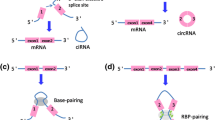
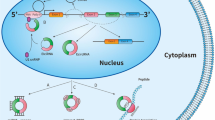
Abstract
Circular RNAs (CircRNAs) are a type of non-coding RNAs (NcRNAs) with a closed annular structure. Until next-generation sequencing (NGS) is developed, the misunderstanding of circRNAs ‘splicing error’ has changed, and the mysterious veil of circRNAs has been revealed. NGS provides an approach to investigate circRNAs. Many scholars point out that circRNAs may play an important role in many diseases, especially cancer. At the same time, exosomes, as a kind of extracellular vesicles loaded with many contents, are a hotspot in recent years. They can act as ‘messengers’ between cells, especially in cancer. Lately, it is interesting circRNAs are enriched and stable in exosomes, also called exo-circRNAs, and there have been several articles on circRNAs associated with exosomes. In this review, we summarize the characteristics of circRNAs, especially its main functions. Then, we briefly introduce exosomes and their function in cancer. Finally, the known relation between circRNAs and exosomes is discussed. With further researches, exo-circRNAs may be a novel pathway for cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73(11):3852–6.
Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976;8(4):547–55.
Kelly S, Greenman C, Cook PR, Papantonis A. Exon skipping is correlated with exon circularization. J Mol Biol. 2015;427(15):2414–7.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA (New York, NY). 2013;19(2):141–57.
Wilusz JE, Sharp PA. Molecular biology. A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science (New York, NY). 2013;340(6131):440–1.
Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(2):99–110.
Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PloS One. 2012;7(2):e30733.
Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee MC, Barrett SP, Hogan GJ, Olsen MN, et al. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PloS One. 2014;9(6):e90859.
Danan M, Schwartz S, Edelheit S, Sorek R. Transcriptome-wide discovery of circular RNAs in Archaea. Nucl Acids Res. 2012;40(7):3131–42.
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015;25(8):981–4.
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159(1):134–47.
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(9):e1003777.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441):333–8.
Hansen TB, Kjems J, Damgaard CK. Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(18):5609–12.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384–8.
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3):353–8.
Zhou B, Yu JW. A novel identified circular RNA, circRNA_010567, promotes myocardial fibrosis via suppressing miR-141 by targeting TGF-beta1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;487(4):769–75.
Tang CM, Zhang M, Huang L, Hu ZQ, Zhu JN, Xiao Z, et al. CircRNA_000203 enhances the expression of fibrosis-associated genes by derepressing targets of miR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in cardiac fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40342.
Xue J, Liu Y, Luo F, Lu X, Xu H, Liu X, et al. Circ100284, via miR-217 regulation of EZH2, is involved in the arsenite-accelerated cell cycle of human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1863(3):753–63.
Xu L, Zhang M, Zheng X, Yi P, Lan C, Xu M. The circular RNA ciRS-7 (Cdr1as) acts as a risk factor of hepatic microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017;143(1):17–27.
Zhao Y, Alexandrov PN, Jaber V, Lukiw WJ. Deficiency in the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2A in alzheimer’s disease (AD) is linked to deficits in a natural circular miRNA-7 sponge (circRNA; ciRS-7). Genes. 2016;7(12):116.
Xu H, Guo S, Li W, Yu P. The circular RNA Cdr1as, via miR-7 and its targets, regulates insulin transcription and secretion in islet cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12453.
Peng L, Chen G, Zhu Z, Shen Z, Du C, Zang R, et al. Circular RNA ZNF609 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate AKT3 expression by sponging miR-150-5p in Hirschsprung’s disease. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):808–18.
Chen L, Zhang S, Wu J, Cui J, Zhong L, Zeng L et al. circRNA_100290 plays a role in oral cancer by functioning as a sponge of the miR-29 family. Oncogene. 2017;36(32):4551–61.
Zhong Z, Lv M, Chen J. Screening differential circular RNA expression profiles reveals the regulatory role of circTCF25-miR-103a-3p/miR-107-CDK6 pathway in bladder carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30919.
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen B, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nature Commun. 2016;7:11215.
