Abstract
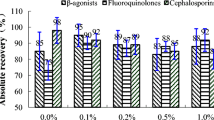
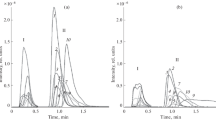
A novel two-dimensional hydrophilic interaction chromatography/reversed phase liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry system was developed to analyze seven categories of antibiotics residues in dairy products. The seven categories were β-lactams, tetracyclines, macrolides, aminoglycosides, amphenicols, quinolones, and sulphonamides, and involved 20 antibiotics. Samples of milk powder or milk samples were extracted by mixed matrix solid phase dispersion using C18 and CN material. The analytes were eluted by acetonitrile and water, and were dried with rotary evaporation. Finally, the residues were dissolved with mobile phase and then analyzed. Under sample pretreatment conditions, chromatographic and mass spectrometric parameters were optimized. Twenty analytes showed good linearities with correlation coefficients of 0.9945 ~ 0.9998. The limits of detection and quantification for milk powder and milk samples were 0.10 ~ 2.40 and 0.33 ~ 7.92 μg/kg, respectively. The proposed method has been applied to the determination of antibiotics residues in milk powder and milk samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera-Luiz MM, Vidal JL, Romero-González R, Frenich AG (2008) Multi-residue determination of veterinary drugs in milk by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1205:10–16
Buszewski B, Noga S (2012) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)—a powerful separation technique. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:231–247
Carretero V, Blasco C, Picó Y (2008) Multi-class determination of antimicrobials in meat by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1209:162–173
Chauve B, Guillarme D, Cléon P, Veuthey JL (2010) Evaluation of various HILIC materials for the fast separation of polar compounds. J Sep Sci 33:752–764
Chico J, Rúbies A, Centrich F, Companyó R, Prat MD, Granados M (2008) High-throughput multiclass method for antibiotic residue analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1213:189–199
Cristofani E, Antonini C, Tovo G, Fioroni L, Piersanti A, Galarini R (2009) A confirmatory method for the determination of tetracyclines in muscle using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. Anal Chim Acta 637:40–46
Dejaegher B, Vander Heyden Y (2010) HILIC methods in pharmaceutical analysis. J Sep Sci 33:698–715
Fountain KJ, Xu J, Diehl DM, Morrison D (2010) Influence of stationary phase chemistry and mobile-phase composition on retention, selectivity, and MS response in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Sep Sci 33:740–751
Gentili A, Perret D, Marchese S (2005) Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for performing confirmatory analysis of veterinary drugs in animal-food products. Trends Anal Chem 24:704–733
Gong Q, Ding L, Zhu S, Jiao Y, Cheng J, Fu S, Wang L (2012) Determination of ten aminoglycoside residues in milk and dairy products using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chinese J Chromatography 30:1143–1147
Goucher E, Kicman A, Wolff K, Smith N, Jickells S (2010) Hydrophilic stationary phases: a practical approach for the co-analysis of compounds with varying polarity in biological matrices. J Sep Sci 33:955–965
Granelli K, Branzell C (2007) Rapid multi-residue screening of antibiotics in muscle and kidney by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 586:289–295
Granelli K, Elgerud C, Lundström A, Ohlsson A, Sjöberg P (2009) Rapid multi-residue analysis of antibiotics in muscle by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 637:87–91
Grumbach ES, Diehl DM, Neue UD (2008) The application of novel 1.7 microm ethylene bridged hybrid particles for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Sep Sci 31:1511–1518
Hemström P, Irgum K (2006) Hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Sep Sci 29:1784–1821
Jandera P (2008) Stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography, their characterization and implementation into multidimensional chromatography concepts. J Sep Sci 31:1421–1437
Jandera P, Hájek T, Skeríková V, Soukup J (2010) Dual hydrophilic interaction-RP retention mechanism on polar columns: structural correlations and implementation for 2-D separations on a single column. J Sep Sci 33:841–852
Jandera P, Hájek T, Staňková M, Vyňuchalová K, Česla P (2012) Optimization of comprehensive two-dimensional gradient chromatography coupling in-line hydrophilic interaction and reversed phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1268:91–101
Kahsay G, Song H, Van Schepdael A, Cabooter D, Adams E (2014) Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) in the analysis of antibiotics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 87:142–154
Kennedy DG, McCracken RJ, Cannavan A, Hewitt SA (1998) Use of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the analysis of residues of antibiotics in meat and milk. J Chromatogr A 812:77–98
Kumar P, Rubies A, Companyó R, Centrich F (2012) Hydrophilic interaction chromatography for the analysis of aminoglycosides. J Sep Sci 35:498–504
Liu M, Chen EX, Ji R, Semin D (2008a) Stability-indicating hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography method for highly polar and basic compounds. J Chromatogr A 1188:255–263
Liu Y, Xue X, Guo Z, Xu Q, Zhang F, Liang X (2008b) Novel two-dimensional reversed-phase liquid chromatography/hydrophilic interaction chromatography, an excellent orthogonal system for practical analysis. J Chromatogr A 1208:133–140
Nakazawa H, Ino S, Kato K, Watanabe T, Ito Y, Oka H (1999) Simultaneous determination of residual tetracyclines in foods by high-performance liquid chromatography with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 732:55–64
Nguyen HP, Yang SH, Wigginton JG, Simpkins JW, Schug KA (2010) Retention behavior of estrogen metabolites on hydrophilic interaction chromatography stationary phases. J Sep Sci 33:793–802
Nováková L, Kaufmannová I, Jánská R (2010) Evaluation of hybrid hydrophilic interaction chromatography stationary phases for ultra-HPLC in analysis of polar pteridines. J Sep Sci 33:765–772
van Holthoon FL, Essers ML, Mulder PJ, Stead SL, Caldow M, Ashwin HM, Sharman M (2009) A generic method for the quantitative analysis of aminoglycosides (and spectinomycin) in animal tissue using methylated internal standards and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 637:135–143
Wang L, Li YQ, Wang HB, Guan YL (2011) Simultaneous determination of twenty veterinary drug residues in milk and meat using matrix solid phase dispersion-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chinese Journal of Anal Chem 39:203–207
Wu J, Bicker W, Lindner W (2008) Separation properties of novel and commercial polar stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction and reversed-phase liquid chromatography mode. J Sep Sci 31:1492–1503
Zurhelle G, Müller-Seitz E, Petz M (2000) Automated residue analysis of tetracyclines and their metabolites in whole egg, egg white, egg yolk and hen's plasma utilizing a modified ASTED system. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 739:191–203
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2012M521703). We thank Prof. Dongtao Lin of the Sichuan University for copyediting the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
Lian Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest, Bixia Yang declares that she has no conflict of interest, Xinshen Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest, and Hongguo Zheng declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yang, B., Zhang, X. et al. Novel Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Twenty Antibiotics Residues in Dairy Products. Food Anal. Methods 10, 2001–2010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0763-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0763-4