Abstract
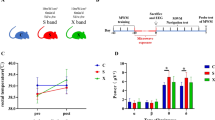
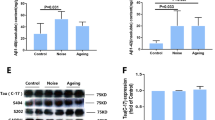
Microwave radiation has been implicated in cognitive dysfunction and neuronal injury in animal models and in human investigations; however, the mechanism of these effects is unclear. In this study, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites in the rat GRIN2B promoter region were screened. The associations of these SNPs with microwave-induced rat brain dysfunction and with rat pheochromocytoma-12 (PC12) cell function were investigated. Wistar rats (n = 160) were exposed to microwave radiation (30 mW/cm2 for 5 min/day, 5 days/week, over a period of 2 months). Screening of the GRIN2B promoter region revealed a stable C-to-T variant at nucleotide position −217 that was not induced by microwave exposure. The learning and memory ability, amino acid contents in the hippocampus and cerebrospinal fluid, and NR2B expression were then investigated in the different genotypes. Following microwave exposure, NR2B protein expression decreased, while the Glu contents in the hippocampus and CSF increased, and memory impairment was observed in the TT genotype but not the CC and CT genotypes. In PC12 cells, the effects of the T allele were more pronounced than those of the C allele on transcription factor binding ability, transcriptional activity, NR2B mRNA, and protein expression. These effects may be related to the detrimental role of the T allele and the protective role of the C allele in rat brain function and PC12 cells exposed to microwave radiation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fritze K, Wiessner C, Kuster N et al (1997) Effect of global system for mobile communication microwave exposure on the genomic response of the rat brain. Neuroscience 81(3):627–639
Elwood JM (2012) Microwaves in the cold war: the Moscow embassy study and its interpretation. Review of a retrospective cohort study. Environ Health : Global Access Sci Source 11:85
Kumar S, Kesari KK, Behari J (2011) The therapeutic effect of a pulsed electromagnetic field on the reproductive patterns of male Wistar rats exposed to a 2.45-GHz microwave field. Clinics 66(7):1237–1245
Baranski S (1972) Histological and histochemical effect of microwave irradiation on the central nervous system of rabbits and guinea pigs. Am J Phys Med 51(4):182–191
Albert EN, DeSantis M (1975) Do microwaves alter nervous system structure? Ann N Y Acad Sci 247:87–108
Albert EN, Sherif M (1988) Morphological changes in cerebellum of neonatal rats exposed to 2.45 GHz microwaves. Prog Clin Biol Res 257:135–151
Hansson HA (1988) Effects on the nervous system by exposure to electromagnetic fields: experimental and clinical studies. Prog Clin Biol Res 257:119–134
Lai H, Horita A, Guy AW (1994) Microwave irradiation affects radial-arm maze performance in the rat. Bioelectromagnetics 15(2):95–104
Salford LG, Brun AE, Eberhardt JL, Malmgren L, Persson BR (2003) Nerve cell damage in mammalian brain after exposure to microwaves from GSM mobile phones. Environ Health Perspect 111(7):881–883, discussion A408
Zhao L, Peng RY, Wang SM et al (2012) Relationship between cognition function and hippocampus structure after long-term microwave exposure. Biomed Environ Sci : BES 25(2):182–188
Rubin GJ, Das Munshi J, Wessely S (2006) A systematic review of treatments for electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Psychother Psychosom 75(1):12–18
Rubin GJ, Hillert L, Nieto-Hernandez R, van Rongen E, Oftedal G (2011) Do people with idiopathic environmental intolerance attributed to electromagnetic fields display physiological effects when exposed to electromagnetic fields? A systematic review of provocation studies. Bioelectromagnetics 32(8):593–609
Carrubba S, Frilot C, Chesson AL, Marino AA (2007) Nonlinear EEG activation evoked by low-strength low-frequency magnetic fields. Neurosci Lett 417(2):212–216
Marino AA, Carrubba S (2009) The effects of mobile-phone electromagnetic fields on brain electrical activity: a critical analysis of the literature. Electromagn Biol Med 28(3):250–274
Gonda X (2012) Basic pharmacology of NMDA receptors. Curr Pharm Des 18(12):1558–1567
Anticevic A, Gancsos M, Murray JD et al (2012) NMDA receptor function in large-scale anticorrelated neural systems with implications for cognition and schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(41):16720–16725
Cull-Candy SG, Leszkiewicz DN (2004) Role of distinct NMDA receptor subtypes at central synapses. Science’s STKE: Signal Transduct Knowl Environ 2004(255):re16
Rebola N, Srikumar BN, Mulle C (2010) Activity-dependent synaptic plasticity of NMDA receptors. J Physiol 588(Pt 1):93–99
Fontan-Lozano A, Suarez-Pereira I, Gonzalez-Forero D, Carrion AM (2011) The A-current modulates learning via NMDA receptors containing the NR2B subunit. PLoS One 6(9):e24915
