Abstract
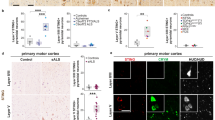
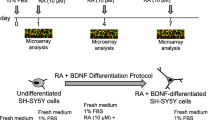
Somatostatin (SST) is a growth hormone inhibitory peptide involved in regulation of several physiological responses of cells including neurotransmission, cell migration, maturation, and neurite formation. In the present study, we examined the role of SST in all-trans retinoic acid (RA)–induced progression of neurite outgrowth in SH-SY5Y cells. We also determined the morphological and developmental changes in prominent intracellular markers of neurite growth including microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), neuron-specific III β-tubulin (TUJ1), and Tau. Here, we present evidence that SST is a molecular determinant in regulating the transition of SH-SY5Y cells from non-neuronal entity to neuronal phenotype in response to RA. The results from present study reveal that SST changes the distributional pattern of MAP2/Tau and TUJ1, and activates extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK1/2) signaling pathway through SST receptors (SSTRs). The expression of MAP2 and Tau remains elevated upon treatment with RA and SST alone or in combination. Importantly, we identified that the cells displaying strong co-expression of SST and TUJ1 are more likely to bear elongated neurite formation than cells devoid of such expression. These findings show that the site-specific expression of MAP2 and TUJ1 is an essential determinant of neurite outgrowth in SH-SY5Y cells in RA-mediated differentiation. Taken together, results presented here further substantiates the role of SST in the promotion of neurite formation and elongation in SH-SY5Y cells in combination with RA. Investigating how SST can improve neurite formation in neurodegenerative disease may help to develop new therapeutic approach in improving cognitive function and memory loss.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Beta-amyloid
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal–regulated kinase
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- hCMEC/D3:
-
Human brain microvascular endothelial cells
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 2
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- NGS:
-
Normal goat serum
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nucleus antigen
- RA:
-
Retinoic acid
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SH-SY5Y:
-
Human neuroblastoma cells
- SST:
-
Somatostatin
- SSTR:
-
Somatostatin receptor
- RT:
-
Room temperature
- TUJ1:
-
βIII tubulin
References
Abdul HM, Butterfield DA (2007) Involvement of PI3K/PKG/ERK1/2 signaling pathways in cortical neurons to trigger protection by cotreatment of acetyl-L-carnitine and alpha-lipoic acid against HNE-mediated oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med 42(3):371–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.11.006
Abemayor E, Sidell N (1989) Human neuroblastoma cell lines as models for the in vitro study of neoplastic and neuronal cell differentiation. Environ Health Perspect 80:3–15
Al-Bassam J, Ozer RS, Safer D, Halpain S, Milligan RA (2002) MAP2 and tau bind longitudinally along the outer ridges of microtubule protofilaments. J Cell Biol 157(7):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200201048
Almeida A, Bolanos JP, Moreno S (2005) Cdh1/Hct1-APC is essential for the survival of postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci 25(36):8115–8121. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1143-05.2005
Basivireddy J, Somvanshi RK, Romero IA, Weksler BB, Couraud PO, Oger J, Kumar U (2013) Somatostatin preserved blood brain barrier against cytokine induced alterations: possible role in multiple sclerosis. Biochem Pharmacol 86(4):497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.06.001
Brill LB 2nd, Bennett JP Jr (2003) Dependence on electron transport chain function and intracellular signaling of genomic responses in SH-SY5Y cells to the mitochondrial neurotoxin MPP(+). Exp Neurol 181(1):25–38
Bulloch AG (1987) Somatostatin enhances neurite outgrowth and electrical coupling of regenerating neurons in Helisoma. Brain Res 412(1):6–17
Caceres A, Banker GA, Binder L (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of tubulin and microtubule-associated protein 2 during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci 6(3):714–722
Chen X, Fu W, Tung CE, Ward NL (2009) Angiopoietin-1 induces neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells in a Tie2-independent, beta1-integrin-dependent manner. Neurosci Res 64(4):348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2009.04.007
