Abstract
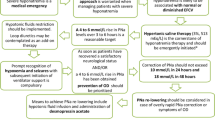
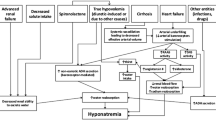
Hypervolemic (dilutional) hyponatremia is the most common dysnatremia in cirrhosis, with a prevalence close to 50% in patients with ascites, while hypovolemic hyponatremia occurs in a minority of cases. Hyponatremia carries a poor prognosis, being associated with increased mortality and reduced survival after liver transplantation. Hypernatremia is rarer and is also associated with an adverse prognosis. Increased non-osmotic secretion of arginine vasopressin and altered renal tubular sodium handling due to impaired free water generation are the mechanisms leading to hypervolemic hyponatremia, while diuretic-induced fluid loss is the main cause of hypovolemic hyponatremia. Hypernatremia usually follows hypotonic fluid losses due to osmotic diuresis (glycosuria) or lactulose-induced diarrhea. The main clinical manifestations of dysnatremias are due to their effects on the central nervous system: astroglial cell hyperhydration follows hyponatremia—an abnormality that exacerbates ammonia neurotoxicity—while the opposite abnormality occurs with hypernatremia. Asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic hypervolemic hyponatremia is mainly managed by correcting of precipitating factors and non-osmotic fluid restriction. Severe, life-threatening hyponatremia requires hypertonic saline infusion, avoiding rapid and complete correction of serum sodium concentration to prevent neurological sequelae such as osmotic demyelination. V2 receptor blockade by vaptans may be considered in patients with sustained hyponatremia waitlisted for liver transplantation. Diuretic withdrawal and plasma volume expansion are required in hypovolemic hypernatremia. Prompt recognition, removal of the precipitating factor(s) and non-osmotic fluid administration represent the mainstays of hypernatremia management. Rapid correction of long-standing hypernatremia can lead to cerebral edema and has to be avoided.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berl T, Schrier RW. Disorders of water metabolism. In: Schrier RW, editor. Renal and electrolyte disorders. 5th ed. Boston: Lippincott-Raven; 1997. p. 1–71.
Bichet DG. Posterior pituitary. In: Melmed S, editor. The pituitary. 1st ed. Cambridge: Blackwell Scientific; 1995. p. 277–306.
Oliet SH, Bourque CW. Mechano-sensitive channels transduce osmosensitivity in supraoptic neurons. Nature. 1993;364:341–3.
Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH, Agre P, Knepper MA. Aquaporins in the kidney: from molecules to medicine. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:205–44.
Jung JS, Bhat RV, Preston GM, Guggino WB, Baraban JM, Agre P. Molecular characterisation of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:13052–6.
Verbalis JG. Disorders of body water homeostasis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;17:471–503.
Schrier RW, Berl T, Anderson RJ. Osmotic and nonosmotic control of vasopressin release. Am J Physiol. 1979;236:F321–32.
Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Hypernatremia. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1493–9.
Sterns RH. Disorders of plasma sodium–causes, consequences, and correction. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:55–65.
Ginés P, Berl T, Bernardi M, Bichet DG, Hamon G, Jiménez W, Liard JF, Martin PY, Schrier RW. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: from pathogenesis to treatment. Hepatology. 1998;28:851–64.
Angeli P, Wong F, Watson H, Gines P. CAPPS Investigators. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: results of a patient population survey. Hepatology. 2006;44:1535–42.
Ginès P, Guevara M. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: pathogenesis, clinical significance, and management. Hepatology. 2008;48:1002–10.
Wang P, Huang G, Tam N, Wu C, Fu S, Hughes BP, Wu L, He X. Influence of preoperative sodium concentration on outcome of patients with hepatitis B virus cirrhosis after liver transplantation. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;28:1210–5.
Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, Epstein M, Henriksen JH, Rodés J. Peripheral vasodilation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988;8:1151–7.
Bernardi M, Moreau R, Angeli P, Schnabl B, Arroyo V. Mechanisms of decompensation and organ failure in cirrhosis: from peripheral arterial vasodilation to systemic inflammation hypothesis. J Hepatol. 2015;63:1272–84.
