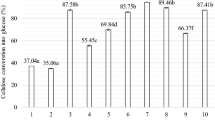
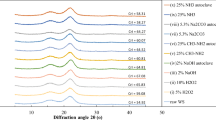
Abstract
Effect of hydrogen bond breaker (urea) addition on the enzymatic hydrolysis of Avicel and eucalyptus pretreated by dilute acid (Eu-DA) was investigated. Urea enhanced the enzymatic hydrolysis of Eu-DA at 50 or 30 °C when the concentration of urea was below 60 g/L, while it inhibited the hydrolysis of Avicel. Low concentration urea (< 240 g/L) had little effect on the cellulase spatial structure and its activity. But it decreased cellulase binding to cellulose surface to inhibit the cellulose hydrolysis. Meanwhile, urea obviously prevented the adsorption of cellobiohydrolase I (CBHI) on the lignin in spite of little effect on the adsorption of β-glucosidase (BGL) and two endoglucanases (EGIII and EGV) on lignin. It was proposed that urea enhanced the enzymatic efficiency of Eu-DA by decreasing the cellulase adsorption on lignin surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Limayem A, Ricke SC (2012) Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production: current perspectives, potential issues and future prospects. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38(4):449–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2012.03.002
Somerville C, Youngs H, Taylor C, Davis SC, Long P (2010) Feedstocks for lignocellulosic biofuels. Science 329(5993):790–791. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189268
Yang B, Wyman CE (2008) Pretreatment: the key to unlocking low-cost cellulosic ethanol. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 2(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.49
Agrawal R, Gaur R, Mathur A, Kumar R, Gupta RP, Tuli DK, Satlewal A (2015) Improved saccharification of pilot-scale acid pretreated wheat straw by exploiting the synergistic behavior of lignocellulose degrading enzymes. RSC Adv 5(87):71462–71471. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra13360b
Gao D, Haarmeyer C, Balan V, Whitehead TA, Dale BE, Chundawat SP (2014) Lignin triggers irreversible cellulase loss during pretreated lignocellulosic biomass saccharification. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-014-0175-x
Banerjee G, Scott-Craig JS, Walton JD (2010) Improving enzymes for biomass conversion: a basic research perspective. BioEnergy Res 3(1):82–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-009-9067-5
Kumar L, Arantes V, Chandra R, Saddler J (2012) The lignin present in steam pretreated softwood binds enzymes and limits cellulose accessibility. Bioresour Technol 103(1):201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.091
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. Method Enzymol 160:87–112
Henrissat B, Driguez H, Viet C, Schülein M (1985) Synergism of cellulases from Trichoderma reesei in the degradation of cellulose. Nat Biotechnol 3:722–726. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0885-722.
Gupta R, Lee YY (2009) Mechanism of cellulase reaction on pure cellulosic substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(6):1570–1581. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22195
Zhang Y-HP, Himmel M, Mielenz JR (2006) Outlook for cellulase improvement: screening and selection strategies. Biotechnol Adv 24(5):452–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.03.003
Sinnott M (1990) Catalytic mechanisms of enzymatic glycosyl transfer. Chem Rev 90(7):1171–1202. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00105a006
Himmel ME, Ding SY, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD (2007) Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315(5813):804–807. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1137016
Guo FF, Shi WJ, Sun W, Li XZ, Wang FF, Zhao J, Qu YB (2014) Differences in the adsorption of enzymes onto lignins from diverse types of lignocellulosic biomass and the underlying mechanism. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-38
Qin CG, Clarke K, Li KC (2014) Interactive forces between lignin and cellulase as determined by atomic force microscopy. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-65
Eriksson T, Börjesson J, Tjerneld F (2002) Mechanism of surfactant effect in enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Enzym Microb Technol 31(2002):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00134-5
Lou H, Zhu JY, Lan TQ, Lai H, Qiu X (2013) pH-induced lignin surface modification to reduce nonspecific cellulase binding and enhance enzymatic saccharification of lignocellulose. ChemSusChem 6(5):919–927. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201200859
Berlin A, Balakshin M, Gilkes N, Kadla J, Maximenko V, Kubo S, Saddler J (2006) Inhibition of cellulase, xylanase and beta-glucosidase activity by softwood lignin preparations. J Biotechnol 125(2):198–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.02.021
Strobel KL, Pfeiffer KA, Blanch HW, Clark DS (2016) Engineering cel7a carbohydrate binding module and linker for reduced lignin inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(6):1369–1374. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25889
Pan X (2008) Role of functional groups in lignin inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose. J Biobased Mater Bioenergy 2(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2008.005
Yu Z, Gwak KS, Treasure T, Jameel H, Chang HM, Park S (2014) Effect of lignin chemistry on the enzymatic hydrolysis of woody biomass. ChemSusChem 7(7):1942–1950. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201400042
