Abstract
Purpose
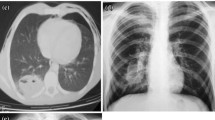
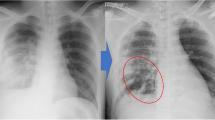
Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts (TPP) are rarely talked about, developing in less than 3% of patients with pulmonary parenchymal injuries. Resolution usually occurs within a few weeks to a few months.
Methods
A retrospective study was undertaken in 30 cases treated in Antalya Training and Research Hospital, Turkey, from January 2014 to December 2017.
Results
The 30 patients with TPP were 28 males (93.3%) and 2 females (6.7%) aged 14–64 years (mean age 31.9 years). Most of them are located in the right lower lobe (50%). The mean size of TPP was 2.07 cm. The overall resolution time for TPP was found to range from 8 to 124 days with a mean of 45.1 ± 32.9 days.
Conclusions
Computed tomography (CT) is a more beneficial than chest radiograph for early diagnosis. Physicians should control follow-up chest radiograph or CT scans until the pseudocyst resolves. Conservative treatment is acceptable in most cases, but intervention may be necessary if complications show up.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Celik B, Basoglu A. Posttraumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: a rare complication of blunt chest trauma. Thorac Cardiovasc. 2006;54:433–5.
Phillips B, Shaw J, Turco L, et al. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: An underreported entity. Injury. 2017;48:214–20.
Chon SH, Lee CB, Kim H, Chung WS, Kim YH. Diagnosis and prognosis of traumatic pulmonary psuedocysts: a review of 12 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;29:819–23.
Kato R, Horinouchi H, Maenaka Y. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst. Report of 12 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989;97:309–12.
Gupta N, George J, Gupta RC, Dixit R. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2013;3:155–8.
Kocer B, Gulbahar G, Gunal N, Dural K, Sakinci U. Traumatic pulmonary pseuodocysts: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2007;1:112.
Santos GH, Mahendra T. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1979;27:359–62.
Athanassiadi K, Gerazounis M, Kalantzi N, Kazakidis P, Fakou A, Kourousis D. Primary traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts: a rare entity. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;23:43–5.
Cho HJ, Jeon YB, Ma DS, Lee JN, Chung M. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts after blunt chest trauma: Prevalence, mechanisms of injury, and computed tomography findings. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;79:425–30.
Luo L, Yin L, Liu Z, Xiang Z. Posttraumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: computed tomography findings and management in 33 patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73:1225–8.
Ulutas H, Celik MR, Ozgel M, Soysal O, Kuzucu A. Pulmonary pseudocyst secondary to blunt or penetrating chest trauma: clinical course and diagnostic issues. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015;41:181–8.
Tsitouridis I, Tsinoglou K, Tsandiridis C, Papastergiou C, Bintoudi A. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts: CT findings. J Thorac Imaging. 2007;22:247–51.
Melloni G, Cremona G, Ciriaco P, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts. J Trauma. 2003;54:737–43.
Yang PJ, Tsai IT, Liu TH. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst. J Pediatr. 2015;167:777.
Sorsdahl OA, Powell JW. Cavitary pulmonary lesions following non-penetrating chest trauma in children. Am J Roentgenol. 1965;95:118–24.
Ganske JG, Dennis DL, Vanderveer JB. Traumatic lung cyst: case report and literature review. J Trauma. 1981;21:493–6.
Stulz P, Schmitt H, Hasse J, Grädel E. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts and paramediastinal air cyst: two rare complications of blunt chest trauma. J Trauma. 1984;24:850–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human rights/ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this study, formal consent was obtained.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bedel, C., Özkaya, M. Diagnosis and prognosis of traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 35, 186–189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-018-0762-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-018-0762-8