Abstract
Purpose
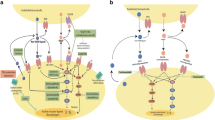
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) is a rare, highly aggressive form of thyroid cancer (TC) characterized by an aggressive behavior and poor prognosis, resulting in patients’ death within a year. Standard treatments, such as chemo and radiotherapy, as well as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, are ineffective for ATC treatment. Cancer immunotherapy is one of the most promising research area in oncology. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis is of particular interest, in light of promising data showing a restoration of host immunity against tumors, with the prospect of long-lasting remissions.
Methods
In this study, we evaluated PD-L1 expression in a large series of TCs (20 cases) showing a progressive dedifferentiation of the thyroid tumor from well differentiated TC to ATC, employing two different antibodies [R&D Systems and VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Rabbit Monoclonal Primary Antibody]. We also tested the anti PD-L1 mAb in an in vivo animal model.
Results
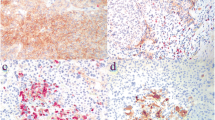
We found that approximately 70–90% of ATC cases were positive for PD-L1 whereas normal thyroid and differentiated TC were negative. Moreover, all analyzed cases presented immunopositive staining in the endothelium of vessels within or in close proximity to the tumor, while normal thyroid vessels were negative. PD-L1 mAb was also effective in inhibiting ATC growth in an in vivo model.
Conclusions
These data suggest that immunotherapy may be a promising treatment specific for ATC suggesting the need to start with clinical TRIALs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Pardoll, The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 252–64 (2012)
H. Borghaei, L. Paz-Ares, L. Horn, D.R. Spigel, M. Steins, N.E. Ready, L.Q. Chow, E.E. Vokes, E. Felip, E. Holgado, F. Barlesi, M. Kohlhäufl, O. Arrieta, M.A. Burgio, J. Fayette, H. Lena, E. Poddubskaya, D.E. Gerber, S.N. Gettinger, C.M. Rudin, N. Rizvi, L. Crinò, G.R. Blumenschein Jr, S.J. Antonia, C. Dorange, C.T. Harbison, F. Graf Finckenstein, J.R. Brahmer, Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 1627–39 (2015)
T.K. Choueiri, M.N. Fishman, B. Escudier, D.F. McDermott, C.G. Drake, H. Kluger, W.M. Stadler, J.L. Perez-Gracia, D.G. McNeel, B. Curti, M.R. Harrison, E.R. Plimack, L. Appleman, L. Fong, L. Albiges, L. Cohen, T.C. Young, S.D. Chasalow, P. Ross-Macdonald, S. Srivastava, M. Jure-Kunkel, J.F. Kurland, J.S. Simon, M. Sznol, Immunomodulatory activity of nivolumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 22, 5461–5471 (2016)
I. Márquez-Rodas, P. Cerezuela, A. Soria, A. Berrocal, A. Riso, M. González-Cao, S. Martín-Algarra, Immune checkpoint inhibitors: therapeutic advances in melanoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 3, 267 (2015)
H. Dong, S.E. Strome, D.R. Salomao, H. Tamura, F. Hirano, D.B. Flies, P.C. Roche, J. Lu, G. Zhu, K. Tamada, V.A. Lennon, E. Celis, L. Chen, Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 8, 793–800 (2002). Erratum Nat. Med. 8, 1039 (2002)
J.M. Taube, R.A. Anders, G.D. Young, H. Xu, R. Sharma, T.L. McMiller, S. Chen, A.P. Klein, D.M. Pardoll, S.L. Topalian, L. Chen, Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7-h1 expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 127ra37 (2012)
B.R. Haugen, American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: what is new and what has changed? Cancer 2017 123, 372–381 (2015)
Z.W. Baloch, V.A. LiVolsi, Special types of thyroid carcinoma. Histopathology 72, 40–52 (2018)
M.E. Cabanillas, M. Zafereo, G.B. Gunn, R. Ferrarotto, Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: treatment in the age of molecular targeted therapy. J. Oncol. Pract. 12, 511–8 (2016)
V. Tiedje, M. Stuschke, F. Weber, H. Dralle, L. Moss, D. Führer, Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: review of treatment protocols. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 25, R153–R161 (2018)
D. Viola, L. Valerio, E. Molinaro, L. Agate, V. Bottici, A. Biagini, L. Lorusso, V. Cappagli, L. Pieruzzi, C. Giani, E. Sabini, P. Passannati, L. Puleo, A. Matrone, B. Pontillo-Contillo, V. Battaglia, S. Mazzeo, P. Vitti, R. Elisei, Treatment of advanced thyroid cancer with targeted therapies: ten years of experience. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 23, R185–205 (2016)
L.L. Cunha, M.A. Marcello, E.C. Morari, S. Nonogaki, F.F. Conte, R. Gerhard, F.A. Soares, J. Vassallo, L.S. Ward, Differentiated thyroid carcinomas may elude the immune system by B7H1 upregulation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 20, 103–10 (2013)
T.E. Angell, M.G. Lechner, J.K. Jang, A.J. Correa, J.S. LoPresti, A.L. Epstein, BRAF V600E in papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with increased programmed death ligand 1 expression and suppressive immune cell infiltration. Thyroid 24, 1385–93 (2014)