Chen J, Zacharek A, Cui X, Shehadah A, Jiang H, Roberts C, Lu M, Chopp M (2010) Treatment of stroke with a synthetic liver X receptor agonist, TO901317, promotes synaptic plasticity and axonal regeneration in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(1):102–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2009.187
Chen A, Xiong LJ, Tong Y, Mao M (2013) The neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Biomed Rep 1(2):167–176. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2012.48
Chen Q, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Xu S, Chen C, Yu Z (2014) The cellular distribution and Ser262 phosphorylation of tau protein are regulated by BDNF in vitro. PLoS One 9(3):e91793. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091793
Cheung YT, Lau WK, Yu MS, Lai CS, Yeung SC, So KF et al (2009) Effects of all-trans-retinoic acid on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma as in vitro model in neurotoxicity research. Neurotoxicology 30(1):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2008.11.001
Clagett-Dame M, McNeill EM, Muley PD (2006) Role of all-trans retinoic acid in neurite outgrowth and axonal elongation. J Neurobiol 66(7):739–756. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.20241
Conn KJ, Ullman MD, Larned MJ, Eisenhauer PB, Fine RE, Wells JM (2003) cDNA microarray analysis of changes in gene expression associated with MPP+ toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res 28(12):1873–1881
Cowley S, Paterson H, Kemp P, Marshall CJ (1994) Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell 77(6):841–852
Cuende J, Moreno S, Bolanos JP, Almeida A (2008) Retinoic acid downregulates Rae1 leading to APC(Cdh1) activation and neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y differentiation. Oncogene 27(23):3339–3344. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210987
Dehmelt L, Smart FM, Ozer RS, Halpain S (2003) The role of microtubule-associated protein 2c in the reorganization of microtubules and lamellipodia during neurite initiation. J Neurosci 23(29):9479–9490
Desbarats J, Birge RB, Mimouni-Rongy M, Weinstein DE, Palerme JS, Newell MK (2003) Fas engagement induces neurite growth through ERK activation and p35 upregulation. Nat Cell Biol 5(2):118–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb916
Ding Q, Bruce-Keller AJ, Chen Q, Keller JN (2004) Analysis of gene expression in neural cells subject to chronic proteasome inhibition. Free Radic Biol Med 36(4):445–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.10.025
Dinsmore JH, Solomon F (1991) Inhibition of MAP2 expression affects both morphological and cell division phenotypes of neuronal differentiation. Cell 64(4):817–826
Encinas M, Iglesias M, Liu Y, Wang H, Muhaisen A, Cena V et al (2000) Sequential treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gives rise to fully differentiated, neurotrophic factor-dependent, human neuron-like cells. J Neurochem 75(3):991–1003
Epelbaum J, Dournaud P, Fodor M, Viollet C (1994) The neurobiology of somatostatin. Crit Rev Neurobiol 8(1–2):25–44
Felgner H, Frank R, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E, Ludin B, Matus A, Schliwa M (1997) Domains of neuronal microtubule-associated proteins and flexural rigidity of microtubules. J Cell Biol 138(5):1067–1075
Ferriero DM, Sheldon RA, Messing RO (1994) Somatostatin enhances nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 80(1–2):13–18
Forster JI, Koglsberger S, Trefois C, Boyd O, Baumuratov AS, Buck L et al (2016) Characterization of differentiated SH-SY5Y as neuronal screening model reveals increased oxidative vulnerability. J Biomol Screen 21(5):496–509. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057115625190
Fujii Y, Gonoi T, Yamada Y, Chihara K, Inagaki N, Seino S (1994) Somatostatin receptor subtype SSTR2 mediates the inhibition of high-voltage-activated calcium channels by somatostatin and its analogue SMS 201-995. FEBS Lett 355(2):117–120
Grimm-Jorgensen Y (1987) Somatostatin and calcitonin stimulate neurite regeneration of molluscan neurons in vitro. Brain Res 403(1):121–126
Harada A, Teng J, Takei Y, Oguchi K, Hirokawa N (2002) MAP2 is required for dendrite elongation, PKA anchoring in dendrites, and proper PKA signal transduction. J Cell Biol 158(3):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200110134
