Abstract
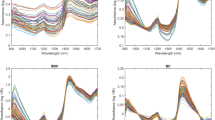
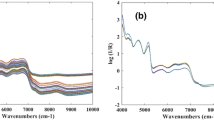
Fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy equipped with attenuated total reflectance (FT-IR–ATR) combined to partial least squares (PLS) regression was used for the quantification of total phenolic contents (TPCs) and antioxidant activities in 98 samples of ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) from the southwest region of Paraná, Brazil. The Pearson’s correlation coefficients were applied, and results ranged from 0.96 to 0.88 and showed higher correlation coefficients among TPC and ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) followed by 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) ABTS and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl hydrate (DPPH). Calibration was performed using a Savitzky-Golay filter (15 pt) and first derivative as well as standard normal variate (SNV) and mean center correction pretreatments. The determination coefficient in the calibration models ranged from 0.95 to 0.87. The range error ratio (RER) indicates the quality of estimation of the models and the results obtained were 10.0, 8.11, 16.8, and 8.99 for TPC, DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP, respectively. Thus, the results obtained for calibration and prediction parameters indicated that the models for DPPH, FRAP, and TPC have a low predictive capacity which complicates the data modeling. However, the ABTS model is validated and can be used for quantification of antioxidant activity of new extracts of propolis, being useful as an alternative to rapid analysis, reducing waste generation and cost, and indicating that the mid-infrared spectroscopy associated with PLS regression can be used to predict ABTS radical scavenger.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ghamdi AA, Bayaqoob NIM, Rushdi AI, Alattal Y, Simoneit BRT, el-Mubarak AH, al-Mutlaq KF (2017) Chemical compositions and characteristics of organic compounds in propolis from Yemen. Saudi J Biol Sci 24(5):1094–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.12.012
Alves E, Kubota EH (2013) Conteúdo de fenólicos, flavonoides totais e atividade antioxidante de amostras de própolis comerciais. Rev Ciências Farm Básica e Apl 34:37–41
Bankova V (2005) Recent trends and important developments in propolis research. Evid-Based Complement Alternat Med 2(1):29–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/neh059
Bankova V (2009) Chemical diversity of propolis makes it a valuable source of new biologically active compounds. J ApiProduct ApiMedical Sci 1(2):23–28. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.4.01.2.01
Banskota AH, Tezuka Y, Kadota S (2001) Recent progress in pharmacological research of propolis. Phyther Res 15(7):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1029
Barbosa KBF, Costa NMB, Alfenas RCG, et al (2010) Estresse oxidativo: Conceito, implicações e fatores modulatórios. Rev Nutr 23:629–643. https://doi.org/10.1159/000320546
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma ( FRAP ) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Brand-Williams M, Cuvelier ME, Berset C (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Leb Technol 28(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Cai R, Wang S, Meng Y et al (2012) Rapid quantification of flavonoids in propolis and previous study for classification of propolis from different origins by using near infrared spectroscopy. Anal Methods 4(8):2388. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ay25184a
Calegari MA, Prasniewski A, Silva C et al (2017) Propolis from southwest of Parana produced by selected bees: influence of seasonality and food supplementation on antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. An Acad Bras Cienc 89(1):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201620160499
Cao J, Peng LQ, Du LJ, Zhang QD, Xu JJ (2017) Ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid-based micellar extraction combined with microcrystalline cellulose as sorbent in dispersive microextraction for the determination of phenolic compounds in propolis. Anal Chim Acta 963:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.01.063
Castro C, Mura F, Valenzuela G, Figueroa C, Salinas R, Zuñiga MC, Torres JL, Fuguet E, Delporte C (2014) Identification of phenolic compounds by HPLC-ESI-MS / MS and antioxidant activity from Chilean propolis. FRIN 64:873–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.08.050
Chang-Bravo L, López-Córdoba A, Martino M (2014) Biopolymeric matrices made of carrageenan and corn starch for the antioxidant extracts delivery of Cuban red propolis and yerba mate. React Funct Polym 85:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2014.09.025
Dal Zotto R, De Marchi M, Cecchinato A et al (2008) Reproducibility and repeatability of measures of milk coagulation properties and predictive ability of mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J Dairy Sci 91(10):4103–4112. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0772
Daneshmand A, Sadeghi G, Karimi A et al (2015) Evaluating complementary effects of ethanol extract of propolis with the probiotic on growth performance, immune response and serum metabolites in male broiler chickens. Livest Sci 178:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2015.04.012
de Cardoso EO, Conti BJ, Santiago KB et al (2017) Phenolic compounds alone or in combination may be involved in propolis effects on human monocytes. J Pharm Pharmacol 69(1):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12660
