Abstract
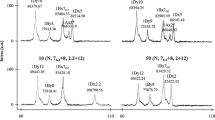
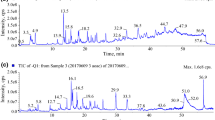
Zeins are important storage proteins and play a role in grain texture and impact on processing. Having a technique to accurately quantify the individual zeins and the size of these proteins would allow for more precise understanding of the impact these individual protein have on grain texture and/or processing. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) was used to characterise zein protein profiles of five South African maize hybrids, grown at three locations, and their respective parental lines. A new, simplified and shortened zein extraction method was used to characterise the zein profiles and to determine any possible relationship between the hybrids and their parents. A matrix solution comprising two matrices, α-cyano-4-hydroxy-cinammic acid (CHCA) and 2-(4-hydroxyphenylazo) benzoic acid (HABA), was required to detect all major zein (α, β, γ and δ) classes. Within the set of hybrids and parents, additional peaks with molecular weights not previously reported were observed. These were identified as belonging to the δ-zein, β-zein and γ-zein. Relationships between the hybrids and their respective parental lines were observed indicating genetic variation for these zein classes exists. The MALDI-TOF MS method identified differences in individual zein proteins and these differences were observed between hybrids. The method shows a potential for accurately quantifying the presence and molecular size of zein proteins which may be important in milling and food processing. Storage proteins play an important role not only in grain composition but also in some processes such as milling, and variation in these individual proteins may impact on efficiency of processing.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- CE-MS:
-
Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry
- CHCA:
-
α-Cyano-4-hydroxy-cinammic acid
- Da:
-
Dalton
- DD:
-
Dried-droplet
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- h:
-
Hour
- HABA:
-
2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo) benzoic acid
- HPLC-TOF-MS:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- IAA:
-
Iodoacetamide
- kDa:
-
Kilodalton
- MALDI-TOF MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- NH4OH:
-
Ammonium hydroxide
- RP-HPLC-ESI-MS:
-
Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Adams WR, Huang S, Kriz AL, Luethy MH (2004) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis of zeins in mature maize kernels. J Agr Food Chem 52:1842–1849
Beavis RC, Chaudhary T, Chait BT (1992) α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid as a matrix for matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry. Org Mass Spectrom 27:156–158
Crank JA, Armstrong DW (2009) Towards a second generation of ionic liquid matrices (ILMs) for MALDI-MS of peptides, proteins, and carbohydrates. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20:1790–1800
De Hoffman E, Stroobant V (2007) Mass spectrometry principles and applications, 3rd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Dombrink-Kurtzman MA, Beitz JA (1993) Zein composition in hard and soft endosperm maize. Cereal Chem 70:105–108
Erny GL, Marina ML, Cifuentes A (2007) CE-MS of zein proteins from conventional and transgenic maize. Electrophoresis 28:4192–4201
Esen A (1986) Separation of alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) from maize into three fraction by differential solubility. Plant Physiol 80:623–627
Esen A (1987) A proposed nomenclature for the alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) of maize (Zea mays L.). J Cereal Sci 5:117–128
Fox G, Manley M (2009) Hardness methods for testing maize kernels. J Agr Food Chem 57:5647–5657
García López MC, Garcia-Cañas V, Alegre MLM (2009) Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry profiling of transgenic and non-transgenic maize for cultivar characterisation. J Chromatogr A 1216:7222–7228
Gorka J, Bahr U, Karas M (2012) Graphite supported preparation (GSP) of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) for peptides and proteins. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 23:1949–1954
Huang S, Kruger DE, Frizzi A, D’Ordine RL, Florida CA, Adams WR, Brown WE, Luethy MH (2005) High-lysine corn produced by the combination of enhanced lysine biosynthesis and reduced zein accumulation. Plant Biotech J 3:555–569
Juhasz P, Costello CE, Biemann K (1993) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry with 2-(4-hydroxyphenylazo) benzoic acid matrix. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 4:399–409
Kirihara JA, Petri JB, Messing J (1988) Isolation and sequence of a gene encoding a methionine-rich 10-kDa zein protein from maize. Gene 71:359–370
Kovtoun SV, English RD, Cotter RF (2002) Mass correlated acceleration in a reflectron MALDI TOF mass spectrometer: an approach for enhanced resolution over a broad mass range. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 13:135–143
Lending CR, Kriz AL, Larkins BA, Bracker CE (1988) Structure of maize protein bodies and immunocytochemical localization of zeins. Protoplasma 143:51–62
Lewis JK, Wei J, Siuzdak G (2000) Maldi mass spectrometry in peptide and protein analysis. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry. Wiley, Chichester
Mestres C, Matencio F (1996) Biochemical basis of kernel milling characteristics and endosperm vitreousness of maize. J Cereal Sci 24:283–290
Morast DL (2012) Hyphenated applications of mass spectrometry for the analysis of biological compounds, PhD Thesis, Iowa State University, Iowa, USA
Nishikaze T, Okumura H, Jinmei H, Amano J (2012) Correlation between sweet spots of glycopeptides and polpymorphism of the matrix crystal in MALDI samples. Mass Spectrom 1:A006 (7 pages). doi:10.5702/massspectrometry.A0006
Prasanna BM, Vasal SK, Kassahun B, Singh NN (2001) Quality protein maize. Current Sci 81:1308–1319
Prat S, Pérez-Grau L, Puigdomènech P (1987) Multiple variability in the sequence of a family of maize endosperm proteins. Gene 52:41–49
Russell DH, Edmondson RD (1997) High-resolution mass spectrometry and accurate mass measurements with emphasis on the characterization of peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-night mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 32:263–227
Shewry PR, Halford NG (2002) Cereal seed storage proteins: structures, properties and role in grain utilisation. J Exp Bot 53:947–958
Shewry PR, Tatham AS (1990) The prolamin storage proteins of cereal seeds: structure and evolution. Biochem J 267:1–12
Shukla R, Cheryan M (2001) Zein: the industrial protein from corn. Ind Crop Prod 13:171–192
Shull JM, Watterson JJ, Kirleis AW (1991) Proposed nomenclature for the alcohol-soluble proteins (kafirins) of Sorghum bicolor (L. Moench) based on molecular weight, solubility and structure. J Agr Food Chem 39:83–87
Signor L, Erba EB (2013) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometric analysis of intact proteins larger than 100 kDa. J Vis Exp 79:e50635. doi:10.3791/50635
Wang JF, Geil PH, Kolling DRJ, Padua GW (2003) Analysis of zein by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry. J Agr Food Chem 51:5849–5854
Wilson CM (1991) Multiple zeins from maize endosperms characterized by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Plant Physiol 95:777–786
Woo YM, Hu DWN, Larkins BA, Jung R (2001) Genomics analysis of genes expressed in maize endosperm identifies novel seed proteins and clarifies patterns of zein gene expression. Plant Cell 13:2297–2317
Acknowledgments
Maize samples were kindly provided by PANNAR (Greytown, South Africa). The authors acknowledge the Maize Trust (Pretoria, South Africa) for project funding and study grant (K O’Kennedy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
K. O’Kennedy declares that she has no conflict of interest. G. Fox declares that he has no conflict of interest. M. Manley declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Kennedy, K., Fox, G. & Manley, M. Zein Characterisation of South African Maize Hybrids and Their Respective Parental Lines Using MALDI-TOF MS. Food Anal. Methods 10, 1661–1668 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0725-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0725-x