Abstract
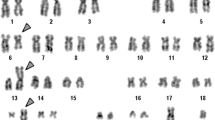
Double-hit lymphoma is typically categorized as “high-grade B-cell lymphoma, with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements”, but in infrequent cases in which terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) expression is positive, it is categorized as B-lymphoblastic lymphoma (B-LBL). BCL2 rearrangements are usually caused by t(14;18)(q32;q21); variant translocations are very rare. Here, we describe an unusual case of double-hit pancreatic B-LBL with a variant translocation t(2;18)(p11;q21). A 69-year-old man was admitted because of an abdominal mass. Computed tomography scans demonstrated a diffusely enlarged pancreas and massive ascites. Cell block preparations of ascites cells revealed marked proliferation of blastic lymphoid cells positive for CD19, CD10, CD79a, PAX5, and TdT, indicating a diagnosis of B-LBL. G-banding and spectral karyotyping showed 45,XY,+X,t(2;18)(p11;q21),-4,der(5)t(1;5)(q12;p15),der(6)t(6;21)(q21;q?),t(8;14)(q24;q32),-15. Fluorescence in situ hybridization detected split BCL2 and IGH/MYC fusion signals. Almost all ascites cells were diffusely and strongly positive for MYC and BCL2. The patient died of progressive disease 20 days after admission. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of MYC and BCL2 double-hit B-LBL with t(2;18)(p11;q21). High coexpression of MYC by t(8;14) and BCL2 by t(2;18) may be implicated in the development of B-LBL. Furthermore, double-hit B-LBL may be associated with a less favorable outcome compared with typical B-LBL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merron B, Davies A. Double hit lymphoma: how do we define it and how do we treat it? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2018;31:233–40.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris NL, Stein H, Siebert R, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375–90.
Johnson NA, Savage KJ, Ludkovski O, Ben-Neriah S, Woods R, Steidl C, et al. Lymphomas with concurrent BCL2 and MYC translocations: the critical factors associated with survival. Blood. 2009;114:2273–9.
McPhail ED, Maurer MJ, Macon WR, Feldman AL, Kurtin PJ, Ketterling RP, et al. Inferior survival in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements is not associated with MYC/IG gene rearrangements. Haematologica. 2018;103:1899–907.
Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F, editors. Mitelman database of chromosome aberrations and gene fusions in cancer. (2019). https://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Chromosomes/Metelman. Accessed 20 Jan 2019.
Aventin A, Mecucci C, Guanyabens C, Brunet S, Soler J, Bordes R, et al. Variant t(2;18) translocation in a Burkitt conversion of follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 1990;74:367–9.
Hillion J, Mecucci C, Aventin A, Leroux D, Wlodarska I, Van Den Berghe H, et al. A variant translocation t(2;18) in follicular lymphoma involves the 5′ end of bcl-2 and Igκ light chain gene. Oncogene. 1991;6:169–72.
Juneja S, Matthews J, Lukeis R, Laidlaw C, Cooper I, Wolf M, et al. Prognostic value of cytogenetic abnormalities in previously untreated patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 1997;25:493–501.
Henderson LJ, Okamoto I, Lestou VS, Ludkovski O, Robichaud M, Chhanabhai M, et al. Delineation of a minimal region of deletion at 6q16.3 in follicular lymphoma and construction of a bacterial artificial chromosome contig spanning a 6-megabase region of 6q16–q21. Genes Chromosmes Cancer. 2004;40:60–5.
Tomita N, Tokunaka M, Nakamura N, Takeuchi K, Koike J, Motomura S, et al. Clinicopathological features of lymphoma/leukemia patients carrying both BCL2 and MYC translocations. Haematologica. 2009;94:935–43.
Bassan R, Maino E, Cortelazzo S. Lymphoblastic lymphoma: an updated review on biology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur J Haematol. 2016;96:447–60.
Kaplan A, Samad A, Dolan MM, Cioc AM, Holman CJ, Schmechel SC, et al. Follicular lymphoma transformed to “double-hit” B lymphoblastic lymphoma presenting in the peritoneal fluid. Diagn Cytopathol. 2013;41:986–90.
Geyer JT, Subramaniyam S, Jiang Y, Elemento O, Ferry JA, de Leval L, et al. Lymphoblastic transformation of follicular lymphoma: a clinicopathologic and molecular analysis of 7 patients. Hum Pathol. 2015;46:260–71.
Liu W, Hu S, Konopleva M, Khoury JD, Kalhor N, Tang G, et al. De Novo MYC and BCL2 double-hit B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) in pediatric and young adult patients associated with poor prognosis. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2015;32:535–47.
Kelemen K, Holden J, Johnson LJ, Davion S, Robetorye RS. Immunophenotypic and cytogenetic findings of B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma associated with combined IGH/BCL2 and MYC rearrangement. Cytom B Clin Cytom. 2017;92:310–4.
Moench L, Sachs Z, Aasen G, Dolan M, Dayton V, Courville EL. Double- and triple-hit lymphomas can present with features suggestive of immaturity, including TdT expression, and create diagnostic challenges. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016;57:2626–35.
Ok CY, Medeiros LJ, Thakral B, Tang G, Jain N, Jabbour E, et al. High-grade B-cell lymphomas with TdT expression: a diagnostic and classification dilemma. Mod Pathol. 2019;32:48–58.
Saif MW. Primary pancreatic lymphomas. JOP. 2006;7:262–73.
Daniel SV, Vani DH, Smith AM, Hill QA, Menon KV. Obstructive jaundice due to a pancreatic mass: a rare presentation of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in an adult. JOP. 2010;11:72–4.
Nakaji S, Hirata N, Shiratori T, Kobayashi M, Fujii H, Ishii E, et al. A case of primary pancreatic lymphoblastic lymphoma diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2014;7:180–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, K., Kawamoto, S., Kitao, A. et al. Double-hit pancreatic B-lymphoblastic lymphoma with a variant translocation t(2;18)(p11;q21). Int J Hematol 110, 107–114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-019-02646-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-019-02646-6