Abstract
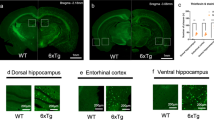
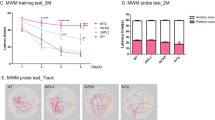
Transgenic mouse has shown great advantages in the study of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and drug screening as AD develops rapidly resent years, while more detail information of these transgenic mice and experience of application are needed. To obtain the basic background information of the B6C3-Tg (APPswe/PSEN1dE9) double-transgenic mouse, which was reported with early onset AD, three- to ten-month-old B6C3-Tg AD mice and normal C57BL/6 mice were selected randomly to test the ability of learning memory by Morris water maze, the brain acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity by AChE kit, and beta amyloid protein level by immunohistochemistry staining. Compared with the control group, the escape latency time of B6C3-Tg AD mice at 9 and 10 months of age is significantly longer (P < 0.05) in Morris maze test, and the activity of brain AChE is higher. β-Amyloid plaques were observed at 3 months of age and developed rapidly. Statistical analysis showed a positive correlation between the area of these plaques and the ages of B6C3-Tg AD mouse (y = 0.0355e0.5557x, R = 0.9557). The model’s behavior is conformed to simulate behaviors of human Alzheimer’s disease at the early stage and may provide detail background information a new choice when transgenic mice are needed in the research of AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand P, Singh B (2013) A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 36:75–399
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 3:186–191
Chapman PF, Falinska AM, Knevet SG, Ramsay MF (2001) Genes, models and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Genet 17:254–261
Cummings JL, Banks SJ, Gary RK, Kinney JW, Lombardo JM, Walsh RR, Zhong K (2013) Alzheimer’s disease drug development: translational neuroscience strategies. CNS Spectr 18:128–138
Hock BJ, Lamb JT, Lamb BT (2001) Transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Genet 17:7–12
Hűll M, Berger M, Heneka M (2006) Disease-modifying therapies in Alzheimer’s disease: how far have we come? Drugs 66:2075–2093
Jankowsky JL, Slunt HH, Ratovitski T, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Borchelt DR (2001) Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: a comparison of strategies. Biomol Eng 17:157–165
Kovács T (2009) Therapy of Alzheimer disease. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung 11:27–33
Lane RM, Potkin SG, Enz A (2006) Targeting acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in dementia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:101–124
Pillai JA, Cummings JL (2013) Clinical trials in predementia stages of Alzheimer disease. Med Clin N Am 97:439–457
Rees T, Hammond PI, Soreq H, Younkin S, Brimijoin S (2003) Acetylcholinesterase promotes beta-amyloid plaques in cerebral cortex. Neuobiol Aging 24:777–787
Salomone S, Caraci F, Leggio GM, Fedotova J, Drago F (2012) New pharmacological strategies for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: focus on disease modifying drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 73:504–517
Schneider LS (2013) Alzheimer disease pharmacologic treatment and treatment research. Continuum 19:339–357
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: gene, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Sturchler-Pierrat C, Abramowski D, Duke M, Wiederhould KH, Mistl C, Rothacher S et al (1997) Two amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse models with Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:13287–13292
Tang JX, Eckenhoff MF (2012) Anesthetic effect in Alzheimer transgenic mouse models. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.06.007
Ulrich J, Meier-Ruge W, Probst A, Meier E, Ipsen S (1990) Senile plaques: staining for acetylcholinesterase and A4 protein: a comparative study in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Acta Neuropathol 86:624–628
Zhang Q, Zhang X, Chen J, Miao Y, Sun A (2009a) Role of caspase-3 in tau truncation at D421 is restricted in transgenic mouse models for tauopathies. J Neurochem 109:476–484, 94, 13287-13292
Zhang Q, Zhang X, Chen J, Miao Y, Sun A (2009b) Role of caspase-3 in tau truncation at D421 is restricted in transgenic mouse models for tauopathies. J Neurochem 109:476–484
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2011B010500013); Foundation of Foshan Cooperation Project, Guangdong Province, China; (2011BY100102) and the Foundation for Medical Science Research of Guangdong Province, China (A2012130). We thank Zhichang Wan (The Chinese University of Hong Kong) and Xianglu Rong (Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine) for the editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Z., Yang, L., Wu, X. et al. Evidences for B6C3-Tg (APPswe/PSEN1dE9) Double-Transgenic Mice Between 3 and 10 Months as an Age-Related Alzheimer’s Disease Model. J Mol Neurosci 53, 370–376 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0203-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0203-5