Fagan CC, Everard C, Donnell CPO et al (2007) Evaluating mid-infrared spectroscopy as a new technique for predicting sensory texture attributes of processed cheese. J Dairy Sci 90(3):1122–1132. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(07)71598-9
González-Martín MI, Revilla I, Vivar-Quintana AM, Betances Salcedo EV (2017) Pesticide residues in propolis from Spain and Chile. An approach using near infrared spectroscopy. Talanta 165:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.12.061
Grdadolnik J (2002) ATR-FTIR spectroscopy: its advantages and limitations. Acta Chim Slov 49:631–642
Jurd L, Geissman TA (1956) Absorption spectra of metal complexes of flavonoid compounds. J Org Chem 88(7):1405–1421. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00089a017
Kapper C, Klont RE, Verdonk JMAJ, Williams PC, Urlings HAP (2012) Prediction of pork quality with near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) 2. Feasibility and robustness of NIRS measurements under production plant conditions. Meat Sci 91(3):300–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.02.006
Laghi L, Versari A, Parpinello GP et al (2011) FTIR spectroscopy and direct orthogonal signal correction preprocessing applied to selected phenolic compounds in red wines. Food Anal Methods 4(4):619–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9240-2
López BG, Morgado E, Eberlin MN, Sawaya ACHF (2014) Phytochemical markers of different types of red propolis. Food Chem 146:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.063
Luis-Villaroya A, Espina L, Garcia-Gonzalo D et al (2015) Bioactive properties of a propolis-based dietary supplement and its use in combination with mild heat for apple juice preservation. Int J Food Microbiol 205:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.03.020
Martins JPA, Ferreira MMC (2013) Qsar modeling: a new open source computational package to generate and validate Qsar models. Quim Nova 36(4):554–U250. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422013000400013
Menezes H (2005) Própolis : Uma Revisão Dos Recentes Estudos. Arq Inst Biol 72:405–411
Morlock GE, Ristivojevic P, Chernetsova ES (2014) Combined multivariate data analysis of high-performance thin-layer chromatography fingerprints and direct analysis in real time mass spectra for profiling of natural products like propolis. J Chromatogr A 1328:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.12.053
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kritz GS, et al (2010) Introduction to Spectroscopy, 4th edn. Brooks Cole: Washington
Pham-Huy LA, He H, Pham-Huy C (2008) Free Radicals, Antioxidants in Disease and Health. Int J Biomed Sci 4:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804252105
Oldoni TLC, Cabral ISR, D’Arce MABR et al (2011) Isolation and analysis of bioactive isoflavonoids and chalcone from a new type of Brazilian propolis. Sep Purif Technol 77(2):208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2010.12.007
Oldoni TLC, Oliveira SC, Andolfatto S et al (2015) Chemical characterization and optimization of the extraction process of bioactive compounds from propolis produced by selected bees. J Braz Chem Soc 26:2054–2062. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150186
Park YK, Alencar SM, Aguiar CL (2002) Botanical origin and chemical composition of Brazilian propolis. J Agric Food Chem 50(9):2502–2056. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011432b
Páscoa RNMJ, Magalhães LM, Lopes JA (2013) FT-NIR spectroscopy as a tool for valorization of spent coffee grounds: application to assessment of antioxidant properties. Food Res Int 51(2):579–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.01.035
Pasupuleti VR, Sammugam L, Ramesh N, Gan SH (2017) Honey, propolis, and royal jelly: a comprehensive review of their biological actions and health benefits. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1259510
Picoli T, Peter CM, Hoffmann JF et al (2016) Caracterização química e ação antibacteriana de extrato de própolis marrom da região sul do Brasil. Rev Bras Med Vet 38:365–371
Popova M, Trusheva B, Bankova V (2017) Content of biologically active compounds in Bulgarian propolis : a basis for its standardization. Bulg Chem Commun 49:115–120
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente a et al (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved Abts radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9-10):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Revilla I, Vivar-Quintana AM, González-Martín I, Escuredo O, Seijo C (2017) The potential of near infrared spectroscopy for determining the phenolic, antioxidant, color and bactericide characteristics of raw propolis. Microchem J 134:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.06.006
Rodriguez-Saona LE, Allendorf ME (2011) Use of FTIR for rapid authentication and detection of adulteration of food. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 2(1):467–483. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-022510-133750
Rufatto LC, dos Santos DA, Marinho F, Henriques JAP, Roesch Ely M, Moura S (2017) Red propolis: chemical composition and pharmacological activity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 7(7):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.06.009
Salami A, Seydi E, Pourahmad J (2013) Use of nutraceuticals for prevention and treatment of cancer. Iran J Pharm Res 12:219–220
Schnitzler P, Neuner A, Nolkemper S, Zundel C, Nowack H, Sensch KH, Reichling J (2010) Antiviral activity and mode of action of propolis extracts and selected compounds. Paul Phyther Res 24(S1):S20–S28. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2868