Murugan R, Karajala-Subramanyam V, Lee M, Yende S, Kong L, Carter M, Angus DC, Kellum JA, Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Investigators. Acute kidney injury in on-severe pneumonia is associated with an increased immune response and lower survival. Kidney Int. 2010;77:527–35.
Gomez H, Ince C, De Backer D, Pickkers P, Payen D, Hotchkiss J, Kellum JA. A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury. Shock. 2014;41:3–11.
Bichet D, Szatalowicz V, Chaimovitz C, Schrier RW. Role of vasopressin in abnormal water excretion in cirrhotic humans. Ann Intern Med. 1982;96:413–6.
Bichet DG, Groves BM, Schrier RW. Mechanisms of improvement of water and sodium excretion by immersion in decompensated cirrhotic patients. Kidney Int. 1983;24:788–94.
Schedl HP, Bartter FC. An explanation for and experimental correction of the abnormal water diuresis in cirrhosis. J Clin Investig. 1960;39:248–61.
Sarafidis PA, Georgianos PI, Lasaridis AN. Diuretics in clinical practice. Part I: mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects and clinical indications of diuretic compounds. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2010;9:243–57.
Warren SE, Mitas JA 2nd, Swerdlin AH. Hypernatremia in hepatic failure. JAMA. 1980;243:1257–60.
Nelson DC, McGrew WR Jr, Hoyumpa AM Jr. Hypernatremia and lactulose therapy. JAMA. 1983;249:1295–8.
Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1581–9.
Córdoba J, García-Martinez R, Simón-Talero M. Hyponatremic and hepatic encephalopathies: similarities, differences and coexistence. Metab Brain Dis. 2010;25:73–80.
Córdoba J, Mìnguez B. Hepatic encephalopathy. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:70–80.
Häussinger D. Low grade cerebral edema and the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2006;43:1187–90.
Restuccia T, Gómez-Ansón B, Guevara M, Alessandria C, Torre A, Alayrach ME, Terra C, Martín M, Castellví M, Rami L, Sainz A, Ginès P, Arroyo V. Effects of dilutional hyponatremia on brain organic osmolytes and water content in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2004;39:1613–22.
Heins J, Zwingmann C. Organic osmolytes in hyponatremia and ammonia toxicity. Metab Brain Dis. 2010;25:81–9.
Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Pettenò E, Mapelli D, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, Muraca M, Musto C, Gerunda G, Rizzo C, Merkel C, Gatta A. Prevalence and prognostic value of quantified electroencephalogram (EEG) alterations in cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol. 2001;35:37–45.
Ginès A, Escorsell A, Ginès P, Saló J, Jiménez W, Inglada L, Navasa M, Clària J, Rimola A, Arroyo V, Rodès J. Incidence, predictive factors, and prognosis of the hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis with ascites. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:229–36.
Guevara M, Baccaro ME, Torre A, Gómez-Ansón B, Ríos J, Torres F, Rami L, Monté-Rubio GC, Martín-Llahí M, Arroyo V, Ginès P. Hyponatremia is a risk factor of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a prospective study with time-dependent analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1382–9.
Sersté T, Gustot T, Rautou PE, Francoz C, Njimi H, Durand F, Valla D, Lebrec D, Moreau R. Severe hyponatremia is a better predictor of mortality than MELDNa in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. J Hepatol. 2012;57:274–80.
Londoño MC, Cárdenas A, Guevara M, Quintó L, de Las Heras D, Navasa M, Rimola A, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Arroyo V, Ginès P. MELD score and serum sodium in the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. Gut. 2007;56:1283–9120.
Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, Wiesner RH, Kamath PS, Benson JT, Edwards E, Therneau TM. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1018–26.
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, D’Amico G, Dickson ER, Kim WR. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464–70.
Biggins SW, Kim WR, Terrault NA, Saab S, Balan V, Schiano T, Benson J, Therneau T, Kremers W, Wiesner R, Kamath P, Klintmalm G. Evidence-based incorporation of serum sodium concentration into MELD. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1652–60.
Yun BC, Kim WR, Benson JT, Biggins SW, Therneau TM, Kremers WK, Rosen CB, Klintmalm GB. Impact of pretransplant hyponatremia on outcome following liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2009;49:1610–5.
