated that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment significantly reduced the viability of OEG in a dose-dependent fashion. Mechanistically, LPS stimuli induced mitochondrial oxidative damage, mitochondrial fragmentation, mitochondrial metabolism disruption, and mitochondrial apoptosis activation. Furthermore, we verified that LPS modulated mitochondrial apoptosis by promoting Bax upregulation, and this process was regulated by the JNK-Bnip3 pathway. Inhibition of the JNK-Bnip3 pathway prevented LPS-mediated Bax activation, thus attenuating OEG apoptosis. Altogether, our data illustrated that LPS-mediated inflammation injury evoked mitochondrial abnormalities in OEG damage via the JNK-Bnip3-Bax pathway. This finding provides a potential target to protect OEG against chronic inflammation stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann M, Kim YO, Wagner WL, Schuppan D, Valenzuela CD, Mentzer SJ, Kreuz S, Stiller D, Wollin L, Konerding MA (2017) Effects of nintedanib on the microvascular architecture in a lung fibrosis model. Angiogenesis 20:359–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9543-z
Alghanem AF, Wilkinson EL, Emmett MS, Aljasir MA, Holmes K, Rothermel BA, Simms VA, Heath VL, Cross MJ (2017) RCAN1.4 regulates VEGFR-2 internalisation, cell polarity and migration in human microvascular endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 20:341–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9542-0
Augestad IL, Nyman AKG, Costa AI, Barnett SC, Sandvig A, Haberg AK, Sandvig I (2017) Effects of neural stem cell and olfactory ensheathing cell co-transplants on tissue remodelling after transient focal cerebral ischemia in the adult rat. Neurochem Res 42:1599–1609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2098-3
Barton MJ, John JS, Clarke M, Wright A, Ekberg J (2017) The glia response after peripheral nerve injury: a comparison between Schwann cells and olfactory ensheathing cells and their uses for neural regenerative therapies. Int J Mol Sci 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020287
Bauer S, Rasika S, Han J, Mauduit C, Raccurt M, Morel G, Jourdan F, Benahmed M, Moyse E, Patterson PH (2003) Leukemia inhibitory factor is a key signal for injury-induced neurogenesis in the adult mouse olfactory epithelium. J Neurosci 23:1792–1803
Blackburn NJR, Vulesevic B, McNeill B, Cimenci CE, Ahmadi A, Gonzalez-Gomez M, Ostojic A, Zhong Z, Brownlee M, Beisswenger PJ, Milne RW, Suuronen EJ (2017) Methylglyoxal-derived advanced glycation end products contribute to negative cardiac remodeling and dysfunction post-myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 112:57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0646-x
Boone CHT, Grove RA, Adamcova D, Seravalli J, Adamec J (2017) Oxidative stress, metabolomics profiling, and mechanism of local anesthetic induced cell death in yeast. Redox Biol 12:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.025
Cao L, Mu L, Qiu Y, Su Z, Zhu Y, Gao L, Yuan Y, Guo D, He C (2010) Diffusible, membrane-bound, and extracellular matrix factors from olfactory ensheathing cells have different effects on the self-renewing and differentiating properties of neural stem cells. Brain Res 1359:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.063
Chang SH, Yeh YH, Lee JL, Hsu YJ, Kuo CT, Chen WJ (2017) Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated CD44/STAT3 signaling contributes to the development of atrial fibrosis and fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol 112:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0647-9
Chehrehasa F, Ekberg JA, St John JA (2014) A novel method using intranasal delivery of EdU demonstrates that accessory olfactory ensheathing cells respond to injury by proliferation. Neurosci Lett 563:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.01.043
Chen WJ, du JK, Hu X, Yu Q, Li DX, Wang CN, Zhu XY, Liu YJ (2017) Protective effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function in the hippocampus improves inflammation-induced depressive-like behavior. Physiol Behav 182:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.09.024
Cho BB, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2008) Caspase-independent programmed cell death following ischemic stroke. J Investig Surg 21:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941930802029945
Cui J, Li Z, Zhuang S, Qi S, Li L, Zhou J, Zhang W, Zhao Y (2018) Melatonin alleviates inflammation-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via suppression of Ca(2+)-XO-ROS-Drp1-mitochondrial fission axis by activation of AMPK/SERCA2a pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0841-6
Das N, Mandala A, Naaz S, Giri S, Jain M, Bandyopadhyay D, Reiter RJ, Roy SS (2017) Melatonin protects against lipid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes and inhibits stellate cell activation during hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Pineal Res:62. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12404