Silva BB, Rosalen PL, Cury JA, Ikegaki M, Souza VC, Esteves A, Alencar SM (2007) Chemical composition and botanical origin of red propolis, a new type of Brazilian propolis. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 5(3):313–316. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nem059
Silva SD, Feliciano RP, Boas LV, Bronze MR (2014) Application of FTIR-ATR to Moscatel dessert wines for prediction of total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant capacity. Food Chem 150:489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.028
Silva-carvalho R, Baltazar F, Almeida-aguiar C (2015) Propolis : a complex natural product with a plethora of biological activities that can be explored for drug development. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2015:206439. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/206439
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventόs RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol 299:152–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
Siqueira ABS, de Rodriguez LRNA, Santos RKB et al (2015) Antifungal activity of propolis against Candida species isolated from cases of chronic periodontitis. Braz Oral Res 29(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2015.vol29.0083
Soares SE (2002) Ácidos Fenólicos como antioxidantes. Rev Nutr 15(1):71–81. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-52732002000100008
Soltani EK, Cerezuela R, Charef N et al (2017) Algerian propolis extracts: chemical composition, bactericidal activity and in vitro effects on gilthead seabream innate immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 62:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.01.009
Sousa CMDM, Silva HRE, Vieira GM et al (2007) Fenóis totais e atividade antioxidante de cinco plantas medicinais. Quim Nova 30(2):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422007000200021
Tan W, Sun L, Yang F, Che W, Ye D, Zhang D, Zou B (2018) Study on bruising degree classification of apples using hyperspectral imaging and GS-SVM. Optik (Stuttg) 154:581–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.10.090
Tiveron AP, Rosalen PL, Franchin M, Lacerda RCC, Bueno-Silva B, Benso B, Denny C, Ikegaki M, Alencar SM (2016) Chemical characterization and antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activities of south Brazilian organic propolis. PLoS One 11(11):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165588
Vargas-Sánchez RD, Mendoza-Wilson AM, Torrescano-Urrutia GR, Sánchez-Escalante A (2015) Antiradical potential of phenolic compounds fingerprints of propolis extracts : DFT approach. Comput Theor Chem 1066:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2015.05.003
Vasconcelos SML, Goulart MOF, Moura JBF, et al (2007) Espécies reativas de oxigênio e de nitrogênio, antioxidantes e marcadores de dano oxidativo em sangue humano: Principais métodos analíticos para sua determinação. Quím Nova 30:1323–1338. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422007000500046
Veiga RS, Mendonça S, Mendes PB et al (2017) Artepillin C and phenolic compounds responsible for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of green propolis and Baccharis dracunculifolia DC. J Appl Microbiol 122(1):911–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12426
Viegas TR, Mata ALML, Duarte MML, Lima KMG (2016) Determination of quality attributes in wax jambu fruit using NIRS and PLS. Food Chem 190:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.063
Wilson RH, Tapp HS (1999) Mid-infrared spectroscopy for food analysis: recent new applications and relevant developments in sample presentation methods. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 18(2):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-9936(98)00107-1
Wu Y-W, Sun S-Q, Zhao J, Li Y, Zhou Q (2008) Rapid discrimination of extracts of Chinese propolis and poplar buds by FT-IR and 2D IR correlation spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 883–884:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.12.009
Xu L, Yan S, Cai C, Yu X (2013) Untargeted detection and quantitative analysis of poplar balata ( PB ) in Chinese propolis by FT-NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Chem 141:4132–4137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.013
Zabaiou N, Fouache A, Trousson A, Baron S, Zellagui A, Lahouel M, Lobaccaro JMA (2017) Biological properties of propolis extracts: something new from an ancient product. Chem Phys Lipids 207(Pt B):214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2017.04.005
Zhou H, Deng Z, Xia Y, Fu M (2016) A new sampling method in particle filter based on Pearson correlation coefficient. Neurocomputing 216:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.07.036
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge fellowship from Federal Technological University of Parana (UTFPR) and Central de Analises.
Funding
This study was funded by Federal Technological University of Paraná (UTFPR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
C. da Silva declares that she has no conflict of interest. A. Prasniewski declares that she has no conflict of interest. M. A. Calegari declares that he has no conflit of interest. V. A. de Lima declares that he has no conflict of interest. T. L. C. Oldoni declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, C., Prasniewski, A., Calegari, M.A. et al. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of Propolis Using ATR–FT-IR Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Anal. Methods 11, 2013–2021 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1161-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1161-x