Xie H, Ren X, Xin S, Lan X, Lu G, Lin Y, et al. Emerging roles of circRNA_001569 targeting miR-145 in the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(18):26680–91.
Wang K, Long B, Liu F, Wang JX, Liu CY, Zhao B, et al. A circular RNA protects the heart from pathological hypertrophy and heart failure by targeting miR-223. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(33):2602–11.
Chen J, Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, He J, Chen B, et al. Circular RNA profile identifies circPVT1 as a proliferative factor and prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:208–19.
Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, Dai L, Fu X, Zhang J, et al. Circular RNA related to the chondrocyte ECM regulates MMP13 expression by functioning as a miR-136 ‘Sponge’ in human cartilage degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572.
Zhang C, Wu H, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Fang X, Chen C, et al. Expression patterns of circular RNAs from primary kinase transcripts in the mammary glands of lactating rats. J Breast Cancer. 2015;18(3):235–41.
Liu YC, Li JR, Sun CH, Andrews E, Chao RF, Lin FM, et al. CircNet: a database of circular RNAs derived from transcriptome sequencing data. Nucl Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D209–15.
Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y, et al. Circular RNA MTO1 acts as the sponge of miR-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology 2017;66(4):1151–64.
Wang K, Gan TY, Li N, Liu CY, Zhou LY, Gao JN, et al. Circular RNA mediates cardiomyocyte death via miRNA-dependent upregulation of MTP18 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24(6):1111–20.
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang X, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nature Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256–64.
Conn VM, Hugouvieux V, Nayak A, Conos SA, Capovilla G, Cildir G, et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nature Plants. 2017;3:17053.
Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nature Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):453–61.
Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xiang JF, Yin QF, Xing YH, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51(6):792–806.
Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular rna that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell. 2017;66(1):22–37.e9.
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell. 2017;66(1):9–21.
Whiteside TL. Tumor-derived exosomes and their role in tumor-induced immune suppression. Vaccines. 2016;4(4):35.
Soung YH, Ford S, Zhang V, Chung J. Exosomes in cancer diagnostics. Cancers. 2017;9(1):8.
Wang J, Deng Z, Wang Z, Wu J, Gu T, Jiang Y, et al. MicroRNA-155 in exosomes secreted from helicobacter pylori infection macrophages immunomodulates inflammatory response. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(9):3700–9.
Hao YX, Li YM, Ye M, Guo YY, Li QW, Peng XM, et al. KRAS and BRAF mutations in serum exosomes from patients with colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(5):3608–16.
Sinha A, Alfaro J, Kislinger T. Characterization of protein content present in exosomes isolated from conditioned media and urine. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2017;87:24.9.1–9.12.
Zheng X, Chen F, Zhang Q, Liu Y, You P, Sun S et al. Salivary exosomal PSMA7: a promising biomarker of inflammatory bowel disease. Protein Cell. 2017;8(9):686–95.
Kong FL, Wang XP, Li YN, Wang HX. The role of exosomes derived from cerebrospinal fluid of spinal cord injury in neuron proliferation in vitro. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(1):200–5.
Kosaka N, Izumi H, Sekine K, Ochiya T. microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk. Silence. 2010;1(1):7.
Koga Y, Yasunaga M, Moriya Y, Akasu T, Fujita S, Yamamoto S, et al. Exosomes can prevent RNase from degrading microRNA in feces. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011;2(4):215–22.
Gopal SK, Greening DW, Rai A, Chen M, Xu R, Shafiq A, et al. Extracellular vesicles: their role in cancer biology and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem J. 2017;474(1):21–45.
Rahman MA, Barger JF, Lovat F, Gao M, Otterson GA, Nana-Sinkam P. Lung cancer exosomes as drivers of epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 2016;7(34):54852–66.
Dhondt B, Rousseau Q, De Wever O, Hendrix A. Function of extracellular vesicles-associated miRNAs in metastasis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365(3):621–41.
Le MT, Hamar P, Guo C, Basar E, Perdigao-Henriques R, Balaj L, et al. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J Clin Investig. 2014;124(12):5109–28.
Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, Somlo G, Liu L, Palomares MR, et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(4):501–15.
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY, Chandra M, Ashby J, et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nature Cell Biol. 2015;17(2):183–94.
