Abstract
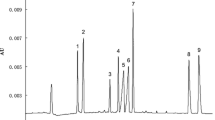
A sensitive and rapid method for the simultaneous analysis of artificial sweeteners, aspartame, acesulfame, cyclamate, saccharine, and phenylalanine in water samples using solid-phase and large-volume sample stacking-capillary electrophoresis (SPE-LVSS-CE) has been developed. Under optimal conditions, the proposed method had a linear range of 0.08 to 2.0 mg L−1, with limits of detection ranging from 0.03 to 0.18 mg L−1 with inter- and intraday repeatabilities < 10% (as a relative standard deviation) in all cases. The enrichment factor obtained was in a range from 20 to 89 times for each artificial sweetener compared with a conventional capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE). The method is adequate to analyze artificial sweeteners in water samples with different ionic strengths. The proposed method was employed in the analysis of 20 samples including drinking water such as mineral water, distilled water, spring water, and tap water. Nine of the tested samples were positive for the presence of aspartame, saccharine, and acesulfame with concentrations between 0.19 and 0.75 mg L−1, 0.08 mg L−1, and 0.08 mg L−1, respectively. The SPE-LVSS-CE is a robust, easy, fast, and efficient strategy for online preconcentration of artificial sweeteners in complex matrices.

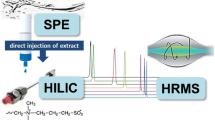
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergamo AB, Fracassi da Silva JA, Pereira de Jesus D (2011) Simultaneous determination of aspartame, cyclamate, saccharin and acesulfame-K in soft drinks and tabletop sweetener formulations by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. J Food Chem 124:1714–1717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.107
Buerge IJ, Buser H-R, Kahle M, Müller MD, Poiger T (2009) Ubiquitous occurrence of the artificial sweetener Acesulfame in the aquatic environment: an ideal chemical marker of domestic wastewater in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 43(12):4381–4385. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900126x
Chen Y, Lü W, Chen X, Teng M (2012) Review of recent developments of on-line sample stacking techniques and their application in capillary electrophoresis. Cent Eur J Chem 10(3):611–638. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-012-0007-4
Cheng C, Li X, Xie X, Chang F, Li M, Zhu Z (2016) Highly sensitive detection of cooper (I) and cooper (II) in cells specimens by CE-UV with a large-volume sample stacking. Anal Methods 8:4272–4276. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00933F
Crevillén AG, De Frutos M, Diez-Masa JC (2017) On-chip single column transient isotachophoresis with free zone electrophoresis for preconcentration and separation of α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin. Microchem J 133:600–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.04.040
Currie LA (1995) Nomencature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl Chem 67:1699–1723. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199567101699
Hashemi M, Habibi A, Jahanshahi N (2011) Determination of cyclamate in artificial sweeteners and beverages using headspace single-drop microextraction and gas chromatography flame-ionisation detection. Food Chem 124:1258–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.057
Kawai T, Koino H, Sueyoshi K, Kitagawa F, Otsuka K (2012) Highly sensitive chiral analysis in capillary electrophoresis with large-volume sample stacking with an electroosmotic flow pump. J Chromatogr A 1246:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.02.001
Lee ISL, Boyce MC, Breadmore MC (2012) Extraction and on-line concentration of flavonoids in Brassica oleracea by capillary electrophoresis using large volume sample stacking. Food Chem 133:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.006
Li J, Huang Y, Huang L, Ye L, Zhou Z, Xiang G, Xu L (2012) Determination of imatinib mesylate and related compounds by field amplified sample stacking with large volume sample injection capillary electrophoresis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 70:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2012.05.010
Lin H, Oturan N, Wu J, Sharma VK, Zhang H, Oturan MA (2017) Removal of artificial sweetener aspartame from aqueous media by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 167:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.143
Malinina J, Kamencev M, Tkach K, Yakimova N, Kuchumova I, Moskvin N (2018) Large-volume sample stacking for the analysis of low molecular mass amines in steam water by CE using novel highly absorbing probe for indirect UV detection. Microchem J 137:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.10.018
Moreno-González D, Krulišová M, Gámiz-Gracia L, García-Campaña AM (2018) Determination of tetracyclines in human urine samples by capillary electrophoresis in combination with field amplified sample injection. Electrophoresis 39:608–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201700288
Murray S, Tulloch A, Criscitelli K, Avena NM (2016) Recent studies of the effects of sugar on brain systems involved in energy balance and reward: relevance to low calorie sweeteners. Physiol Behav 164:504–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.04.004
Ni Y, Xiao W, Kokot S (2009) A differential kinetic spectrophotometric method for determination of three sulphanilamide artificial sweeteners with the aid of chemometrics. Food Chem 113:1339–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.08.068
Núñez M, Borrul F, Pocurull E, Fontanals N (2017) Pressurised liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry to determine high-intensity sweeteners in fish samples. J Chromatogr A 1479:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.006
Oliveira VN, Bellozi L, Pereira J, Vincenzi A, Tonin FG, Leal MA (2013) Simultaneous analysis of aspartame, cyclamate, saccharin and acesulfame-K by CZE under UV detection. Anal Methods 5:1524–1532. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AY26187E
Ordoñez EY, Quintana JB, Rodil R, Cela R (2013) Determination of artificial sweeteners in sewage sludge samples using pressurised liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1320:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.049
Puig P, Tempels FWA, Somsen GW, de Jong JG, Borrull F, Aguilar C, Calull M (2008) Use of large-volume sample stacking in on-line solid-phase extraction-capillary electrophoresis for improved sensitivity. Electrophoresis 29:1339–1346. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200700636.
