Abstract
Objective
Whole-body dynamic imaging using positron emission tomography (PET) facilitates the quantification of tracer kinetics. It is potentially valuable for the differential diagnosis of tumors and for the evaluation of therapeutic efficacy. In whole-body dynamic PET with continuous bed motion (CBM) (WBDCBM-PET), the pass number and bed velocity are key considerations. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the effect of a combination of pass number and bed velocity on the quantitative accuracy and quality of WBDCBM-PET images.
Methods
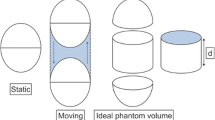
In this study, WBDCBM-PET imaging was performed at a body phantom using seven bed velocity settings in combination with pass numbers. The resulting image quality was evaluated. For comparing different acquisition settings, the dynamic index (DI) was obtained using the following formula: [P/S], where P represents the pass number, and S represents the bed velocity (mm/s). The following physical parameters were evaluated: noise equivalent count at phantom (NECphantom), percent background variability (N10 mm), percent contrast of the 10 mm hot sphere (QH, 10 mm), the QH, 10 mm/N10 mm ratio, and the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax). Furthermore, visual evaluation was performed.
Results
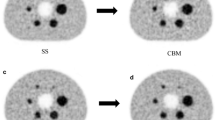
The NECphantom was equivalent for the same DI settings regardless of the bed velocity. The N10 mm exhibited an inverse correlation (r < − 0.89) with the DI. QH,10 mm was not affected by DI, and a correlation between QH,10 mm/N10 mm ratio and DI was found at all the velocities (r > 0.93). The SUVmax of the spheres was not influenced by the DI. The coefficient of variations caused by bed velocity decreased in larger spheres. There was no significant difference between the bed velocities on visual evaluation.
Conclusion
The quantitative accuracy and image quality achieved with WBDCBM-PET was comparable to that achieved with non-dynamic CBM, regardless of the pass number and bed velocity used during imaging for a given acquisition time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cutler PD, Xu M. Strategies to improve 3D whole-body PET image reconstruction. Phys Med Biol. 1996;41:1453–67.
Boellaard R, Oyen WJ, Hoekstra CJ, Hoekstra OS, Visser EP, Willemsen AT, et al. The Netherlands protocol for standardisation and quantification of FDG whole body PET studies in multi-centre trials. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:2320–33.
Daisaki H, Shinohara H, Terauchi T, Murano T, Shimada N, Moriyama N, et al. Multi-bed-position acquisition technique for deep inspiration breath-hold PET/CT: a preliminary result for pulmonary lesions. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:179–88.
McKeown C, Gillen G, Dempsey MF, Findlay C. Influence of slice overlap on positron emission tomography image quality. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61:1259–77.
Panin VY, Smith AM, Hu J, Kehren F, Casey ME. Continuous bed motion on clinical scanner: design, data correction, and reconstruction. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59:6153–74.
Acuff SN, Osborne D. Clinical workflow considerations for implementation of continuous-bed-motion PET/CT. J Nucl Med Technol. 2016;44:55–8.
Osborne DR, Acuff S, Cruise S, Syed M, Neveu M, Stuckey A, et al. Quantitative and qualitative comparison of continuous bed motion and traditional step and shoot PET/CT. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;5:56–64.
Owaki Y, Nakahara T, Shimizu T, Smith AM, Luk WK, Inoue K, et al. Effects of breathing motion on PET acquisitions: step and shoot versus continuous bed motion. Nucl Med Commun. 2018;39:665–71.
Schatka I, Weiberg D, Reichelt S, Owsianski-Hille N, Derlin T, Berding G, et al. A randomized, double-blind, crossover comparison of novel continuous bed motion versus traditional bed position whole-body PET/CT imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:711–7.
Rausch I, Cal-Gonzalez J, Dapra D, Gallowitsch HJ, Lind P, Beyer T, et al. Performance evaluation of the Biograph mCT Flow PET/CT system according to the NEMA NU2-2012 standard. EJNMMI Phys. 2015;2:26.
Yamashita S, Yamamoto H, Nakaichi T, Yoneyama T, Yokoyama K. Comparison of image quality between step-and-shoot and continuous bed motion techniques in whole-body (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with the same acquisition duration. Ann Nucl Med. 2017;31:686–95.
Karakatsanis NA, Lodge MA, Tahari AK, Zhou Y, Wahl RL, Rahmim A. Dynamic whole-body PET parametric imaging: I. Concept, acquisition protocol optimization and clinical application. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:7391–418.