Hashemi SH, Li JY, Ahlman H, Dahlstrom A (2003) SSR2(a) receptor expression and adrenergic/cholinergic characteristics in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res 28(3–4):449–460
Hirokawa N, Hisanaga S, Shiomura Y (1988a) MAP2 is a component of crossbridges between microtubules and neurofilaments in the neuronal cytoskeleton: quick-freeze, deep-etch immunoelectron microscopy and reconstitution studies. J Neurosci 8(8):2769–2779
Hirokawa N, Shiomura Y, Okabe S (1988b) Tau proteins: the molecular structure and mode of binding on microtubules. J Cell Biol 107(4):1449–1459
Holst JJ, Harling H, Messell T, Coy DH (1990) Identification of the neurotransmitter/neuromodulator functions of the neuropeptide gastrin-releasing peptide in the porcine antrum, using the antagonist (Leu13-psi-CH2 NH-Leu14)-bombesin. Scand J Gastroenterol 25(1):89–96
Hu X, Ballo L, Pietila L, Viesselmann C, Ballweg J, Lumbard D, Stevenson M, Merriam E, Dent EW (2011) BDNF-induced increase of PSD-95 in dendritic spines requires dynamic microtubule invasions. J Neurosci 31(43):15597–15603. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2445-11.2011
Kaplan DR, Matsumoto K, Lucarelli E, Thiele CJ (1993) Induction of TrkB by retinoic acid mediates biologic responsiveness to BDNF and differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. Eukaryotic Signal Transduction Group. Neuron 11(2):321–331
Kentroti S, Vernadakis A (1991) Survival and proliferation in developing neuroblasts in cultures derived from embryos treated with ethanol during early neuroembryogenesis: effects attenuated by somatostatin. J Neurosci Res 30(4):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.490300407
Kharbanda S, Saleem A, Emoto Y, Stone R, Rapp U, Kufe D (1994) Activation of Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinases during monocytic differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 269(2):872–878
Kito K, Ito T, Sakaki Y (1997) Fluorescent differential display analysis of gene expression in differentiating neuroblastoma cells. Gene 184(1):73–81
Lasorella A, Stegmuller J, Guardavaccaro D, Liu G, Carro MS, Rothschild G et al (2006) Degradation of Id2 by the anaphase-promoting complex couples cell cycle exit and axonal growth. Nature 442(7101):471–474. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04895
Leugers CJ, Lee G (2010) Tau potentiates nerve growth factor-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and neurite initiation without a requirement for microtubule binding. J Biol Chem 285(25):19125–19134. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.105387
Liu Y, Lee JW, Ackerman SL (2015) Mutations in the microtubule-associated protein 1A (Map1a) gene cause Purkinje cell degeneration. 35(11):4587–4598. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2757-14.2015
Lopez-Carballo G, Moreno L, Masia S, Perez P, Barettino D (2002) Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by retinoic acid is required for neural differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 277(28):25297–25304. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M201869200
Maden M (2002) Retinoid signalling in the development of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(11):843–853. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn963
Maubert E, Slama A, Ciofi P, Viollet C, Tramu G, Dupouy JP, Epelbaum J (1994) Developmental patterns of somatostatin-receptors and somatostatin-immunoreactivity during early neurogenesis in the rat. Neuroscience 62(1):317–325
Miloso M, Villa D, Crimi M, Galbiati S, Donzelli E, Nicolini G, Tredici G (2004) Retinoic acid-induced neuritogenesis of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells is ERK independent and PKC dependent. J Neurosci Res 75(2):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10848
Morooka T, Nishida E (1998) Requirement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase for neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 273(38):24285–24288
Nguyen TT, Scimeca JC, Filloux C, Peraldi P, Carpentier JL, Van Obberghen E (1993) Co-regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, and the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase in PC12 cells. Distinct effects of the neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and the mitogenic factor, epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 268(13):9803–9810
Pahlman S, Ruusala AI, Abrahamsson L, Mattsson ME, Esscher T (1984) Retinoic acid-induced differentiation of cultured human neuroblastoma cells: a comparison with phorbolester-induced differentiation. Cell Differ 14(2):135–144