Zhang XH, Wu LJ, Gong B, Ren M, Li BM, Zhuo M (2008) Induction- and conditioning-protocol dependent involvement of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in synaptic potentiation and contextual fear memory in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats. Mol Brain 1:9
Sacchetti E, Scassellati C, Minelli A et al (2013) Schizophrenia susceptibility and NMDA-receptor mediated signalling: an association study involving 32 tagSNPs of DAO, DAOA, PPP3CC, and DTNBP1 genes. BMC Med Genet 14:33
Alonso P, Gratacos M, Segalas C et al (2012) Association between the NMDA glutamate receptor GRIN2B gene and obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci : JPN 37(4):273–281
Zhao Q, Che R, Zhang Z et al (2011) Positive association between GRIN2B gene and bipolar disorder in the Chinese Han Population. Psychiatry Res 185(1–2):290–292
Wu SL, Wang WF, Shyu HY et al (2010) Association analysis of GRIN1 and GRIN2B polymorphisms and Parkinson's disease in a hospital-based case–control study. Neurosci Lett 478(2):61–65
Chen C, Li X, Wang T et al (2010) Association between NMDA receptor subunit 2b gene polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease in Chinese Han population in Shanghai. Neurosci Bull 26(5):395–400
Jiang H, Jia J (2009) Association between NR2B subunit gene (GRIN2B) promoter polymorphisms and sporadic Alzheimer's disease in the North Chinese population. Neurosci Lett 450(3):356–360
Seripa D, Matera MG, Franceschi M et al (2008) Association analysis of GRIN2B, encoding N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 2B subunit, and Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 25(3):287–292
Martucci L, Wong AH, De Luca V et al (2006) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR2B subunit gene GRIN2B in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: Polymorphisms and mRNA levels. Schizophr Res 84(2–3):214–221
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Hansson MK (2013) Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology : Off J Int Soc Pathophysiol / ISP 20(2):85–110
Yang Y, Jin X, Yan C, Tian Y, Tang J, Shen X (2008) Case-only study of interactions between DNA repair genes (hMLH1, APEX1, MGMT, XRCC1 and XPD) and low-frequency electromagnetic fields in childhood acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 49(12):2344–2350
Zhang Y, Yu Z, Xie Y, Fang Q (2008) Effects of microwave irradiation on NMDA receptor subunits mRNA expressions in rat hippocampus. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu = J Hyg Res 37(1):25–28
Xu S, Ning W, Xu Z, Zhou S, Chiang H, Luo J (2006) Chronic exposure to GSM 1800-MHz microwaves reduces excitatory synaptic activity in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 398(3):253–257
Bai G, Kusiak JW (1995) Functional analysis of the proximal 5'-flanking region of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit gene, NMDAR1. J Biol Chem 270(13):7737–7744
Klein M, Pieri I, Uhlmann F, Pfizenmaier K, Eisel U (1998) Cloning and characterization of promoter and 5'-UTR of the NMDA receptor subunit epsilon 2: evidence for alternative splicing of 5'-non-coding exon. Gene 208(2):259–269
Sasner M, Buonanno A (1996) Distinct N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 2B subunit gene sequences confer neural and developmental specific expression. J Biol Chem 271(35):21316–21322
Durand GM, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (1993) Splice variants of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 identify domains involved in regulation by polyamines and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(14):6731–6735
Malyapa RS, Ahern EW, Straube WL, Moros EG, Pickard WF, Roti Roti JL (1997) Measurement of DNA damage after exposure to 2450 MHz electromagnetic radiation. Radiat Res 148(6):608–617
Lagroye I, Anane R, Wettring BA et al (2004) Measurement of DNA damage after acute exposure to pulsed-wave 2450 MHz microwaves in rat brain cells by two alkaline comet assay methods. Int J Radiat Biol 80(1):11–20
Belyaev IY, Koch CB, Terenius O et al (2006) Exposure of rat brain to 915 MHz GSM microwaves induces changes in gene expression but not double stranded DNA breaks or effects on chromatin conformation. Bioelectromagnetics 27(4):295–306
Sarkar S, Ali S, Behari J (1994) Effect of low power microwave on the mouse genome: a direct DNA analysis. Mutat Res 320(1–2):141–147
Lai H, Singh NP (1995) Acute low-intensity microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain cells. Bioelectromagnetics 16(3):207–210
Lai H, Singh NP (1996) Single- and double-strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 69(4):513–521
Lai H, Singh NP (1997) Acute exposure to a 60 Hz magnetic field increases DNA strand breaks in rat brain cells. Bioelectromagnetics 18(2):156–165
