Abstract
Purpose
This study investigates the usefulness of long-term interferon (IFN) therapy following radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
This is a retrospective observational study. Patients underwent pegylated IFN-α/ribavirin combination therapy for 48 weeks and then were maintained on IFN-α administration on average for 68 weeks (mean total duration 116 weeks). Patients who underwent IFN monotherapy were maintained on IFN administration on average for 78 weeks.
Results
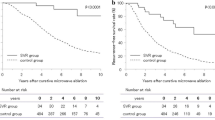
There were biases in the background factors between the IFN and non-IFN groups. Therefore, a covariate adjustment was performed using the propensity score. An analysis of 20-matched patients from each group showed the 5-year cumulative survival rate was higher in the IFN group than in the non-IFN group (100 and 76%, respectively), and the 3-year cumulative recurrence rate was significantly lower in the IFN group than in the non-IFN group (38.0 and 64.2%, respectively). In 14 patients (i.e., IFN responders), the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level remained normalized at 30 IU/mL or lower, regardless of disappearance of serum HCV RNA. In these patients, the cumulative recurrence rate was low, the hazard ratio was 0.158 (95% confidence interval = 0.045–0.561, P = 0.004), and the serum albumin level was retained.
Conclusion
These results show the importance of maintaining the liver function and suggest that long-term IFN administration after RFA inhibits recurrence and contributes to an improved outcome in patients (in particular, IFN responders) who initially develop HCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashem B, Lenhard R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007;132:2557–2576
Koike K, Tsutsumi T, Fujie H, Shintani Y, Moriya K. Molecular mechanism of viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncology 2002;62(Suppl 19):29–37
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T, Kawasaki S, Makuuchi M. Risk factor contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol 2003;38:200–203
Ikeda K, Arase Y, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, Someya T, Hosaka T, Suzuki Y, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Akuta N, Kumada H. Significance of multicentric cancer recurrence after potentially curative ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a longterm cohort study of 892 patients with viral cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 2003;38:865–876
Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, Nakatani S, Morimoto H, Takeda T, Nakajima S, Shiomi S, Seki S, Kobayashi K, Otani S. Randomised trial of effects of Interferon-α on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic active hepatitis C with cirrhosis. Lancet 1995;346:1051–1055
Nishiguchi S, Shiomi S, Nakatani S, Takeda T, Fukuda K, Tamori A, Habu D, Tanaka T. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic active hepatitis C and cirrhosis. Lancet 2001;357:196–197
Yoshida H, Arakawa Y, Sata M, Nishiguchi S, Yano M, Fujiyama S, Yamada G, Yokosuka O, Shiratori Y, Omata M. Interferon therapy prolonged life expectancy among chronic hepatitis C patients. Gastroenterology 2002;123:483–491
Shiratori Y, Ito Y, Yokosuka O, Imazeki F, Nakata R, Tanaka N, Arakawa Y, Hashimoto E, Hirata K, Yoshida H, Ohashi Y, Omata M. Antiviral therapy for cirrhotic hepatitis C: association with reduced hepatocellular carcinoma development and improved survival. Ann Intern Med 2005;142:105–114
Kurokawa M, Hiramatsu N, Oze T, Mochizuki K, Yakushijin T, Kurashige N, Inoue Y, Igura T, Imanaka K, Yamada A, Oshita M, Hagiwara H, Ito T, Inui Y, Hijioka T, Yoshihara H, Inoue A, Imai Y, Kato M, Kiso S, Kanto T, Takehara T, Kasahara A, Hayashi N. Effect of interferon α-2b plus ribavirin therapy on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis. Hepatol Res 2009;39:432–438
Ikeda K, Arase Y, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Chayama K, Murashima N, Kumada H. Interferon beta prevents recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after complete resection or ablation of the primary tumor―a prospective randomized study of hepatitis C virus-related liver cancer. Hepatology 2000;32:228–232
Kubo S, Nishiguchi S, Hirohashi K, Tanaka H, Shuto T, Kinoshita H. Randomized clinical trial of long-term outcome after resection of hepatitis C virus-related hapatocellular carcinoma by postoperative interferon therapy. Br J Surg 2002;89:418–422
Shiratori Y, Shiina S, Teratani T, Imamura M, Obi S, Sato S, Koike Y, Yoshida H, Omata M. Interferon therapy after tumor ablation improves prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis C virus. Ann Intern Med 2003;138:299–306
Nishiguchi S, Tamori A, Kubo S. Effect of long-term postoperative interferon therapy on intrahepatic recurrence and survival rate after resection of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Intervirology 2005;48:71–75