Abbasoglu O, Goldstein RM, Vodapally MS, Jennings LW, Levy MF, Husberg BS, Klintmalm GB. Liver transplantation in hyponatremic patients with emphasis on central pontine myelinolysis. Clin Transpl. 1998;12:263–9.
Londoño MC, Guevara M, Rimola A, Navasa M, Taurà P, Mas A, García-Valdecasas JC, Arroyo V, Ginès P. Hyponatremia impairs early post-transplantation outcome in patients with cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1135–43.
Neeff H, Mariaskin D, Spangenberg HC, Hopt UT, Makowiec F. Perioperative mortality after non-hepatic general surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis: an analysis of 138 operations in the 2000s using Child and MELD scores. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:1–11.
Neeff HP, Streule GC, Drognitz O, Tittelbach-Helmrich D, Spangenberg HC, Hopt UT, Makowiec F. Early mortality and long-term survival after abdominal surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis. Surgery. 2014;155:623–32.
Salerno F, Cammà C, Enea M, Rössle M, Wong F. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for refractory ascites: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:825–34.
Pockros PJ, Reynolds TB. Rapid diuresis in patients with ascites from chronic liver disease: the importance of peripheral edema. Gastroenterology. 1986;90:1827–33.
Saló J, Ginès A, Ginès P, Piera C, Jiménez W, Guevara M, Fernández-Esparrach G, Sort P, Bataller R, Arroyo V, Rodès J. Effect of therapeutic paracentesis on plasma volume and transvascular escape rate of albumin in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1997;27:645–53.
Ruiz-del-Arbol L, Monescillo A, Jimenéz W, Garcia-Plaza A, Arroyo V, Rodés J. Paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction: mechanism and effect on hepatic hemodynamics in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:579–86.
Ginès A, Fernández-Esparrach G, Monescillo A, Vila C, Domènech E, Abecasis R, Angeli P, Ruiz-Del-Arbol L, Planas R, Solà R, Ginès P, Terg R, Inglada L, Vaqué P, Salerno F, Vargas V, Clemente G, Quer JC, Jiménez W, Arroyo V, Rodés J. Randomized trial comparing albumin, dextran 70, and polygeline in cirrhotic patients with ascites treated by paracentesis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1002–10.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69:406–60.
Bernardi M, Caraceni P, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Albumin infusion in patient undergoing large-volume paracentesis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2012;55:172–81.
Jalan R, Fernandez J, Wiest R, Schnabl B, Moreau R, Angeli P, Stadlbauer V, Gustot T, Bernardi M, Canton R, Albillos A, Lammert F, Wilmer A, Mookerjee R, Vila J, Garcia-Martinez R, Wendon J, Such J, Cordoba J, Sanyal A, Garcia-Tsao G, Arroyo V, Burroughs A, Ginès P. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: a position statement based on the EASL special conference 2013. J Hepatol. 2014;60:1310–24.
Follo A, Llovet JM, Navasa M, Planas R, Forns X, Francitorra A, Rimola A, Gassull MA, Arroyo V, Rodès J. Renal impairment after spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: incidence, clinical course, predictive factors and prognosis. Hepatology. 1994;20:1495–501.
Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, Aldeguer X, Planas R, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, Castells L, Vargas V, Soriano G, Guevara M, Ginès P, Rodés J. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:403–9.
Guevara M, Terra C, Nazar A, Solà E, Fernández J, Pavesi M, Arroyo V, Ginès P. Albumin for bacterial infections other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. A randomized, controlled study. J Hepatol. 2012;57:759–65.
Thévenot T, Bureau C, Oberti F, Anty R, Louvet A, Plessier A, Rudler M, Heurgué-Berlot A, Rosa I, Talbodec N, Dao T, Ozenne V, Carbonell N, Causse X, Goria O, Minello A, De Ledinghen V, Amathieu R, Barraud H, Nguyen-Khac E, Becker C, Paupard T, Botta-Fridlung D, Abdelli N, Guillemot F, Monnet E, Di Martino V. Effect of albumin in cirrhotic patients with infection other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A randomized trial. J Hepatol. 2015;62:822–30.
Sanyal AJ, Boyer T, Garcia-Tsao G, Regenstein F, Rossaro L, Appenrodt B, Blei A, Gilber V, Sigal S, Teuber P, Terlipressin Study Group. A randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of terlipressin for type 1 hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1360–8.