H. Wu, Y. Sun, H. Ye, S. Yang, S.L. Lee, A. de las Morenas, Anaplastic thyroid cancer: outcome and the mutation/expression profiles of potential targets. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 21, 695–701 (2015)
J.J. Bastman, H.S. Serracino, Y. Zhu, M.R. Koenig, V. Mateescu, S.B. Sams, K.D. Davies, C.D. Raeburn, R.C. McIntyre Jr, B.R. Haugen, J.D. French, Tumor-infiltrating T cells and the PD-1 checkpoint pathway in advanced differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101, 2863–73 (2016)
S. Chowdhury, J. Veyhl, F. Jessa, O. Polyakova, A. Alenzi, C. MacMillan, R. Ralhan, P.G. Walfish, Programmed death-ligand 1 overexpression is a prognostic marker for aggressive papillary thyroid cancer and its variants. Oncotarget 7, 32318–28 (2016)
S. Ahn, T.H. Kim, S.W. Kim, C.S. Ki, H.W. Jang, J.S. Kim, J.H. Kim, J.H. Choe, J.H. Shin, S.Y. Hahn, Y.L. Oh, J.H. Chung, Comprehensive screening for PD-L1 expression in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 24, 97–106 (2017)
M.W. Rosenbaum, B.J. Gigliotti, S.I. Pai, S. Parangi, H. Wachtel, M. Mino-Kenudson, V. Gunda, W.C. Faquin, PD-L1 and IDO1 are expressed in poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 29, 59–67 (2018)
R. A. DeLellis, R. V. Lloyd, P. U. Heitz, C. Eng, eds. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of Endocrine Organs. WHO Classification of Tumors, 3rd edn. vol 8, 2004
P. Workman, E.O. Aboagye, F. Balkwill, A. Balmain, G. Bruder, D.J. Chaplin, J.A. Double, J. Everitt, D.A.H. Farningham, M.J. Glennie, L.R. Kelland, V. Robinson, I.J. Stratford, G.M. Tozer, S. Watson, S.R. Wedge, S.A. Eccles, An ad hoc committee of the National Cancer Research Institute. Guidelines for the welfare and use of animals in cancer research. Br. J. Cancer 102, 1555–1577 (2010)
J.R. Brahmer, S.S. Tykodi, L.Q. Chow, W.J. Hwu, S.L. Topalian, P. Hwu, C.G. Drake, L.H. Camacho, J. Kauh, K. Odunsi, H.C. Pitot, O. Hamid, S. Bhatia, R. Martins, K. Eaton, S. Chen, T.M. Salay, S. Alaparthy, J.F. Grosso, A.J. Korman, S.M. Parker, S. Agrawal, S.M. Goldberg, D.M. Pardoll, A. Gupta, J.M. Wigginton, Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 2455–2465 (2012)
I. Yamauchi, Y. Sakane, Y. Fukuda, T. Fujii, D. Taura, M. Hirata, K. Hirota, Y. Ueda, Y. Kanai, Y. Yamashita, E. Kondo, M. Sone, A. Yasoda, N. Inagaki, Clinical features of nivolumab-induced thyroiditis: a case series study. Thyroid 27, 894–901 (2017)
F.R. Hirsch, A. McElhinny, D. Stanforth, J. Ranger-Moore, M. Jansson, K. Kulangara, W. Richardson, P. Towne, D. Hanks, B. Vennapusa, A. Mistry, R. Kalamegham, S. Averbuch, J. Novotny, E. Rubin, K. Emancipator, I. McCaffery, J.A. Williams, J. Walker, J. Longshore, M.S. Tsao, K.M. Kerr, PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for lung cancer: results from phase 1 of the Blueprint PD-L1 IHC assay comparison project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 12, 208–222 (2017)
M.S. Tsao, K.M. Kerr, M. Kockx, M.B. Beasley, A.C. Borczuk, J. Botling, L. Bubendorf, L. Chirieac, G. Chen, T.Y. Chou, J.H. Chung, S. Dacic, S. Lantuejoul, M. Mino-Kenudson, A.L. Moreira, A.G. Nicholson, M. Noguchi, G. Pelosi, C. Poleri, P.A. Russell, J. Sauter, E. Thunnissen, I. Wistuba, H. Yu, M.W. Wynes, M. Pintilie, Y. Yatabe, F.R. Hirsch, PD-L1Immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life clinical samples: results of Blueprint phase 2 project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 3, 1302–1311 (2018)
M.J. Eppihimer, J. Gunn, G.J. Freeman, E.A. Greenfield, T. Chernova, J. Erickson, J.P. Leonard, Expression and regulation of the PD-L1 immunoinhibitory molecule on microvascular endothelial cells. Microcirculation 9, 133–145 (2002)
N. Rodig, T. Ryan, J.A. Allen, H. Pang, N. Grabie, C. Tatyana, E.A. Greenfield, S.C. Liang, A.H. Sharpe, A.H. Lichtman, G.J. Freeman, Endothelial expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 downregulates CD8+ T cell activation and cytolysis. Eur. J. Immunol. 33, 3117–3126 (2003)
S. Korehisa, T. Ikeda, S. Okano, H. Saeki, E. Oki, Y. Oda, M. Hashizume, Y. Maehara, A novel histological examination with dynamic three-dimensional reconstruction from multiple immunohistochemically stained sections of a PD-L1-positive colon cancer. Histopathology 72, 697–703 (2018)
L.C. Dieterich, K. Ikenberg, T. Cetintas, K. Kapaklikaya, C. Hutmahcer, M. Detmar, Tumor-associated lymphatic vessels upregulate PDL1 to inhibit T-cell activation. Front. Immunol. 8, 66 (2017)
E. Allen, A. Jabouille, L.B. Rivers, I. Lodewijckx, R. Missiaen, V. Steri, K. Feyen, J. Tawney, D. Hanahan, I.P. Michael, G. Bergers, Combined antiangiogenic and anti-PD-L1 therapy stimulates tumor immunity through HEV formation. Sci. Transl. Med 9(385), pii: eaak9679 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtain from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cantara, S., Bertelli, E., Occhini, R. et al. Blockade of the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) as potential therapy for anaplastic thyroid cancer. Endocrine 64, 122–129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01865-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01865-5