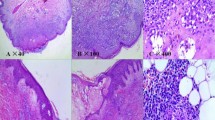
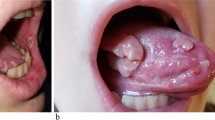
Abstract
Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is a rare, fatal, paraneoplastic autoimmune mucocutaneous blistering disease, commonly associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, including malignant lymphomas. Lymphoproliferative disorders associated with PNP are sometimes associated with a serious lung complication, bronchiolitis obliterans (BO). Due to its rarity, guidelines for the management of PNP have not been established. Furthermore, most patients die within 1 year. Here we report the successful treatment of lymphoma-associated PNP and BO using R-CHOP chemotherapy. A 53-year-old Japanese man was admitted to our hospital for severe erosive stomatitis. Computed tomography and positron emission tomography showed multiple lymphadenopathies. He was diagnosed with follicular lymphoma (Ann Arbor stage IVA) and PNP-related BO. The patient underwent six cycles of R-CHOP and an additional cycle of rituximab. Both the erosive stomatitis and the obstructive lung disease persisted, but complete response of the follicular lymphoma was achieved. The patient survived 27 months after diagnosis. Although he died from progressive respiratory failure due to BO, we note that this patient achieved the longest survival of any reported case of PNP-related BO associated with a lymphoproliferative disorder. The present case suggests that intensive immunochemotherapy for underlying lymphoma may improve the prognosis in patients with PNP-related BO associated with lymphoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, Korman NJ, Jabs DA, Kory M, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1729–35.
Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Bassler KD, Shults LD, Shields MC, Ruben BS, et al. Classification, clinical manifestations, and immunopathological mechanisms of the epithelial variant of paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome: a reappraisal of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:193–206.
Oursler JR, Labib RS, Ariss-Abdo L, Burke T, O’keefe EJ, Anhalt GJ, et al. Human autoantibodies against desmoplakins in paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Clin Investig. 1992;89:1775–82.
Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Watanabe K, Chorzelski TP, Black MM, Stevens HP, et al. Characterization of paraneoplastic pemphigus autoantigens by immunoblot analysis. J Investig Dermatol. 1995;104:829–34.
Frew JW, Murrell DF. Current management strategies in paraneoplastic pemphigus (paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome). Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:419–25.
Leger S, Picard D, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Arnault JP, Aubin F, Carsuzaa F, et al. Prognostic factors of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:1165–72.
Animesh A. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: autoimmune-cancer nexus in the skin. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15:1215–23.
Sehgal VN, Srivastava G. Paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:162–9.
Nousari HC, Deterding R, Wojtczack H, Aho S, Uitto J, Hashimoto T, et al. The mechanism of respiratory failure in paraneoplastic pemphigus. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1406–10.
Maldonado F, Pittelkow MR, Ryu JH. Constrictive bronchiolitis associated with paraneoplastic autoimmune multi-organ syndrome. Respirology. 2009;14:129–33.
Nikolskaia OV, Nousari CH, Anhalt GJ. Paraneoplastic pemphigus in association with Castleman’s disease. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:1143–51.
Joly P, Richard C, Gilbert D, Couville P, Chosidow O, Roujeau JC, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of clinical, histologic, and immunologic features in the diagnosis of paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:619–26.
Meyer KC, Raghu G, Verleden GM, Corris PA, Aurora P, Wilson KC, et al. An international ISHLT/ATS/ERS clinical practice guideline: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1479–503.
Anderson KM, Smith P, Norton A, Hancock BW, Hoskin PJ, MacLennan KA, et al. Long-term effect of a watch and wait policy versus immediate systemic treatment for asymptomatic advanced-stage non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;362:516–22.
Brice P, Bastion Y, Lepage E, Brousse N, Haioun C, Moreau P, et al. Comparison in low-tomor-burden follicular lymphoma between an initial no-treatment policy, prednimustine, or interferon alfa: a randomized study from the Group d’Etude des Lymphomes Folliculares. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:1110–7.
Solal-Celigny P, Lepage E, Brousse N, Tendler CL, Brice P, Haioun C, et al. Doxorubicin-containing regimen with or without interferon alfa-2b for advanced follicular lymphomas: final analysis of survival and toxicity in the Group d’Etude des Lymphomes Folliculares 86 trial. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2332–8.
Ohzono A, Sogame R, Li X, Teye K, Tsuchiasaka A, Numata S, et al. Clinical immunological findings in 104 cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1447–52.
Kaplan I, Hodak E, Ackerman L, Mimouni D, Calderon S. Neoplasms associated with paraneoplastic pemphigus: a review with emphasis on non-hematologic malignancy and oral mucosal manifestations. Oral Oncol. 2004;40:553–62.
Hirano T, Higuchi Y, Yuki H, Hirata S, Nosaka K, Ishii N, et al. Rituximab monotherapy and rituximab-containing chemotherapy were effective for paraneoplastic pemphigus accompanying follicular lymphoma, but not for subsequent bronchiolitis obliterans. J Clin Exp Hematol. 2015;55:83–8.
Hoffman MA, Qiao X, Anhalt GJ. CD8+ T lymphocytes in bronchiolitis obliterans, paraneoplastic pemphigus, and solitary Castleman’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:407–8.
Chang JM, Lee HJ, Goo JM, Lee HY, Lee JJ, Chung JK, et al. False positive and false negative FDG-PET scans in various thoracic diseases. Korean J Radiol. 2006;7:57–9.
Estenne M, Hertz MI. Bronchiolitis obliterans after human lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care. 2002;16:440–4.
Tateishi U, Hasegawa T, Terauchi T, Moriyama N, Arai Y. Disease activity and 18F-FDG uptake in organizing pneumonia: semi-quantitative evaluation using computed tomography and position emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:906–12.
Takahashi M, Shimatsu Y, Kazama T, Kimura K, Otuka T, Hashimoto T, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with bronchiolitis obliterans. Chest. 2000;117:603–7.
Gudi VS, Ormerod AD, Weir J, Kerr KM, Devereux G. Severe breathlessness, mouth ulcers and skin blistering in a female. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:884–7.
Wang SH, Chu CY, Chen HH, Chang YL, Chen KY, Chiu HC, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus and bronchiolitis obliterans in a patient with splenic B-cell lymphoma. J Formos Med Assoc. 2007;106:768–73.
Park KY, Choi SY, Seo SJ, Hong CK. Case or paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with retroperitoneal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and fetal bronchiolitis obliterans-like lung disease. J Dermatol. 2013;40:142–4.
Kanaoka M, Matsukura S, Ishikawa H, Matsuura M, Ishii N, Hashimoto T, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with fetal bronchiolitis obliterans and appearance of anti-BP180 antibodies in the late stage of the disease. J Dermatol. 2014;41:628–30.
Morikawa K, Tsuji T, Yamasaka H, Egashira S, Kaguchi A, Kido M, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus occurs most commonly in indolent B call lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 2014;132:73–4.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. K. Takeuchi and Dr. M. Ohta for their scientific advice. The first author would like to thank her husband, Dr. T. Morishita, for useful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Yamauchi, T., Ishii, N. et al. Achievement of the longest survival of paraneoplastic pemphigus with bronchiolitis obliterans associated with follicular lymphoma using R-CHOP chemotherapy. Int J Hematol 106, 852–859 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-017-2305-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-017-2305-2