Campisi A, Gulino M, Acquaviva R et al (2010) Reactive oxygen species levels and DNA fragmentation on astrocytes in primary culture after acute exposure to low intensity microwave electromagnetic field. Neurosci Lett 473(1):52–55
Liu C, Duan W, Xu S et al (2013) Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation induces oxidative DNA base damage in a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Toxicol Lett 218(1):2–9
Wang LF, Peng RY, Hu XJ et al (2007) Influence of microwave radiation on synaptic structure and function of hippocampus in Wistar rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi = Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zhiyebing Zazhi = Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis 25(4):211–214
Zhao YL, Peng XD, Yang YH, Ma HB, Song JP, Pu JS (2004) Effects of 2450 MHz microwave on long-term potentiation of hippocampus and lipofuscin contents in rat brain. Hang Tian Yi Xue Yu Yi Xue Gong Cheng = Space Med Med Eng 17(2):111–113
Xu ZW, Hou B, Li YF et al (2007) Theophylline attenuates microwave-induced impairment of memory acquisition. Neurosci Lett 412(2):129–133
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD, Tripathi AK, Abegaonkar MP (2012) Microwave radiation induced oxidative stress, cognitive impairment and inflammation in brain of Fischer rats. Indian J Exp Biol 50(12):889–896
Li YH, Lu GB, Shi CH, Zhang Z, Xu Q (2011) Effects of 2000 muW/cm2; electromagnetic radiation on expression of immunoreactive protein and mRNA of NMDA receptor 2A subunit in rats hippocampus. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi = Chin J Cell Mol Immunol 27(1):15–18
Mausset-Bonnefont AL, Hirbec H, Bonnefont X, Privat A, Vignon J, de Seze R (2004) Acute exposure to GSM 900-MHz electromagnetic fields induces glial reactivity and biochemical modifications in the rat brain. Neurobiol Dis 17(3):445–454
Crozier RA, Bi C, Han YR, Plummer MR (2008) BDNF modulation of NMDA receptors is activity dependent. J Neurophysiol 100(6):3264–3274
Aliaga E, Rage F, Bustos G, Tapia-Arancibia L (1998) BDNF gene transcripts in mesencephalic neurons and its differential regulation by NMDA. Neuroreport 9(9):1959–1962
Wang LF, Peng RY, Hu XJ et al (2008) Influence of microwave radiation on synapsin I expression in PC12 cells and its mechanism. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi = Chin J Cell Mol Immunol 24(7):655–659
Baumbauer KM, Huie JR, Hughes AJ, Grau JW (2009) Timing in the absence of supraspinal input II: regularly spaced stimulation induces a lasting alteration in spinal function that depends on the NMDA receptor, BDNF release, and protein synthesis. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 29(46):14383–14393
Zeni O, Sannino A, Sarti M, Romeo S, Massa R, Scarfi MR (2012) Radiofrequency radiation at 1950 MHz (UMTS) does not affect key cellular endpoints in neuron-like PC12 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 33(6):497–507
Nakazawa K, Sun LD, Quirk MC, Rondi-Reig L, Wilson MA, Tonegawa S (2003) Hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors are crucial for memory acquisition of one-time experience. Neuron 38(2):305–315
Varas MM, Perez MF, Ramirez OA, de Barioglio SR (2003) Increased susceptibility to LTP generation and changes in NMDA-NR1 and -NR2B subunits mRNA expression in rat hippocampus after MCH administration. Peptides 24(9):1403–1411
Loftis JM, Janowsky A (2003) The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B: localization, functional properties, regulation, and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 97(1):55–85
Mawhinney LJ, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Alonso OF et al (2012) Isoflurane/nitrous oxide anesthesia induces increases in NMDA receptor subunit NR2B protein expression in the aged rat brain. Brain Res 1431:23–34
Yoshii A, Constantine-Paton M (2007) BDNF induces transport of PSD-95 to dendrites through PI3K-AKT signaling after NMDA receptor activation. Nat Neurosci 10(6):702–711
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB503706) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970871). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We thank Professor Gang-Qiao Zhou and Professor Ling-Qiang Zhang in Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine for their kind help with SNP exploration.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Li-Feng Wang and Da-Wei Tian are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LF., Tian, DW., Li, HJ. et al. Identification of a Novel Rat NR2B Subunit Gene Promoter Region Variant and Its Association with Microwave-Induced Neuron Impairment. Mol Neurobiol 53, 2100–2111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9169-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9169-3