Qin C, Clarke K, Li K (2014) Interactive forces between lignin and cellulase as determined by atomic force microscopy. Biotechnol biofuels 7:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-65
Rahikainen JL, Evans JD, Mikander S, Kalliola A, Puranen T, Tamminen T, Marjamaa K, Kruus K (2013) Cellulase-lignin interactions-the role of carbohydrate-binding module and pH in non-productive binding. Enzym Microb Technol 53(5):315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.07.003
Agrawal R, Satlewal A, Kapoor M, Mondal S, Basu B (2017) Investigating the enzyme-lignin binding with surfactants for improved saccharification of pilot scale pretreated wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 224:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.026
Börjesson J, Engqvist M, Sipos B, Tjerneld F (2007) Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) on enzymatic hydrolysis and adsorption of cellulase enzymes to pretreated lignocellulose. Enzym Microb Technol 41(1–2):186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.01.003
Lan T, Lou H, Zhu JY (2013) Enzymatic saccharification of lignocelluloses should be conducted at elevated pH 5.2–6.2. Bioenerg Res 6:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-012-9273-4
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. Methods Enzymol 160:87–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(88)60109-1
Cai C, Qiu X, Lin X, Lou H, Pang Y, Yang D, Chen S, Cai K (2016) Improving enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates with pre-hydrolysates by adding cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to neutralize lignosulfonate. Bioresour Technol 216:968–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.043
Pan X, Kadla JF, Ehara K, Gilkes N, Saddler J (2006) Organosolv ethanol lignin from hybrid poplar as a radical scavenger: relationship between lignin structure, extraction conditions, and antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem 54:5806–5813. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0605392
Nakagame S, Chandra RP, Saddler JN (2011) The influence of lignin on the enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass substrates. ACS Symp Ser 1067:145–167. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1067.ch006
Mandels M, Andreotti R, Roche C (1976) Measurement of saccharifying cellulase. Biotechnol Bioeng Syrup 6:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-2-21
Turner MB, Spear SK, Huddleston JG, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD (2003) Ionic liquid salt-induced inactivation and unfolding of cellulase from Trichoderma reesei. Green Chem 5(4):443. https://doi.org/10.1039/b302570e
Norgren M, Notley SM, Majtnerova A, Gellerstedt G (2006) Smooth model surfaces from lignin derivatives. i. Preparation and characterization. Langmuir 22:1209–1214. https://doi.org/10.1021/la052284c
Fawcett JK, Scott JE (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Path 13:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.13.2.156
Toyosawa Y, Ikeo M, Taneda D, Okino S (2017) Quantitative analysis of adsorption and desorption behavior of individual cellulase components during the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass with the addition of lysozyme. Bioresour Technol 234:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.132
Lu X, Zheng X, Li X, Zhao J (2016) Adsorption and mechanism of cellulase cellulases onto lignin isolated from corn Stover pretreated with liquid hot water. Biotechnol biofuels 9:118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0531-0
Yarbrough JM, Mittal A, Mansfield E, Taylor LE 2nd, Hobdey SE, Sammond DW, Bomble YJ, Crowley MF, Decker SR, Himmel ME, Vinzant TB (2015) New perspective on glycoside hydrolase binding to lignin from pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:214. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0397-6
Hui JP, Lanthier P, White TC, McHugh SG, Yaguchi M, Roy R, Thibault P (2001) Characterization of cellobiohydrolase I (Cel7A) glycoforms from extracts of Trichoderma reeseiusing capillary isoelectric focusing and electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 752:349–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00373-X
Rahikainen J, Mikander S, Marjamaa K, Tamminen T, Lappas A, Viikari L, Kruus K (2011) Inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis by residual lignins from softwood—study of enzyme binding and inactivation on lignin-rich surface. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(12):2823–2834. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23242
Ko JK, Ximenes E, Kim Y (2015) Adsorption of enzyme onto lignins of liquid hot water pretreated hardwoods. Biotechnol Bioeng 112(3):447–456. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25359/abstract
Rahikainen J (2013) Cellulase-lignin interactions in the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Dissertation, the university of Helsinki
Yang Z, Zhang C (2009) Adsorption/desorption behavior of protein on nanosized hydroxyapatite coatings: a quartz crystal microbalance study. Appl Surf Sci 255(8):4569–4574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.11.078
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21676109, 21376100), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (201707020025), and Guangdong Special Support Plan (2016TX03Z298).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, H., Lin, M., Zeng, M. et al. Effect of Urea on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Substrate and Its Mechanism. Bioenerg. Res. 11, 456–465 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-018-9910-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-018-9910-7