Dong W, Li Z, Chen Y, Zhang L, Ye Z, Liang H, Li R, Xu L, Zhang B, Liu S, Wang W, Li C, Shi W, Liang X (2018) Necrostatin-1 attenuates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by promoting autophagosome elimination in renal tubular epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep 17:3194–3199. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8214
Errea O, Moreno B, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Garcia-Roves PM, Villoslada P (2015) The disruption of mitochondrial axonal transport is an early event in neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 12:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0375-8
Feng D et al (2017) Pre-ischemia melatonin treatment alleviated acute neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent autophagy via PERK and IRE1 signalings. J Pineal Res 62. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12395
Fuhrmann DC, Brune B (2017) Mitochondrial composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol 12:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.012
Gadicherla AK, Wang N, Bulic M, Agullo-Pascual E, Lissoni A, de Smet M, Delmar M, Bultynck G, Krysko DV, Camara A, Schlüter KD, Schulz R, Kwok WM, Leybaert L (2017) Mitochondrial Cx43 hemichannels contribute to mitochondrial calcium entry and cell death in the heart. Basic Res Cardiol 112:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0618-1
Ho DH, Je AR, Lee H, Son I, Kweon HS, Kim HG, Seol W (2018) LRRK2 kinase activity induces mitochondrial fission in microglia via Drp1 and modulates neuroinflammation. Exp Neurobiol 27:171–180. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2018.27.3.171
Hu SY, Zhang Y, Zhu PJ, Zhou H, Chen YD (2017) Liraglutide directly protects cardiomyocytes against reperfusion injury possibly via modulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis. J Geriatr Cardiol 14:57–66. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.01.008
Hunter R, Ojha U, Bhurtel S, Bing G, Choi DY (2017) Lipopolysaccharide-induced functional and structural injury of the mitochondria in the nigrostriatal pathway. Neurosci Res 114:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2016.09.007
Jin Q, Li R, Hu N, Xin T, Zhu P, Hu S, Ma S, Zhu H, Ren J, Zhou H (2018) DUSP1 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK pathways. Redox Biol 14:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.004
Jinbo L, Zhiyuan L, Zhijian Z, WenGe D (2013) Olfactory ensheathing cell-conditioned medium protects astrocytes exposed to hydrogen peroxide stress. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:699–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9937-4
Jing X, Yang J, Jiang L, Chen J, Wang H (2018) MicroRNA-29b regulates the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway by targeting Bax in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:692–704. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491896
Kaizaki A, Tien LT, Pang Y, Cai Z, Tanaka S, Numazawa S, Bhatt AJ, Fan LW (2013) Celecoxib reduces brain dopaminergic neuronal dysfunction, and improves sensorimotor behavioral performance in neonatal rats exposed to systemic lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroinflammation 10:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-10-45
Lalier L, Cartron PF, Juin P, Nedelkina S, Manon S, Bechinger B, Vallette FM (2007) Bax activation and mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis 12:887–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0749-1
Lane AP, Turner J, May L, Reed R (2010) A genetic model of chronic rhinosinusitis-associated olfactory inflammation reveals reversible functional impairment and dramatic neuroepithelial reorganization. J Neurosci 30:2324–2329. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4507-09.2010
Lankford KL, Arroyo EJ, Kocsis JD (2017) Chronic TNFalpha exposure induces robust proliferation of olfactory Ensheathing cells, but not Schwann cells. Neurochem Res 42:2595–2609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2285-x
Lei Q, Tan J, Yi S, Wu N, Wang Y, Wu H (2018) Mitochonic acid 5 activates the MAPK-ERK-yap signaling pathways to protect mouse microglial BV-2 cells against TNFalpha-induced apoptosis via increased Bnip3-related mitophagy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 23:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0081-5
Li A, Sun X, Ni Y, Chen X, Guo A (2013) HIF-1alpha involves in neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci 51:1052–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0084-7
Li H, He F, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Chu X, Hua C, Qu Y, Duan Y, Ming L (2017a) YAP inhibits the apoptosis and migration of human rectal cancer cells via suppression of JNK-Drp1-mitochondrial fission-HtrA2/Omi pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:2073–2089. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485946
Li Y, Zou T, Xue L, Yin ZQ, Huo S, Xu H (2017b) TGF-beta1 enhances phagocytic removal of neuron debris and neuronal survival by olfactory ensheathing cells via integrin/MFG-E8 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci 85:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2017.08.006