Roca-Saavedra P, Mendez-Vilabrille V, Miranda JM, Nebot C, Cardelle-Cobas A, Franco CM, Cepeda A (2018) Food additives, contaminants and other minor components: effects on human gut microbiota-a review. J Physiol Biochem 74:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0564-2
Salas D, Borrul F, Fontanals N, Marcé RM (2015) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry to determine artificial sweeteners in environmental waters. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:4277–4285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8330-6
Stojkovic M, Mai TD, Hauser PC (2013) Determination of artificial sweeteners by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection optimized by hydrodynamic pumping. Anal Chim Acta 787:254–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.05.039
Tran NH, Hu J, Li J, Ong SL (2014) Suitability of artificial sweeteners as indicators of raw wastewater contamination in surface water and groundwater. Wat Res 48:443–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.053
Vistuba JP, Dolzan MD, Vitali L, Leal de Oliveira MA, Micke GA (2015) Sub-minute method for simultaneous determination of aspartame, cyclamate, acesulfame-K and saccharin in food and pharmaceutical samples by capillary zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1396:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.070
Vuorensola K, Sirén H, Kostiainen R, Kotiaho T (2002) Analysis of catecholamines by capillary electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis-nanospray mass spectrometry Use of aqueous and non-aqueous solutions compared with physical parameters. J Chromatogr A 979:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(02)01256-6
Wang N, Su M, Liang S, Sun H (2016) Sensitive residue analysis of quinolones and sulfonamides in aquatic product by capillary zone electrophoresis using large-volume sample stacking with polarity switching combined with accelerated solvent extraction. Food Anal Methods 9:1020–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0269-5
Xu X, Jia Z, Shu Y, Liu L (2015) Dynamic pH junction–sweeping technique for on-line concentration of acidic amino acids in human serum by capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV detection. J Chromatogr B 980:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.12.009
Yang L, Zhou S, Xiao Y, Tang Y, Xie T (2015) Sensitive simultaneous determination of three sulfanilamide artificial sweeters by capillary electrophoresis with on-line preconcentration and contact less conductivity detection. Food Chem 188:446–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.04.060
Yang Y-Y, Zhao J-L, Liu Y-S, Liu W-R, Zhang Q-Q, Yao L, Hu L-X, Zhang J-N, Jiang Y-X, Ying G-G (2018) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and artificial sweeteners (ASs) in surface and ground waters and their applications as indication of wastewater contamination. Sci Total Environ 616–617:816–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.241
Zygler A, Wasik A, Namiésnik J (2009) Analytical methodologies for determination of artificial sweeteners in foodstuffs. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 28:1082–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2009.06.008
Zygler A, Wasik A, Namiésnik J (2010) Retention behaviour of some high-intensity sweeteners on different SPE sorbents. Talanta 82:1742–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.07.070
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Programa para el Desarrollo Profesional Docente, para el Tipo Superior (PRODEP) for the approved project in the incorporation of new PTC (Profesores de Tiempo Completo)
Funding
This study was financially supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) (Project INFR-2014-227999 and Retention Grant no. 251112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
Lorena Camargo Medrano declares that she has no conflict of interest. Juan Francisco Flores-Aguilar declares that he has no conflict of interest. Gabriela Islas declares that she has no conflict of interest. José Antonio Rodríguez declares that he has no conflict of interest. Israel Samuel Ibarra declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medrano, L.C., Flores-Aguilar, J.F., Islas, G. et al. Solid-Phase Extraction and Large-Volume Sample Stacking-Capillary Electrophoresis for Determination of Artificial Sweeteners in Water Samples. Food Anal. Methods 12, 526–533 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1383-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1383-y