Abstract
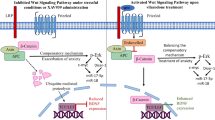
Studies have shown that the removal of the cholinergic innervation to the hippocampus induces dysfunction of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis and decreases the number of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs). Subsequent studies have revealed that the loss of cholinergic input to the hippocampus reduces the expression of GRs and activates nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling through interactions with the cytoplasmic catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PKAc). We examined the effects of chronic stress on cognitive status and GR-PKAc-NF-κB signaling in rats with a loss of cholinergic input to the hippocampus and cortex. Male Sprague-Dawley rats received 192 IgG-saporin injections to selectively eliminate cholinergic neurons in their basal forebrain. Two weeks later, rats were subjected to 1 h of restraint stress per day for 14 days. Rats subjected to both chronic stress and cholinergic depletion showed more severe memory impairments compared to those that received either treatment alone. The reduction in nuclear GR levels induced by cholinergic depletion was unaffected by chronic stress. The activation of NF-κB signaling in the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex induced by cholinergic depletion was augmented by chronic stress, resulting in the increased expression of pro-inflammatory markers, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. The activation of NF-κB induced by cholinergic depletion appears to be aggravated by chronic stress, and this might explain the increased susceptibility of patients with Alzheimer’s disease to stress since activation of NF-κB is associated with stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sapolsky RM, Krey LC, McEwen BS (1984) Glucocorticoid-sensitive hippocampal neurons are involved in terminating the adrenocortical stress response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81(19):6174–6177
Han JS, Bizon JL, Chun HJ, Maus CE, Gallagher M (2002) Decreased glucocorticoid receptor mRNA and dysfunction of HPA axis in rats after removal of the cholinergic innervation to hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 16(7):1399–1404
Helm KA, Han JS, Gallagher M (2002) Effects of cholinergic lesions produced by infusions of 192 IgG-saporin on glucocorticoid receptor mRNA expression in hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex of the rat. Neuroscience 115(3):765–774
Lim CS, Kim YJ, Hwang YK, Banuelos C, Bizon JL, Han JS (2012) Decreased interactions in protein kinase A-glucocorticoid receptor signaling in the hippocampus after selective removal of the basal forebrain cholinergic input. Hippocampus 22(3):455–465. doi:10.1002/hipo.20912
Helm KA, Ziegler DR, Gallagher M (2004) Habituation to stress and dexamethasone suppression in rats with selective basal forebrain cholinergic lesions. Hippocampus 14(5):628–635. doi:10.1002/hipo.10203
Baxter MG, Chiba AA (1999) Cognitive functions of the basal forebrain. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9(2):178–183
Kopp EB, Ghosh S (1995) NF-kappa B and rel proteins in innate immunity. Adv Immunol 58:1–27
Quan N, He L, Lai W, Shen T, Herkenham M (2000) Induction of IkappaBalpha mRNA expression in the brain by glucocorticoids: a negative feedback mechanism for immune-to-brain signaling. J Neurosci 20(17):6473–6477
Unlap MT, Jope RS (1997) Dexamethasone attenuates NF-kappa B DNA binding activity without inducing I kappa B levels in rat brain in vivo. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 45(1):83–89
Haske T, Nakao M, Moudgil VK (1994) Phosphorylation of immunopurified rat liver glucocorticoid receptor by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biochem 132(2):163–171
Doucas V, Shi Y, Miyamoto S, West A, Verma I, Evans RM (2000) Cytoplasmic catalytic subunit of protein kinase a mediates cross-repression by NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(22):11893–11898. doi:10.1073/pnas.220413297
Zhong H, SuYang H, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Ghosh S (1997) The transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB is regulated by the IkappaB-associated PKAc subunit through a cyclic AMP-independent mechanism. Cell 89(3):413–424
Lim CS, Hwang YK, Kim D, Cho SH, Banuelos C, Bizon JL, Han JS (2011) Increased interactions between PKA and NF-kappaB signaling in the hippocampus following loss of cholinergic input. Neuroscience 192:485–493. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.05.074
Koo JW, Russo SJ, Ferguson D, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2010) Nuclear factor-kappaB is a critical mediator of stress-impaired neurogenesis and depressive behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(6):2669–2674. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910658107
Meffert MK, Baltimore D (2005) Physiological functions for brain NF-kappaB. Trends Neurosci 28(1):37–43. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.11.002
Madrigal JL, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Lorenzo P, Castrillo A, Bosca L, Leza JC (2001) Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in brain cortex after acute restraint stress is regulated by nuclear factor kappaB-mediated mechanisms. J Neurochem 76(2):532–538
Bierhaus A, Wolf J, Andrassy M, Rohleder N, Humpert PM, Petrov D, Ferstl R, von Eynatten M et al (2003) A mechanism converting psychosocial stress into mononuclear cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(4):1920–1925. doi:10.1073/pnas.0438019100
Munhoz CD, Lepsch LB, Kawamoto EM, Malta MB, Lima Lde S, Avellar MC, Sapolsky RM, Scavone C (2006) Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J Neurosci 26(14):3813–3820. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4398-05.2006