Bobrie A, Thery C. Exosomes and communication between tumours and the immune system: are all exosomes equal? Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):263–7.
Bu N, Wu H, Zhang G, Zhan S, Zhang R, Sun H, et al. Exosomes from dendritic cells loaded with chaperone-rich cell lysates elicit a potent T cell immune response against intracranial glioma in mice. J Mol Neurosci MN. 2015;56(3):631–43.
Marton A, Vizler C, Kusz E, Temesfoi V, Szathmary Z, Nagy K, et al. Melanoma cell-derived exosomes alter macrophage and dendritic cell functions in vitro. Immunol Lett. 2012;148(1):34–8.
Jia Y, Chen Y, Wang Q, Jayasinghe U, Luo X, Wei Q, et al. Exosomes: emerging biomarker in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(25):41717–33.
Eichelser C, Stuckrath I, Muller V, Milde-Langosch K, Wikman H, Pantel K, et al. Increased serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2014;5(20):9650–63.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21.
Choi PW, Ng S. The functions of MicroRNA-200 family in ovarian cancer: beyond epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6):1207.
Tang MK, Wong AS. Exosomes: emerging biomarkers and targets for ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;367(1):26–33.
Rabinowits G, Gercel-Taylor C, Day JM, Taylor DD, Kloecker GH. Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10(1):42–6.
Sun Y, Li L, Liu J, Wang L. Body fluids-derived exosomes: paving the novel road to lung cancer diagnosis and therapy. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(13):1734–40.
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M, Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN, et al. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(9):1156–62.
Rolfo C, Castiglia M, Hong D, Alessandro R, Mertens I, Baggerman G, et al. Liquid biopsies in lung cancer: the new ambrosia of researchers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846(2):539–46.
Ye SB, Li ZL, Luo DH, Huang BJ, Chen YS, Zhang XS, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes promote tumor progression and T-cell dysfunction through the regulation of enriched exosomal microRNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5(14):5439–52.
Tanaka Y, Kamohara H, Kinoshita K, Kurashige J, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M, et al. Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2013;119(6):1159–67.
Takeshita N, Hoshino I, Mori M, Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Yoneyama Y, et al. Serum microRNA expression profile: miR-1246 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(3):644–52.
Que R, Ding G, Chen J. Cao L Analysis of serum exosomal microRNAs and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:219.
Liu J, Sun H, Wang X, Yu Q, Li S, Yu X, et al. Increased exosomal microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a levels in the cervicovaginal lavage specimens of patients with cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(1):758–73.
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K, et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PloS One. 2014;9(4):e92921.
Roth P, Wischhusen J, Happold C, Chandran PA, Hofer S, Eisele G, et al. A specific miRNA signature in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. J Neurochem. 2011;118(3):449–57.
Manterola L, Guruceaga E, Gallego Perez-Larraya J, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Jauregui P, Tejada S, et al. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro-oncology. 2014;16(4):520–7.
Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs co-precipitate with extracellular vesicles: a possible mechanism for circRNA clearance. PloS One. 2016;11(2):e0148407.
Alhasan AA. Izuogu OG Circular RNA enrichment in platelets is a signature of transcriptome degradation. Blood. 2016;127(9):e1–11.
Dou Y, Cha DJ, Franklin JL, Higginbotham JN, Jeppesen DK, Weaver AM, et al. Circular RNAs are down-regulated in KRAS mutant colon cancer cells and can be transferred to exosomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37982.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of our laboratory for support and advice. Jun-chen Hou and Wen Jiang contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Program on Key Research Project (No. 2016YFC0905900), Medical Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by Jiangsu Provincial Department of health (No. 17 [2016]), the 333 Talent Project of Jiangsu Province, top-level (No. 4 [2016]), the National key clinical specialist construction Programs of China (No. 544 [2013]), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20151579), A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD, JX10231802), the Key Research Program for the Social Development of Jiangsu Province, China (BE2015718) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81602551).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
There are no human and animal in this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Jiang, W., Zhu, L. et al. Circular RNAs and exosomes in cancer: a mysterious connection. Clin Transl Oncol 20, 1109–1116 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-018-1839-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-018-1839-y