Jeong SC, Aikata H, Katamura Y, Azakami T, Kuwaoka T, Saneto H, Uka K, Mori N, Takaki S, Kodama H, Waki K, Imamura M, Shirakawa H, Kawakami Y, Takahashi S, Chayama K. Effects of a 24-week course of interferon-α therapy after curative treatment of hepatitis C virus- associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:5343–5350
Kudo M, Sakaguchi Y, Chung H, Hatanaka K, Hagiwara S, Ishikawa E, Takahashi S, Kitai S, Inoue T, Minami Y, Ueshima K. Long-term interferon maintenance therapy improves survival in patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after curative radiofrequency ablation. Oncology 2007;72(Suppl 1):132–138
Mazzaferro V, Romito R, Schiavo M, Mariani L, Camerini T, Bhoori S, Capussotti L, Calise F, Pellicci R, Belli G, Tagger A, Colombo M, Bonino F, Majno P, Liovet JM. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence with alpha-interferon after liver resection in hepatitis C virus cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006;44:1543–1554
Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 1983;70:41–55
D’Agostino RB Jr. Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group. Stat Med 1998;17:2265–2281
Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese Tumor-Node-Metastasis and American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer Tumor-Node-Metastasis systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg 2007;245:909–922
Weitzen S, Lapane KL, Toledano AY, Hume AL, Mor V. Weaknesses of goodness-of-fit tests for evaluating propensity score models. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2005;14:227–238
Koike K. Pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: dual-pass carcinogenesis through activation of oxidative stress and intracellular signaling. Hepatol Res 2007;37:115–120
Kumada T, Nakano S, Takeda I, Sugiyama K, Osada T, Kiriyama S, Sone Y, Toyoda H, Shimada S, Takahashi M, Sassa T. Pattern of recurrence after initial treatment in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1997;25:87–92
Tsukuma H, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Nakao M, Yabuubhi T, Kitamura T, Nakanishi K, Fujimoto I, Inoue A, Yamazaki H, Kawashima T. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1797–1801
Iwashyna TJ, Lamont EB. Effectiveness of adjuvant fluorouracil in clinical practice: a population-based cohort study of elderly patients with stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 2002;20:3992–3998
Wang PS, Schneeweiss S, Avorn J, Fischer MA, Mogun H, Solomon DH, Brookhart MA. Risk of death in elderly users of conventional versus atypical antipsychotic medications. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2335–2341
Yano H, Iemura A, Haramaki M, Ogasawara S, Takayama A, Akiba J, Kojiro M. Interferon alfa receptor expression and growth inhibition by interferon alfa in human liver cancer cell lines. Hepatology 1999;29:1708–1717
Lai CL, Lau JY, Wu PC, Ngan H, Chung HT, Mitchell S, Corbett TJ, Chow AW, Lin HJ. Recombinant interferon-alpha in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 1993;17:389–394
Ota H, Nagano H, Sakon M, Eguchi H, Kondo M, Yamamoto T, Nakamura M, Damdinsuren B, Wada H, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Done K, Umeshita K, Nakamori S, Wakasa K, Monden M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein thrombosis by combination of subcutaneous interferon-α and intraarterial 5-fluorouracil: role of expression of type 1 interferon receptor. Br J Cancer 2005;93:557–564
Yano H, Ogasawara S, Momosaki S, Akiba J, Kojiro S, Fukahori S, Ishizaki H, Kuratomi K, Basaki Y, Oie S, Kuwano M, Kojiro M. Growth inhibitory effects of pegylated interferon alpha-2b on human liver cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Liver Int 2006;26:964–975
Wang L, Tang ZY, Qin LX, Wu XF, Sun HC, Xue Q, Ye SL. High-dose and long-term therapy with interferon-alfa inhibits tumor growth and recurrence in nude mice bearing human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts with high metastatic potential. Hepatology 2000;32:43–48
Uenishi T, Nishiguchi S, Tamori A, Yamamoto T, Shuto T, Hirohashi K, Takemura S, Tanaka H, Kubo S. Influence of interferon therapy on outcome after surgery for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 2006;36:195–200
Zhang CH, Xu GL, Jia WD, Ge YS. Effects of interferon alpha treatment on recurrence and survival after complete resection or ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cancer 2009;124:2982–2988
Shen YC, Hsu C, Chen LT, Cheng CC, Hu FC, Cheng AL. Adjuvant interferon therapy after curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a meta-regression approach. J Hepatol 2010;52:889–894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Shimomura and N. Ikeda equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimomura, S., Ikeda, N., Saito, M. et al. Long-term interferon therapy after radiofrequency ablation is effective in treating patients with HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 5, 559–566 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9214-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9214-2