Baxter MG, Bucci DJ, Gorman LK, Wiley RG, Gallagher M (1995) Selective immunotoxic lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic cells: effects on learning and memory in rats. Behav Neurosci 109(4):714–722
Baxter MG, Gallagher M (1996) Intact spatial learning in both young and aged rats following selective removal of hippocampal cholinergic input. Behav Neurosci 110(3):460–467
Morris RG, Garrud P, Rawlins JN, O'Keefe J (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297(5868):681–683
Gallagher M, Burwell R, Burchinal M (1993) Severity of spatial learning impairment in aging: development of a learning index for performance in the Morris water maze. Behav Neurosci 107(4):618–626
Adzic M, Djordjevic J, Djordjevic A, Niciforovic A, Demonacos C, Radojcic M, Krstic-Demonacos M (2009) Acute or chronic stress induce cell compartment-specific phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptor and alter its transcriptional activity in Wistar rat brain. J Endocrinol 202(1):87–97. doi:10.1677/JOE-08-0509
Frick KM, Kim JJ, Baxter MG (2004) Effects of complete immunotoxin lesions of the cholinergic basal forebrain on fear conditioning and spatial learning. Hippocampus 14(2):244–254. doi:10.1002/hipo.10169
Baxter MG, Bucci DJ, Sobel TJ, Williams MJ, Gorman LK, Gallagher M (1996) Intact spatial learning following lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Neuroreport 7(8):1417–1420
Shirazi SN, Friedman AR, Kaufer D, Sakhai SA (2015) Glucocorticoids and the brain: Neural mechanisms regulating the stress response. Adv Exp Med Biol 872:235–252. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2895-8_10
Meaney MJ, Diorio J, Francis D, Widdowson J, LaPlante P, Caldji C, Sharma S, Seckl JR et al (1996) Early environmental regulation of forebrain glucocorticoid receptor gene expression: implications for adrenocortical responses to stress. Dev Neurosci 18(1–2):49–72
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, Han SS, Keum YS, Park KK, Lee SS (2001) Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat Res 480-481:243–268
Craig LA, Hong NS, Kopp J, McDonald RJ (2008) Emergence of spatial impairment in rats following specific cholinergic depletion of the medial septum combined with chronic stress. Eur J Neurosci 27(9):2262–2271. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06179.x
McDonald RJ, Craig LA, Hong NS (2008) Enhanced cell death in hippocampus and emergence of cognitive impairments following a localized mini-stroke in hippocampus if preceded by a previous episode of acute stress. Eur J Neurosci 27(8):2197–2209. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06151.x
Finsterwald C, Alberini CM (2014) Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: from adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol Learn Mem 112:17–29. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2013.09.017
De Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E, Oitzl MS, Joels M (1998) Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease. Endocr Rev 19(3):269–301. doi:10.1210/edrv.19.3.0331
Sapolsky RM (1996) Why stress is bad for your brain. Science 273(5276):749–750
Hortnagl H, Berger ML, Havelec L, Hornykiewicz O (1993) Role of glucocorticoids in the cholinergic degeneration in rat hippocampus induced by ethylcholine aziridinium (AF64A). J Neurosci 13(7):2939–2945
Paul S, Jeon WK, Bizon JL, Han JS (2015) Interaction of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons with the glucocorticoid system in stress regulation and cognitive impairment. Front Aging Neurosci 7:43. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00043
Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB (2004) IkappaB kinases: key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci 29(2):72–79. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2003.12.003
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: Implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30(1):43–52. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.009
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:86. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-86
Kassed CA, Herkenham M (2004) NF-kappaB p50-deficient mice show reduced anxiety-like behaviors in tests of exploratory drive and anxiety. Behav Brain Res 154(2):577–584. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2004.03.026
Shelton RC, Mainer DH, Sulser F (1996) cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 153(8):1037–1042
Gallagher M, Colombo PJ (1995) Ageing: the cholinergic hypothesis of cognitive decline. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5(2):161–168
Ridder S, Chourbaji S, Hellweg R, Urani A, Zacher C, Schmid W, Zink M, Hortnagl H et al (2005) Mice with genetically altered glucocorticoid receptor expression show altered sensitivity for stress-induced depressive reactions. J Neurosci 25(26):6243–6250. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0736-05.2005
Kolber BJ, Wieczorek L, Muglia LJ (2008) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation and behavioral analysis of mouse mutants with altered glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptor function. Stress 11(5):321–338. doi:10.1080/10253890701821081
Levy ML, Cummings JL, Kahn-Rose R (1999) Neuropsychiatric symptoms and cholinergic therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Gerontology 45(Suppl 1):15–22
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea grants 2011-0015725 and 2015M3C7A1031395 to J.S.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Y.L. and J.S.H. designed the research; S.Y.L. and W.H.C. performed the research; S.Y.L. and J.S.H. analyzed the data; S.Y.L. and J.S.H. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SY., Cho, WH., Lee, YS. et al. Impact of Chronic Stress on the Spatial Learning and GR-PKAc-NF-κB Signaling in the Hippocampus and Cortex in Rats Following Cholinergic Depletion. Mol Neurobiol 55, 3976–3989 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0620-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0620-5