Pahlman S, Hoehner JC, Nanberg E, Hedborg F, Fagerstrom S, Gestblom C et al (1995) Differentiation and survival influences of growth factors in human neuroblastoma. Eur J Cancer 31a(4):453–458
Pan J, Kao YL, Joshi S, Jeetendran S, Dipette D, Singh US (2005) Activation of Rac1 by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vivo: role in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 93(3):571–583. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03106.x
Patel YC (1999) Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 20(3):157–198. https://doi.org/10.1006/frne.1999.0183
Pool M, Thiemann J, Bar-Or A, Fournier AE (2008) NeuriteTracer: a novel ImageJ plugin for automated quantification of neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Methods 168(1):134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.08.029
Qui MS, Green SH (1992) PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity. Neuron 9(4):705–717
Riese U, Ziegler E, Hamburger M (2004) Militarinone A induces differentiation in PC12 cells via MAP and Akt kinase signal transduction pathways. FEBS Lett 577(3):455–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.045
Roca CA, Su TP, Elpern S, McFarland H, Rubinow DR (1999) Cerebrospinal fluid somatostatin, mood, and cognition in multiple sclerosis. Biol Psychiatry 46(4):551–556
Rossino P, Defilippi P, Silengo L, Tarone G (1991) Up-regulation of the integrin alpha 1/beta 1 in human neuroblastoma cells differentiated by retinoic acid: correlation with increased neurite outgrowth response to laminin. Cell Regul 2(12):1021–1033
Saito T, Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Takano J, Huang SM, Suemoto T, Higuchi M, Saido TC (2005) Somatostatin regulates brain amyloid beta peptide Abeta42 through modulation of proteolytic degradation. Nat Med 11(4):434–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1206
Schmid LC, Mittag M, Poll S, Steffen J, Wagner J, Geis HR, Schwarz I, Schmidt B, Schwarz MK, Remy S, Fuhrmann M (2016) Dysfunction of somatostatin-positive interneurons associated with memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease model. Neuron 92(1):114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.08.034
Shipley MM, Mangold CA, Szpara ML (2016) Differentiation of the SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line. J Vis Exp (108):53193. https://doi.org/10.3791/53193
Sorensen KV (1987) Somatostatin in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 75(3):161–167
Taniwaki T, Schwartz JP (1995) Somatostatin enhances neurofilament expression and neurite outgrowth in cultured rat cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 88(1):109–116
Truckenmiller ME, Vawter MP, Cheadle C, Coggiano M, Donovan DM, Freed WJ et al (2001) Gene expression profile in early stage of retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Restor Neurol Neurosci 18(2–3):67–80
Van den Steen PE, Van Aelst I, Hvidberg V, Piccard H, Fiten P, Jacobsen C et al (2006) The hemopexin and O-glycosylated domains tune gelatinase B/MMP-9 bioavailability via inhibition and binding to cargo receptors. J Biol Chem 281(27):18626–18637. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512308200
Wang CX, Song JH, Song DK, Yong VW, Shuaib A, Hao C (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 prevents neuronal apoptosis through ERK-mediated upregulation of Bcl-2. Cell Death Differ 13(7):1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401804
War SA, Kim B, Kumar U (2015) Human somatostatin receptor-3 distinctively induces apoptosis in MCF-7 and cell cycle arrest in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 413:129–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.06.019
Xie HR, Hu LS, Li GY (2010) SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line: in vitro cell model of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Chin Med J 123(8):1086–1092
Acknowledgments
SP is the recipient of CIHR Doctoral Research Award (GSD 134858) and UBC 4 Year Fellowship.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (MOP 74465) and NSERC (402594-11 and 16-05171) Canada to UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paik, S., Somvanshi, R.K. & Kumar, U. Somatostatin-Mediated Changes in Microtubule-Associated Proteins and Retinoic Acid–Induced Neurite Outgrowth in SH-SY5Y Cells. J Mol Neurosci 68, 120–134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01291-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01291-2