Martín-Llahí M, Pépin MN, Guevara M, Díaz F, Torre A, Monescillo A, Soriano G, Terra C, Fábrega E, Arroyo V, Rodés J, Ginès P, TAHRS Investigators. Terlipressin and albumin vs albumin in patients with cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome: a randomized study. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1352–9.
Prakoso E, Jones C, Koorey DJ, Strasser SI, Bowen D, McCaughan GW, Shackel NA. Terlipressin therapy for moderate-to-severe hyponatraemia in patients with liver failure. Intern Med J. 2013;43:240–6.
Caraceni P, Riggio O, Angeli P, Alessandria C, Neri S, Foschi FG, Levantesi F, Airoldi A, Boccia S, Svegliati-Baroni G, Fagiuoli S, Romanelli RG, Cozzolongo R, Di Marco V, Sangiovanni V, Morisco F, Toniutto P, Tortora A, De Marco R, Angelico M, Cacciola I, Elia G, Federico A, Massironi S, Guarisco R, Galioto A, Ballardini G, Rendina M, Nardelli S, Piano S, Elia C, Prestianni L, Cappa FM, Cesarini L, Simone L, Pasquale C, Cavallin M, Andrealli A, Fidone F, Ruggeri M, Roncadori A, Baldassarre M, Tufoni M, Zaccherini G, Bernardi M, ANSWER Study Investigators. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2417–29.
Yunos NM, Bellomo R, Hegarty C, Story D, Ho L, Bailey M. Association between a chloride-liberal vs chloride-restrictive intravenous fluid administration strategy and kidney injury in critically ill adults. JAMA. 2012;308:1566–72.
Semler MW, Self WH, Wanderer JP, Ehrenfeld JM, Wang L, Byrne DW, Stollings JL, Kumar AB, Hughes CG, Hernandez A, Guillamondegui OD, May AK, Weavind L, Casey JD, Siew ED, Shaw AD, Bernard GR, Rice TW, SMART Investigators and the Pragmatic Critical Care Research Group. Balanced crystalloids versus saline in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:829–39.
McCormick PA, Mistry P, Kaye G, Burroughs AK, McIntyre N. Intravenous albumin infusion is an effective therapy for hyponatraemia in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Gut. 1990;31:204–7.
Spasovski G, Vanholder R, Allolio B, Annane D, Ball S, Bichet D, Decaux G, Fenske W, Hoorn EJ, Ichai C, Joannidis M, Soupart A, Zietse R, Haller M, van der Veer S, Van Biesen W, Nagler E. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:320–31.
Holtkamp M, Othman J, Buchheim K, Meierkord H. Predictors and prognosis of refractory status epilepticus treated in a neurological intensive care unit. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:534–9.
Cagnin A, Taylor-Robinson SD, Forton DM, Banati RB. In vivo imaging of cerebral “peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites” in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 2006;55:547–53.
Butterworth RF. The astrocytic (“peripheral-type”) benzodiazepine receptor: role in the pathogenesis of portal-systemic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int. 2000;36:411–6.
Rössle M, Gerbes AL. TIPS for the treatment of refractory ascites, hepatorenal syndrome and hepatic hydrothorax: a critical update. Gut. 2010;59:988–1000.
Cardenas A, Ginès P, Marotta P, Czerwiec F, Oyuang J, Guevara M, Afdhal NH. Tolvaptan, an oral vasopressin antagonist, in the treatment of hyponatremia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012;56:571–8.
Ginès P, Wong F, Watson H, Milutinovic S, del Arbol LR, Olteanu D, HypoCAT Study Investigators. Effects of satavaptan, a selective vasopressin V(2) receptor antagonist, on ascites and serum sodium in cirrhosis with hyponatremia: a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2008;48:204–13.
Gerbes AL, Gülberg V, Ginès P, Decaux G, Gross P, Gandjini H, Djian J, VPA Study Group. Therapy of hyponatremia in cirrhosis with a vasopressin receptor antagonist: a randomized double-blind multicenter trial. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:933–9.
O’Leary JG, Favis G. Conivaptan increases serum sodium in hyponatremic patients with end stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2009;15:1325–9.
