Abstract
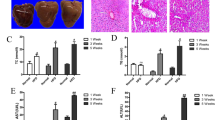
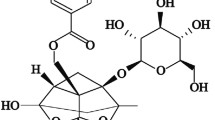
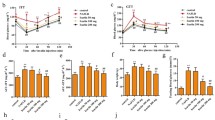
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the leading causes of chronic liver diseases around the world and commonly associated with insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia. Chlorogenic acid (CG) was reported to have insulin-sensitizing activity and exert hypocholesterolemic and hypoglycemic effect. However, the involvement of CG in NAFLD remains far from being addressed. In this study, a high-fat diet-induced NAFLD rat model was used to investigate the biological roles and underlying mechanism of CG in NAFLD. The results showed that high-fat diet-fed rats exhibited an increase in body weight, glucose tolerance, liver injury, insulin resistance, as well as autophagy and C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. Nevertheless, all these effects were alleviated by CG treatment. Moreover, angiotensin treatment in CG group activated the JNK pathway, and promoted autophagy, insulin resistance, and liver injury. In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that CG ameliorated liver injury and insulin resistance by suppressing autophagy via inactivation of JNK pathway in a rat model of NAFLD. Therefore, CG might be a potential application for the treatment of NAFLD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato A, Caldara GF, Nuzzo D, et al. 2017 NAFLD and atherosclerosis are prevented by a natural dietary supplement containing curcumin, silymarin, guggul, chlorogenic acid and inulin in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients. 9 E492
Azuma K, Ippoushi K, Nakayama M, et al. 2000 Absorption of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid in rats after oral administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48 5496–5500
Cimini FA, Barchetta I, Carotti S, et al. 2017 Relationship between adipose tissue dysfunction, vitamin D deficiency and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 23 3407–3417
Czaja MJ 2016 Function of autophagy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 61 1304–1313
Dongiovanni P, Meroni M, Baselli GA, et al. 2017 Insulin resistance promotes Lysyl Oxidase Like 2 induction and fibrosis accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Sci. 131 1301–1315
Ghadieh HE, Smiley ZN, Kopfman MW, et al. 2015 Chlorogenic acid/chromium supplement rescues diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity in mice. Nutr. Metab. 12 19
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, et al. 2002 A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420 333–336
Jiang F and Dusting GJ 2003 Natural phenolic compounds as cardiovascular therapeutics: potential role of their antiinflammatory effects. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 1 135–156
Kodama Y and Brenner DA 2009 c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Multiple roles in multiple steps. Hepatology 49 6–8
Li L, Hai J, Li Z, et al. 2014 Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-kappaB activity in a murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 63 166–173
Li SY, Chang CQ, Ma FY, et al. 2009 Modulating effects of chlorogenic acid on lipids and glucose metabolism and expression of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in golden hamsters fed on high fat diet. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 22 122–129
Lim S, Oh TJ and Koh KK 2015 Mechanistic link between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiometabolic disorders. Int. J. Cardiol. 201 408–414
Liu G and Rondinone CM 2005 JNK: bridging the insulin signaling and inflammatory pathway. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs. 6 979–987
Ma D, Molusky MM, Song J, et al. 2013 Autophagy deficiency by hepatic FIP200 deletion uncouples steatosis from liver injury in NAFLD. Mol. Endocrinol. 27 1643–1654
Ma Y, Gao M and Liu D 2015 Chlorogenic acid improves high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice. Pharm. Res. 32 1200–1209
Mao Y, Yu F, Wang J, et al. 2016 Autophagy: a new target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease therapy. Hepat. Med. 8 27–37
McCarty MF 2005 A chlorogenic acid-induced increase in GLP-1 production may mediate the impact of heavy coffee consumption on diabetes risk. Med. Hypotheses 64 848–853
Mubarak A, Hodgson JM, Considine MJ, et al. 2013 Supplementation of a high-fat diet with chlorogenic acid is associated with insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61 4371–4378
Ozturk ZA and Kadayifci A 2014 Insulin sensitizers for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 6 199–206
Pal M, Febbraio MA and Lancaster GI 2016 The roles of c‐Jun NH2‐terminal kinases (JNKs) in obesity and insulin resistance. J. Physiol. 594 267–279
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Zavos C, et al. 2012 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: multimodal treatment options for a pathogenetically multiple-hit disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 46 272–284
Salomone F, Godos J and Zelber-Sagi S 2016 Natural anti-oxidants for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: molecular targets and clinical perspectives. Liver Int. 36 5–20
Schattenberg JM, Singh R, Wang Y, et al. 2006 JNK1 but not JNK2 promotes the development of steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 43 163–172
Sethi JK and Hotamisligil GS 1999 The role of TNF alpha in adipocyte metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 10 19–29
Singh R, Wang Y, Xiang Y, et al. 2009 Differential effects of JNK1 and JNK2 inhibition on murine steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. Hepatology 49 87–96
Solinas G and Becattini B 2017 JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Metab. 6 174–184
Wan CW, Wong CN, Pin WK, et al. 2013 Chlorogenic acid exhibits cholesterol lowering and fatty liver attenuating properties by up-regulating the gene expression of PPAR-alpha in hypercholesterolemic rats induced with a high-cholesterol diet. Phytother. Res. 27 545–551
Xiang M, Wang PX, Wang AB, et al. 2016 Targeting hepatic TRAF1-ASK1 signaling to improve inflammation, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. J. Hepatol. 64 1365–1377
Yan H, Gao Y and Zhang Y 2017 Inhibition of JNK suppresses autophagy and attenuates insulin resistance in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 15 180–186
Zhu X, Zhang H and Lo R 2004 Phenolic compounds from the leaf extract of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and their antimicrobial activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52 7272–7278
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2016JM8142)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by ULLAS KOLTHUR.
Corresponding editor: Ullas Kolthur
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Gao, YQ., Zhang, Y. et al. Chlorogenic acid alleviates autophagy and insulin resistance by suppressing JNK pathway in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biosci 43, 287–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9746-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9746-5