Li R, Xin T, Li D, Wang C, Zhu H, Zhou H (2018) Therapeutic effect of sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol 18:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011
Liu Y, Bao L, Xuan L, Song B, Lin L, Han H (2015) Chebulagic acid inhibits the LPS-induced expression of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in endothelial cells by suppressing MAPK activation. Exp Ther Med 10:263–268. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2447
Liu Q, Qin Q, Sun H, Zhong D, An R, Tian Y, Chen H, Jin J, Wang H, Li G (2018) Neuroprotective effect of olfactory ensheathing cells co-transfected with Nurr1 and Ngn2 in both in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. Life Sci 194:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.038
McFarland AJ, Davey AK, McDermott CM, Grant GD, Lewohl J, Anoopkumar-Dukie S (2018) Differences in statin associated neuroprotection corresponds with either decreased production of IL-1beta or TNF-alpha in an in vitro model of neuroinflammation-induced neurodegeneration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 344:56–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.03.005
Moon C, Yoo JY, Matarazzo V, Sung YK, Kim EJ, Ronnett GV (2002) Leukemia inhibitory factor inhibits neuronal terminal differentiation through STAT3 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:9015–9020. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.132131699
Nan B, Getchell ML, Partin JV, Getchell TV (2001) Leukemia inhibitory factor, interleukin-6, and their receptors are expressed transiently in the olfactory mucosa after target ablation. J Comp Neurol 435:60–77
Noh H, Jeon J, Seo H (2014) Systemic injection of LPS induces region-specific neuroinflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in normal mouse brain. Neurochem Int 69:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.02.008
O'Neill P, Lindsay SL, Pantiru A, Guimond SE, Fagoe N, Verhaagen J, Turnbull JE, Riddell JS, Barnett SC (2017) Sulfatase-mediated manipulation of the astrocyte-Schwann cell interface. Glia 65:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23047
Prabhakaran K, Chapman GD, Gunasekar PG (2009) BNIP3 up-regulation and mitochondrial dysfunction in manganese-induced neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 30:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2009.02.012
Ramon-Cueto A, Avila J (1998) Olfactory ensheathing glia: properties and function. Brain Res Bull 46:175–187
Reyna DE, Gavathiotis E (2016) Self-regulation of BAX-induced cell death. Oncotarget 7:66326–66327. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11948
Rigillo G, Vilella A, Benatti C, Schaeffer L, Brunello N, Blom JMC, Zoli M, Tascedda F (2018) LPS-induced histone H3 phospho(Ser10)-acetylation(Lys14) regulates neuronal and microglial neuroinflammatory response. Brain Behav Immun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.019
Santuy A, Turegano-Lopez M, Rodriguez JR, Alonso-Nanclares L, DeFelipe J, Merchan-Perez A (2018) A quantitative study on the distribution of mitochondria in the neuropil of the juvenile rat somatosensory cortex. Cereb Cortex 28:3673–3684. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy159
Shao L, Liu X, Zhu S, Liu C, Gao Y, Xu X (2018) The role of Smurf1 in neuronal necroptosis after lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:809–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0553-6
Sheng J, Li H, Dai Q, Lu C, Xu M, Zhang J, Feng J (2018) DUSP1 recuses diabetic nephropathy via repressing JNK-Mff-mitochondrial fission pathways. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27124
Shi C, Cai Y, Li Y, Li Y, Hu N, Ma S, Hu S, Zhu P, Wang W, Zhou H (2018) Yap promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and mobilization via governing cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis by regulation of JNK/Bnip3/SERCA/CaMKII pathways. Redox Biol 14:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.013
Tan AM, Zhang W, Levine JM (2005) NG2: a component of the glial scar that inhibits axon growth. J Anat 207:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00452.x
Tang YY, Guo WX, Lu ZF, Cheng MH, Shen YX, Zhang YZ (2017) Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes the migration of olfactory ensheathing cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway to repair rat spinal cord injury. Biol Pharm Bull 40:1630–1637. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00896
Tao-Cheng JH (2018) Stimulation-induced structural changes at the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of hippocampal neurons. Mol Brain 11:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-018-0387-2
Wang JW, Stifani S (2017) Roles of Runx genes in nervous system development. Adv Exp Med Biol 962:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_8