Jia JD, Xie W, Ding HG, Mao H, Guo H, Li Y, Wang X, Wang JF, Lu W, Li CZ, Mao Y, Wang GQ, Gao YQ, Wang B, Zhang Q, Ge Y, Wong VW. Utility and safety of tolvaptan in cirrhotic patients with hyponatremia: a prospective cohort study. Ann Hepatol. 2017;16:123–32.
Ahluwalia V, Heuman DM, Feldman G, Wade JB, Thacker LR, Gavis E, Gilles H, Unser A, White MB, Bajaj JS. Correction of hyponatraemia improves cognition, quality of life, and brain oedema in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2015;62:75–82.
Yan L, Xie F, Lu J, Ni Q, Shi C, Tang C, Yang J. The treatment of vasopressin V2-receptor antagonists in cirrhosis patients with ascites: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015;15:65.
Wong F, Gines P, Watson H, Horsmans Y, Angeli P, Gow P, Minini P, Bernardi M. Effects of a selective vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist, satavaptan, on ascites recurrence after paracentesis in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2010;53:283–90.
Wong F, Watson H, Gerbes A, Vilstrup H, Badalamenti S, Bernardi M, Ginès P, Satavaptan Investigators Group. Satavaptan for the management of ascites in cirrhosis: efficacy and safety across the spectrum of ascites severity. Gut. 2012;61:108–16.
Kogiso T, Tokushige K, Hashimoto E, Ikarashi Y, Kodama K, Taniai M, Torii N, Shiratori K. Safety and efficacy of long-term tolvaptan therapy for decompensated liver cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 2016;46:E194–200.
Uojima H, Hidaka H, Nakayama T, Sung JH, Ichita C, Tokoro S, Masuda S, Sasaki A, Koizumi K, Egashira H, Kako M. Efficacy of combination therapy with natriuretic and aquaretic drugs in cirrhotic ascites patients: a randomized study. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:8062–72.
Hiramine Y, Uto H, Imamura Y, Hiwaki T, Kure T, Ijuin S, Oda K, Mawatari S, Kumagai K, Tokunaga K, Higashi H, Kanetsuki I, Kubozono O, Maenohara S, Ido A. Efficacy of vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist tolvaptan in treatment of hepatic edema. Hepatol Res. 2017;47:542–57.
Tajiri K, Tokimitsu Y, Ito H, Atarashi Y, Kawai K, Minemura M, Yasumura S, Takahara T, Shimizu Y, Sugiyama T. Survival benefit of Tolvaptan for refractory ascites in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Dig Sci. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489258.
Pose E, Solà E, Piano S, Gola E, Graupera I, Guevara M, Cárdenas A, Angeli P, Ginés P. Limited efficacy of tolvaptan in patients with cirrhosis and severe hyponatremia: real-life experience. Am J Med. 2017;130:372–5.
Chishina H, Hagiwara S, Nishida N, Ueshima K, Sakurai T, Ida H, Minami Y, Takita M, Kono M, Minami T, Iwanishi M, Umehara Y, Watanabe T, Komeda Y, Arizumi T, Kudo M. Clinical factors predicting the effect of Tolvaptan for refractory ascites in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Dig Dis. 2016;34:659–64.
Atsukawa M, Tsubota A, Kato K, Abe H, Shimada N, Asano T, Ikegami T, Koeda M, Okubo T, Arai T, Nakagawa-Iwashita A, Yoshida Y, Hayama K, Itokawa N, Kondo C, Chuganji Y, Matsuzaki Y, Iwakiri K. Analysis of factors predicting the response to tolvaptan in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatic edema. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33:1256–63.
Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, Gansevoort RT, Grantham JJ, Higashihara E, Perrone RD, Krasa HB, Ouyang J, Czerwiec FS, Sergeyeva O, REPRISE Trial Investigators. Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;20:2407–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mauro Bernardi and Giacomo Zaccherini declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The study involves a review of literature on dysnatremias in cirrhosis and is in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Ethical Committee.
Informed consent
The study does not involve patients, provides a review of existing literature on the concerned subject.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernardi, M., Zaccherini, G. Approach and management of dysnatremias in cirrhosis. Hepatol Int 12, 487–499 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9894-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9894-6