Karakatsanis NA, Lodge MA, Zhou Y, Wahl RL, Rahmim A. Dynamic whole-body PET parametric imaging: II. Task-oriented statistical estimation. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:7419–45.
Zhu W, Li Q, Bai B, Conti PS, Leahy RM. Patlak image estimation from dual time-point list-mode PET data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014;33:913–24.
Houshmand S, Salavati A, Hess S, Werner TJ, Alavi A, Zaidi H. An update on novel quantitative techniques in the context of evolving whole-body PET imaging. PET Clin. 2015;10:45–58.
Karakatsanis NA, Casey ME, Lodge MA, Rahmim A, Zaidi H. Whole-body direct 4D parametric PET imaging employing nested generalized Patlak expectation-maximization reconstruction. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61:5456–85.
Palard-Novello X, Blin AL, Bourhis D, Garin E, Salaun PY, Devillers A, et al. Comparison of choline influx from dynamic (18)F-Choline PET/CT and clinicopathological parameters in prostate cancer initial assessment. Ann Nucl Med. 2018;32:281–7.
Taddio MF, Mu L, Keller C, Schibli R, Kramer SD. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling with dynamic PET data to study the in vivo effects of transporter inhibition on hepatobiliary clearance in mice. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018;2018:5849047.
Osborne DR, Acuff S. Whole-body dynamic imaging with continuous bed motion PET/CT. Nucl Med Commun. 2016;37:428–31.
Burger IA, Vargas HA, Apte A, Beattie BJ, Humm JL, Gonen M, et al. PET quantification with a histogram derived total activity metric: superior quantitative consistency compared to total lesion glycolysis with absolute or relative SUV thresholds in phantoms and lung cancer patients. Nucl Med Biol. 2014;41:410–8.
Boellaard R, Delgado-Bolton R, Oyen WJ, Giammarile F, Tatsch K, Eschner W, et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: version 2.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:328–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2961-x.
Maus J, Hofheinz F, Schramm G, Oehme L, Beuthien-Baumann B, Lukas M, et al. Evaluation of PET quantification accuracy in vivo. Comparison of measured FDG concentration in the bladder with urine samples. Nuklearmedizin. 2014;53:67–77.
Fukukita H, Suzuki K, Matsumoto K, Terauchi T, Daisaki H, Ikari Y, et al. Japanese guideline for the oncology FDG-PET/CT data acquisition protocol: synopsis of Version 2.0. Ann Nucl Med. 2014;28:693–705.
Strother SC, Casey ME, Hoffman EJ. Measuring PET scanner sensitivity: relating countrates to image signal-to-noise ratios using noise equivalents counts. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1990;37(2):783–788.
Akamatsu G, Ishikawa K, Mitsumoto K, Taniguchi T, Ohya N, Baba S, et al. Improvement in PET/CT image quality with a combination of point-spread function and time-of-flight in relation to reconstruction parameters. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1716–22.
Vandenberghe S, Mikhaylova E, D’Hoe E, Mollet P, Karp JS. Recent developments in time-of-flight PET. EJNMMI Phys. 2016;3:3.
Hashimoto N, Morita K, Tsutsui Y, Himuro K, Baba S, Sasaki M. Time-of-flight information improved the detectability of sub-centimeter sphere using clinical positron emission tomography/computed tomography scanner. J Nucl Med Technol. 2018;46:268–73.
Lee YS, Kim JS, Kim KM, Kang JH, Lim SM, Kim HJ. Performance measurement of PSF modeling reconstruction (True X) on Siemens Biograph TruePoint TrueV PET/CT. Ann Nucl Med. 2014;28:340–8.
Ashrafinia S, Mohy-Ud-Din H, Karakatsanis NA, Jha AK, Casey ME, Kadrmas DJ, et al. Generalized PSF modeling for optimized quantitation in PET imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2017;62:5149–79.
Rahmim A, Qi J, Sossi V. Resolution modeling in PET imaging: theory, practice, benefits, and pitfalls. Med Phys. 2013;40:064301.
Kidera D, Kihara K, Akamatsu G, Mikasa S, Taniguchi T, Tsutsui Y, et al. The edge artifact in the point-spread function-based PET reconstruction at different sphere-to-background ratios of radioactivity. Ann Nucl Med. 2016;30:97–103.
Acknowledgements
A part of this study was presented at the Annual Meeting of SNMMI in Philadelphia, USA, Jun 23, 2018. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, H., Takemoto, S., Maebatake, A. et al. Verification of image quality and quantification in whole-body positron emission tomography with continuous bed motion. Ann Nucl Med 33, 288–294 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-019-01334-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-019-01334-z