Abstract
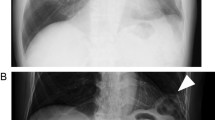
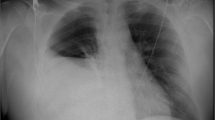
A 3-yr-old boy presented with respiratory distress of 2 days duration. There was a history of blunt trauma to the lower chest having occurred 5 days earlier. Although missed initially, serial chest X-rays and a computed tomographic (CT) scan revealed an isolated traumatic right-sided diaphragmatic hernia without any injury to the viscera or the ribcage. Laparotomy with reduction of the herniated right lobe of the liver and the transverse colon was performed. Recovery was uneventful. The presentation, diagnosis and management of this relatively uncommon injury is discussed. The need for a high index of suspicion and critical evaluation of appropriate investigations to prevent diagnostic delay and optimize management in patients with traumatic diaphragmatic injury is emphasized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers BF, McCabe CJ. Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia: Occult marker of serious injury. Am J surg 1993;218: 783–790.
Brandt ML, Luks FI, Spigland NA, DiLaorenzo M, Laberge JM, Ouimet A. Diaphragmatic injury in children. J Trauma 1992; 32: 298–301.
Karnak I, Senocak ME, Tanyel FC, Buyukpamuckcu N. Diaphragmatic injuries in children. Surgery Today 2001; 31: 5–11.
Soundappann SVS, Holland AJA, Cass DT, Farrow GB. Farrow. Blunt traumatic diaphragmatic injuries in children. Injury Int J Care Injured 2005; 36:51–54.
Ramos CT, Koplewitz BZ, Babyn PS, Manson PS, Ein SH. What we have learned about traumatic diaphragmatic hernias in children? J Pediatr Surg 2000; 35: 601–604.
Sola JE, Mattie P, Pegoli W, Paidas CN. Rupture of the right diaphragm following blunt trauma in an infant: case report. J Trauma 1994; 36: 417–420.
Eren S., Kantarci M, Okur A. Imaging of diaphragmatic rupture after trauma. Clinical Radiology 2006; 61: 467–477.
Killen KL, Mirvis SE, Shamuganathan K. Helical CT of diaphragmatic rupture caused by blunt trauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999; 173: 1611–1616.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, P., Kushwaha, A.S., Pant, N. et al. Isolated post-traumatic right-sided diaphragmatic hernia. Indian J Pediatr 76, 1167–1168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0282-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0282-z