Abstract
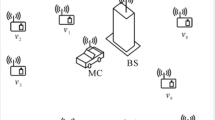
Recent advancement in wireless charging technologies has enabled us to design and development of Wireless Rechargeable Sensor Networks (WRSNs) for sensing and data gathering tasks for a very long duration. The fundamental research challenge in WRSN is to design efficient path scheduling for Mobile Wireless Charging Vehicles (MWCVs) such that it maximizes utility of energy resource of MWCVs and minimizes average delay in charging process of the network. Most of the existing solutions for path scheduling of MWCVs suffer from high charging latency,poor energy usage efficiency, and low scalability issues. In order to overcome these issues, this research paper proposed a novel algorithm for scheduling of multiple mobile rechargers using Hybrid meta-heuristic technique. In the proposed Hybrid meta-heuristic-based algorithm, best features of Cuckoo Search and Genetic Algorithm are combined to optimize the path scheduling problem. This work derives a novel fitness function for optimizing the performance of the scheduling. To show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, an extensive simulation experiments are performed under different network scenarios and results are compared with the latest state-of-art schemes. Result analysis confirms advantages of the proposed scheme in terms of charging latency, total travel distance and energy usage efficiency.













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-021-01090-w
References
Kurs A, Karalis A, Moffatt R, Joannopoulos J, Fisher P, Soljacic M (2007) Wireless power transfer via strongly coupled magnetic resonances. Science 317(5834):83–86. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1143254
Lu X, Wang P, Niyato D, Kim D, Han Z (2016) Wireless charging technologies: fundamentals, standards, and network applications. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 18(2):1413–1452. https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2015.2499783
Akan O, Cetinkaya O, Koca C, Ozger M (2018) Internet of hybrid energy harvesting things. IEEE Internet Things J 5(2):736–746. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2017.2742663
Tong B, Wang G, Zhang W, Wang C (2011) Node reclamation and replacement for long-lived sensor networks. IEEE Transactions On Parallel And Distributed Systems 22(9):1550–1563. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpds.2011.25
Liang W, Ren X, Jia X, Xu X (2013) Monitoring quality maximization through fair rate allocation in harvesting sensor networks. IEEE Transactions On Parallel And Distributed Systems 24(9):1827–1840. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpds.2013.136
Jonah O, Georgakopoulos S (2013) Wireless power transfer in concrete via strongly coupled magnetic resonance. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 61(3):1378–1384. https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2012.2227924
Ma Y, Liang W, Xu W (2018) Charging utility maximization in wireless rechargeable sensor networks by charging multiple sensors simultaneously. IEEE/ACM Trans Networking 26(4):1591–1604. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnet.2018.2841420
He L, Zhuang Y, Pan J, Xu J (2010) Evaluating on-demand data collection with mobile elements in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE 72nd Vehicular Technology Conference - Fall, Ottawa, ON, 2010, pp. 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1109/VETECF.2010.5594515
He L, Kong L, Gu Y, Pan J, Zhu T (2015) Evaluating the on-demand Mobile charging in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 14(9):1861–1875. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmc.2014.2368557
Shi Y, Xie L, Hou YT, Sherali HD (2011) On renewable sensor networks with wireless energy transfer. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 1350–1358
Peng Y, Li Z, Zhang W, Qiao D (2010) Prolonging sensor network lifetime through wireless charging. In: Proc. IEEE Real-Time Syst. Symp., Nov. 2010, pp. 129–139
Guo S, Wang C, Yang Y (2013) Mobile data gathering with wireless energy replenishment in rechargeable sensor networks. In: Proc. IEEE Int.Conf. Comput. Commun., Apr. 2013, pp. 1932–1940
Tomar A, Jana PK (2017) Designing energy efficient traveling paths for multiple mobile chargers in wireless rechargeable sensor networks. In: Proc. 10th Int. Conf. Contemp. Comput. (IC3), Aug. 2017, pp. 1–6
Kaswan A, Tomar A, Jana PK (2018) An efficient scheduling scheme for mobile charger in on-demand wireless rechargeable sensor networks. J Netw Comput Appl 114(15):123–134
Xu W, Liang W, Jia X, Xu Z, Li Z, Liu Y (2018) Maximizing sensor lifetime with the minimal service cost of a mobile charger in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 17(11):2564–2577
Lin C, Wei S, Deng J, Obaidat MS, Song H, Wang L, Wu G (2018) GTCCS: a game theoretical collaborative charging scheduling for on demand charging architecture. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(12):12124–12136
Lyu Z, Wei Z, Pan J, Chen H, Xia C, Han J, Shi L (2019) Periodic charging planning for a mobile WCE in wireless rechargeable sensor networks based on hybrid PSO and GA algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 75(1):388–403
Liu K, Peng J, He L, Pan J, Li S, Ling M, Huang Z (2019) An active mobile charging and data collection scheme for clustered sensor networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(5):5100–5113
Lyu Z, Wei Z, Lu Y, Wang X, Li M, Xia C, Han J (2019) Multi-node charging planning algorithm with an energy-limited WCE in WRSNs. IEEE Access 7:47154–47170
Tomar A, Muduli L, Jana PK (2019) An efficient scheduling scheme for on-demand mobile charging in wireless rechargeable sensor networks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, Volume 59, 101074, ISSN 1574-1192
He S, Chen J, Jiang F, Yau DKY, Xing G, Sun Y (2013) Energy provisioning in wireless rechargeable sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 12(10):1931–1942
Shu Y, Yousefi H, Cheng P, Chen J, Gu YJ, He T, Shin KG (2016) Near-optimal velocity control for mobile charging in wireless rechargeable sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 15(7):1699–1713
Hoang DC, Kumar R, Panda SK (2010) Fuzzy C-means clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, pp. 3477–3482, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIE.2010.5637779
Gupta GP, Jha S (2018) Integrated clustering and routing protocol for wireless sensor networks using Cuckoo and Harmony Search based metaheuristic techniques. Eng Appl Artif Intell 68:101–109
Valian E, Valian, E (2012) A cuckoo search algorithm by Lévy flights for solving reliability redundancy allocation problems, Eng Optim, 1–14
Yang X-S, Deb S (2013) Cuckoo search: recent advances and applications,” Neural Comput & Applic, 1–6
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Seed research Grant Project (NITRR/Seed Grant/2016-17/21) by the NIT, Raipur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chawra, V.K., Gupta, G.P. Hybrid meta-heuristic techniques based efficient charging scheduling scheme for multiple Mobile wireless chargers based wireless rechargeable sensor networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 1303–1315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-01052-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-01052-8