Abstract
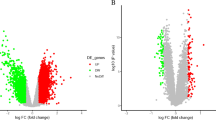
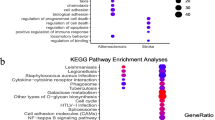
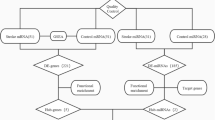
This study aimed to explore the molecular mechanism of stroke and provide a new target in the clinical management. The miRNA dataset GSE97532 (3 blood samples from middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and 3 from sham operation) and mRNA dataset GSE97533 (3 blood samples from MCAO and 3 from sham operation) were obtained from GEO database. Differentially expressed mRNA (DEGs) and miRNAs (DEMIRs) were screened out between MCAO and sham operation groups. Then, DEMIR–DEG interactions were explored and visualized using Cytoscape software. Moreover, the enrichment analysis was performed on these DEMIRs and DEGs. Furthermore, protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed. Finally, the DEG-target transcription factors (TFs) were investigated using the WebGestal software. The current bioinformatics analysis revealed 38 DEMIRs and 546 DEGs between MCAO and sham operation groups. The DEMIR–DEG analysis revealed 370 relations, such as miR-107-5p-Furin. The top 10 up- and downregulated DEMIRs were mainly enriched in pathways like cAMP signaling pathway. The PPI network analysis revealed 2 modules. The target DEGs of the 10 up- and downregulated DEMIRs in 2 modules were mainly assembled in functions like ATP binding and pathway including ABC transporters. Furthermore, the DEG–TF network analysis identified 5 outstanding TFs including androgen receptor (AR). miR107-5p might take part in the progression of stroke via inhibiting the expression of Furin. TFs like AR might be used as a novel gene therapy target for stroke. Furthermore, cAMP signaling pathway and ATP binding function might be a novel breakthrough for stroke treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife Sciences 4:1–18
Aronica SM, Kraus WL, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Estrogen action via the cAMP signaling pathway: stimulation of adenylate cyclase and cAMP-regulated gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:8517–8521
Atkins CM, Jr OA, Alonso OF, Pearse DD, Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2007) Modulation of the cAMP signaling pathway after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 208:145–158
Ayala P, Uchida M, Akiyoshi K, Cheng J, Hashimoto J, Jia T, Ronnekleiv OK, Murphy SJ, Wiren KM, Hurn PD (2011) Androgen receptor overexpression is neuroprotective in experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res 2:346–357
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C, Booker O, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY, Arai AE (2012) MultiContrast delayed enhancement (MCODE) improves detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:83
Bao J, Zhou S, Pan S, Zhang Y (2018) Molecular mechanism exploration of ischemic stroke by integrating mRNA and miRNA expression profiles. Clin Lab 64:559–568
Berardini TZ, Li D, Jaiswal P 2009. The Gene Ontology in 2010: extensions and refinements.
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C, Leslie C (2010) Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol 11:R90–R90
Chan DK, Cordato D, O'Rourke F, et al (2012). Comprehensive stroke units: a review of comparative evidence and experience. Int J Stroke
Cronin CA, Weisman CJ, Llinas RH (2008) Stroke treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1142:159–178
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22:391–397
Dweep H, Gretz N (2015) miRWalk2.0: a comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods 12:697–697
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14863–14868
Hein M, Zoremba N, Bleilevens C, Bruells C, Rossaint R, Roehl AB (2013) Levosimendan limits reperfusion injury in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model. BMC Neurol 13:106
Hörnsten C, Weidung B, Littbrand H et al (2016) High blood pressure as a risk factor for incident stroke among very old people: a population-based cohort study. J Hypertens 34:1
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2008) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F et al (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 4:249–264
Jin R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87:779–789
Johansson BB (2010) Hypertension mechanisms causing stroke. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:563–565
Karin M (1990) Too many transcription factors: positive and negative interactions. The New Biologist 2:126–131
Khedr EM, El SO, Khedr T, Abdel aY, Awad EM (2015) Assessment of corticodiaphragmatic pathway and pulmonary function in acute ischemic stroke patients. Eur J Neurol 7:509–516
Lee TI, Young RA (2000) Transcription of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Annu Rev Genet 34:77–137
Li Y, Mao L, Gao Y, Baral S, Zhou Y, Hu B (2015) MicroRNA-107 contributes to post-stroke angiogenesis by targeting Dicer-1. Sci Rep 5:13316
Liu DZ, Jickling GC, Ander BP, Hull H, Zhan X, Cox C, Shroff N, Dykstra-Aiello C, Stamova B, Sharp FR (2016) Elevating microRNA-122 in blood improves outcomes after temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:1374–1383
Megraw M, Sethupathy P, Corda B, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2007) miRGen: a database for the study of animal microRNA genomic organization and function. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D149
