Abstract
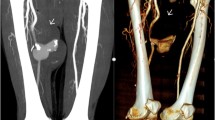
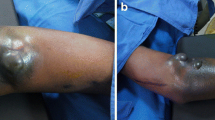
Pseudoaneurysms arise from a disruption of arterial wall continuity and are most commonly related to a penetrating trauma, an arterial wall inflammation or iatrogenic causes. They differ from real aneurysms due to a lack of one or more layers of the arterial wall. The frequency of peripheral artery pseudoaneurysms in the upper extremities is less than in the lower extremities and its most common cause is a gunshot or a stab wound. The risk of a rupture is higher than in true aneurysms due to a lack of wall layers, therefore requiring surgical treatment in most cases. Here we describe an unusual case of an 8-year-old girl who presented to the emergency department complaining of swelling and pain in her left distal forearm. One month before admission she experienced a penetrating trauma in the same area due to a self inflicted stab wound. After clinical and duplex ultrasonography evaluation the tumefaction proved to be a posttraumatic pseudoaneurysm of the left radial artery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haimovici H. Peripheral arterial aneurysms. In: Haimovici H, Ascer E, Hollier L, Strandness DJ, Towne J, editors. Haimovici’s Vascular Surgery. USA: Blackwell Science; 1996. p. 893–909.
Davidovic LB, Banzić I, Rich N, Dragaš M, Cvetkovic SD, Dimic A. False traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas: retrospective analysis. World J Surg. 2011;35:1378–86.
Amrani A, Dandane M, El Alami Z, El Madhi T, Gourinda H, Miri A. False aneurysm of the radial artery: unusual complication of both-bone forearm fracture in children: a case report. Cases J. 2008;1:170.
Crawford ES, De Bakey ME, Cooley DA. Surgical considerations of peripheral arterial aneurysms; analysis of one hundred seven cases. AMA Arch Surg. 1959;78:226–38.
Wielenberg A, Borge MA, Demos TC, Lomasney L, Marra G. Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the brachial artery. Orthopedics. 2000;23(1250):1322–4.
Napolitano AM, Napolitano L, Francomano F, Colalongo C, Ucchino S. Aneurysms of the subclavian artery: clinical experience. Ann Ital Chir. 1998;69:311–5.
Johnston KW, Rutherford RB, Tilson MD, Shah DM, Hollier L, Stanley JC. Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 1991;13:452–8.
Yilmaz AT, Arslan M, Demirkiliç U, et al. Missed arterial injuries in military patients. Am J Surg. 1997;173:110–4.
Ho PK, Weiland AJ, McClinton MA, Wilgis EF. Aneurysms of the upper extremity. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1987;12:39–46.
Kerr CD, Duffey TP. Traumatic false aneurysm of the radial artery. J Trauma. 1988;28:1603–4.
Crawford DL, Yuschak JV, McCombs PR. Pseudoaneurysm of the brachial artery from blunt trauma. J Trauma. 1997;42:327–9.
Gu A, Kam AJ. A rare pediatric case of posttraumatic pseudoaneurysm: case report and literature review. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001236.
Clark ET, Mass DP, Bassiouny HS, Zarins CK, Gewertz BL. True aneurysmal disease in the hand and upper extremity. Ann Vasc Surg. 1991;5:276–81.
Jutte E. Pseudoaneurysm of the brachial artery due to blunt trauma in a child. Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;10:52–3.
Yetkin U, Gurbuz A. Post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the brachial artery and its surgical treatment. Tex Heart Inst J. 2003;30:293–7.
Payne FM. Traumatic aneurysm of the radial artery. J Natl Med Assoc. 1941;33:152–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djuricic, G., Milosevic, Z., Radovic, T. et al. A posttraumatic pseudoaneurysm of the left radial artery as a result of a stab wound in an 8-year-old girl. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 14, 406–409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-9975-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-9975-9