Westphal D, Dewson G, Czabotar PE, Kluck RM (2011) Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:521–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.019
Wright AA, Todorovic M, Tello-Velasquez J, Rayfield AJ, St John JA, Ekberg JA (2018) Enhancing the therapeutic potential of olfactory ensheathing cells in spinal cord repair using neurotrophins. Cell Transplant 27:867–878. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718759472
Yan H, Xiao F, Zou J, Qiu C, Sun W, Gu M, Zhang L (2018) NR4A1-induced increase in the sensitivity of a human gastric cancer line to TNFalpha-mediated apoptosis is associated with the inhibition of JNK/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Int J Oncol 52:367–378. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4216
Yao R, Murtaza M, Velasquez JT, Todorovic M, Rayfield A, Ekberg J, Barton M, St John J (2018) Olfactory ensheathing cells for spinal cord injury: sniffing out the issues. Cell Transplant 27:879–889. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718779353
Zhou H et al (2017a) Mff-dependent mitochondrial fission contributes to the pathogenesis of cardiac microvasculature ischemia/reperfusion injury via induction of mROS-mediated cardiolipin oxidation and HK2/VDAC1 disassociation-involved mPTP opening. J Am Heart Assoc 6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.005328
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Hu S, Shi C, Zhu P, Ma Q, Jin Q, Cao F, Tian F, Chen Y (2017b) Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res 63:e12413. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12413
Zhou H, du W, Li Y, Shi C, Hu N, Ma S, Wang W, Ren J (2018a) Effects of melatonin on fatty liver disease: the role of NR4A1/DNA-PKcs/p53 pathway, mitochondrial fission, and mitophagy. J Pineal Res 64. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12450
Zhou H, Shi C, Hu S, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018b) BI1 is associated with microvascular protection in cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury via repressing Syk-Nox2-Drp1-mitochondrial fission pathways. Angiogenesis 21:599–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9611-z
Zhou H, Wang J, Zhu P, Hu S, Ren J (2018c) Ripk3 regulates cardiac microvascular reperfusion injury: the role of IP3R-dependent calcium overload, XO-mediated oxidative stress and F-action/filopodia-based cellular migration. Cell Signal 45:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.01.020
Zhou H, Wang J, Zhu P, Zhu H, Toan S, Hu S, Ren J, Chen Y (2018d) NR4A1 aggravates the cardiac microvascular ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy and promoting Mff-required mitochondrial fission by CK2alpha. Basic Res Cardiol 113:23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0682-1
Zhou H, Wang S, Hu S, Chen Y, Ren J (2018e) ER-mitochondria microdomains in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: a fresh perspective. Front Physiol 9:755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00755
Zhou H, Zhu P, Wang J, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018f) Pathogenesis of cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury is associated with CK2alpha-disturbed mitochondrial homeostasis via suppression of FUNDC1-related mitophagy. Cell Death Differ 25:1080–1093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0086-7
Zhu H, Jin Q, Li Y, Ma Q, Wang J, Li D, Zhou H, Chen Y (2018a) Melatonin protected cardiac microvascular endothelial cells against oxidative stress injury via suppression of IP3R-[Ca(2+)]c/VDAC-[Ca(2+)]m axis by activation of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0827-4
Zhu P, Hu S, Jin Q, Li D, Tian F, Toan S, Li Y, Zhou H, Chen Y (2018b) Ripk3 promotes ER stress-induced necroptosis in cardiac IR injury: a mechanism involving calcium overload/XO/ROS/mPTP pathway. Redox Biol 16:157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.019
Zuo WQ, Hu YJ, Yang Y, Zhao XY, Zhang YY, Kong W, Kong WJ (2015) Sensitivity of spiral ganglion neurons to damage caused by mobile phone electromagnetic radiation will increase in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro model. J Neuroinflammation 12:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0300-1
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the major project of logistic scientific Research of PLA (AWS14C003–5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MWH, ZMX, and JMC were involved in the conception and design, performance of experiments, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing. LBX, YTD, FQL, and JMC were involved in data analysis and interpretation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
ESM 1
(DOCX 426 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Xiang, Z., Xu, L. et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces human olfactory ensheathing glial apoptosis by promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and activating the JNK-Bnip3-Bax pathway. Cell Stress and Chaperones 24, 91–104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0945-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0945-7