Musibay ED, Milbauer L, Enenstein J, Wells A, Hebbel RP (2008) Association of inflammatory transcription factors in human blood outgrowth endothelial cells and development of stroke in sickle cell disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:1853–1867
Patak P, Hermann DM (2011) ATP-binding cassette transporters at the blood-brain barrier in ischaemic stroke. Curr Pharm Des 17:5
Pulliam JVK, Xu Z, Ford GD, Liu C, Li Y, Stovall KC, Cannon VS, Tewolde T, Moreno CS, Ford BD (2013) Computational identification of conserved transcription factor binding sites upstream of genes induced in rat brain by transient focal ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1495:76–85
Rao VLR, Bowen KK, Dhodda VK et al (2010) Gene expression analysis of spontaneously hypertensive rat cerebral cortex following transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 83:1072–1086
Rexrode KM, Ridker PM, Hegener HH, Buring JE, Manson JE, Zee RY (2008) Genetic variation of the androgen receptor and risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke in women. Stroke 39:1590–1592
Rickhag M, Wieloch T, Gidö G et al (2010) Comprehensive regional and temporal gene expression profiling of the rat brain during the first 24 h after experimental stroke identifies dynamic ischemia-induced gene expression patterns, and reveals a biphasic activation of genes in surviving tissue. J Neurochem 96:14–29
Rigoutsos I, Miranda K, Huynh T (2007). rna22: a unified computational framework for discovering miRNA precursors, localizing mature miRNAs, identifying 3′ UTR target-islands, and determining the targets of mature-miRNAs. Ibm Corporation
Rink C, Khanna S (2011) MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics 43:521–528
Rongyao H, Xiaoyan Z, Xudong P, Ruiyou G, Teng M, Xiang X (2014) ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 R219K polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in the Chinese population: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 336:57–61
Saenger AK, Christenson RH (2010) Stroke biomarkers: progress and challenges for diagnosis, prognosis, differentiation, and treatment. Clin Chem 56:21–33
Sawada Y, Inoue M, Kanda T, Sakamaki T, Tanaka S, Minamino N, Nagai R, Takeuchi T (1997) Co-elevation of brain natriuretic peptide and proprotein-processing endoprotease furin after myocardial infarction in rats. FEBS Lett 400:177–182
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and Bioconductor. Springer New York, New York, pp 397–420
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al (2014). STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res, gku1003
Tadevosyan KTG (2015). Variations in immediate-early genes encoding c-Fos, c-Jun and IER5 transcription factors are associated with ischemic stroke. Advancements in Genetic Engineering
Takuma A, Abe A, Saito Y, Nito C, Ueda M, Ishimaru Y, Harada H, Abe K, Kimura K, Asakura T (2017) Gene expression analysis of the effect of ischemic infarction in whole blood. Int J Mol Sci 18:2335
Tanaka K, Fukuuchi Y, Nogawa S et al (1999) Alteration of cAMP-mediated signal transduction in cerebral ischemia—binding activity of PKA and phosphorylation of CREB. Rinshō Shinkeigaku 39:1298
Taylor TN, Davis PH, Torner JC, Holmes J, Meyer JW, Jacobson MF (1996) Lifetime cost of stroke in the United States. Stroke 27:1459–1466
Teoh NC (2011) Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: contemporary perspectives on pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection—the good, bad and deadly. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:180–187
Tiedt S, Prestel M, Malik R, et al (2017). Seq identifies circulating miR-125a-5p, miR-125b-5p and miR-143-3p as potential biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Circ Res, 121, CIRCRESAHA.117.311572
Vejnar CE, Zdobnov EM (2012) MiRmap: comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res 40:11673–11683
Wan D, Zhou Y, Wang K, Hou Y, Hou R, Ye X (2016) Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by inhibiting phosphodiesterases and regulating the cAMP/AMPK/SIRT1 pathway after stroke in rats. Brain Res Bull 121:255–262
Wong N, Wang X (2015) miRDB: an online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D146
Yang ZB, Zhang Z, Li TB, Lou Z, Li SY, Yang H, Yang J, Luo XJ, Peng J (2014) Up-regulation of brain-enriched miR-107 promotes excitatory neurotoxicity through down-regulation of glutamate transporter-1 expression following ischaemic stroke. Clin Sci 127:679–689
Yokota N, Uchijima M, Nishizawa S, Namba H, Koide Y (2001) Identification of differentially expressed genes in rat hippocampus after transient global cerebral ischemia using subtractive cDNA cloning based on polymerase chain reaction. Stroke 32:168–174
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 16:284–287
Zhang B, Kirov S, Snoddy J (2005) WebGestalt: an integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W741–W748
Zhang ZL, Wu WC, Liu JQ et al (2014) Screening of differentially expressed genes related to ischemic stroke and functional analysis with DNA microarray. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18:1181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhang, Q. & Liao, Z. Microarray Data Analysis of Molecular Mechanism Associated with Stroke Progression. J Mol Neurosci 67, 424–433 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1247-3