Abstract
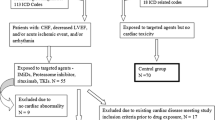
Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity is a growing concern. The cardiotoxic impact of new drugs such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors is unknown, especially the ones used for chronic myeloid leukemia. We aim to evaluate nilotinib- and imatinib-induced cardiotoxicity. Single-center prospective study of consecutive patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors was conducted during 2015. Patients underwent an initial clinical, laboratorial and echocardiographic evaluation, repeated after 1 year. Eleven patients were included [60.0 (11) years, 63.6% of males; seven patients treated with imatinib and four with nilotinib]. After 1 year of follow-up, all patients remained in functional NYHA class I, with a similar Minnesota quality of life score. Also there was no difference in the biomarkers evaluated (cystatin-C and NT-proBNP). Likewise, no modification in systolic or diastolic function evaluated by echocardiography was observed. All patients presented normal values of longitudinal, circumferential and radial strain in the baseline study, without changes during follow-up. In addition, there were no differences between the two tyrosine kinase inhibitors used, considering all the aforementioned variables. No clinical, laboratory or echocardiographic evidence of nilotinib- and imatinib-induced cardiotoxicity was observed. However, these results should be confirmed in multicenter studies given the low incidence of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, B., & Papoian, T. (2012). Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) induced cardiotoxicity: Approaches to narrow the gaps between preclinical safety evaluation and clinical outcome. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 32(12), 945–951.
Volkova, M., & Russell, R. (2011). Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: Prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment. Current Cardiology Reviews, 7(4), 214–220.
Nemeth, B. T., Varga, Z. V., Wu, W. J., & Pacher, P. (2017). Trastuzumab cardiotoxicity: From clinical trials to experimental studies. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(21), 3727–3748.
Groarke, J. D., Nguyen, P. L., Nohria, A., Ferrari, R., Cheng, S., & Moslehi, J. (2014). Cardiovascular complications of radiation therapy for thoracic malignancies: The role for non-invasive imaging for detection of cardiovascular disease. European Heart Journal, 35(10), 612–623.
Krause, D. S., & Van Etten, R. A. (2005). Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(2), 172–187.
Zhang, J., Yang, P. L., & Gray, N. S. (2009). Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nature Reviews Cancer, 9(1), 28–39.
Hartmann, J. T., Haap, M., Kopp, H.-G., & Lipp, H.-P. (2009). Tyrosine kinase inhibitors—A review on pharmacology, metabolism and side effects. Current Drug Metabolism, 10(5), 470–481.
Zamorano, J. L., Lancellotti, P., Rodriguez Munoz, D., Aboyans, V., Asteggiano, R., Galderisi, M., et al. (2016). ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. European Heart Journal, 37(36), 2768–2801.
Heath, E. I., Infante, J., Lewis, L. D., Luu, T., Stephenson, J., Tan, A. R., et al. (2013). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effect of repeated oral doses of pazopanib on cardiac conduction in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 71(3), 565–573.
Chu, T. F., Rupnick, M. A., Kerkela, R., Dallabrida, S. M., Zurakowski, D., Nguyen, L., et al. (2007). Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet, 370(9604), 2011–2019.
Abdel-Rahman, O., & Fouad, M. (2014). Risk of cardiovascular toxicities in patients with solid tumors treated with sorafenib: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol, 10(12), 1981–1992.
Force, T., Krause, D. S., & Van Etten, R. A. (2007). Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nature Reviews Cancer, 7(5), 332–344.
Chen, M. H., Kerkelä, R., & Force, T. (2008). Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor cancer therapeutics. Circulation, 118(1), 84–95.
Moen, M. D., McKeage, K., Plosker, G. L., & Siddiqui, M. A. A. (2007). Imatinib: A review of its use in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Drugs, 67(2), 299–320.
Keskin, D., Sadri, S., & Eskazan, A. E. (2016). Dasatinib for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: Patient selection and special considerations. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 10, 3355–3361.
Emole, J., Talabi, T., & Pinilla-Ibarz, J. (2016). Update on the management of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia: Role of nilotinib. Biologics, 10, 23–31.
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Murray, T., Xu, J., Smigal, C., et al. (2016). Cancer statistics, 2006. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 56(2), 106–130.
Lang, R. M., Badano, L. P., Mor-Avi, V., Afilalo, J., Armstrong, A., Ernande, L., et al. (2016). Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of, Cardiovascular Imaging. European Heart Journal: Cardiovascular Imaging, 17(4), 412.
Kleijn, S. A., Pandian, N. G., Thomas, J. D., Perez de Isla, L., Kamp, O., Zuber, M., et al. (2015). Normal reference values of left ventricular strain using three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: Results from a multicentre study. European Heart Journal: Cardiovascular Imaging, 16(4), 410–416.
Kerkelä, R., Grazette, L., Yacobi, R., Iliescu, C., Patten, R., Beahm, C., et al. (2006). Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate. Nature Medicine, 12(8), 908–916.
Wolf, A., Couttet, P., Dong, M., Grenet, O., Heron, M., Junker, U., et al. (2010). Imatinib does not induce cardiotoxicity at clinically relevant concentrations in preclinical studies. Leukemia Research, 34(9), 1180–1188.
Herman, E. H., Knapton, A., Rosen, E., Thompson, K., Rosenzweig, B., Estis, J., et al. (2011). A multifaceted evaluation of imatinib-induced cardiotoxicity in the rat. Toxicologic Pathology, 39(7), 1091–1106.
Kaya, Z., & Karanfil, M. (2012). Assessment of left ventricular systolic and diastolic function with conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiography imaging techniques in patients administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Turk Kardiyol Dern Arş, 40(7), 597–605.
Verstovsek, S., Golemovic, M., Kantarjian, H., Manshouri, T., Estrov, Z., Manley, P., et al. (2005). AMN107, a novel aminopyrimidine inhibitor of p190 Bcr-Abl activation and of in vitro proliferation of Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer, 104(6), 1230–1236.
Tiwari, A. K., Sodani, K., Wang, S. R., Kuang, Y. H., Ashby, C. R., Jr., Chen, X., et al. (2009). Nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the activity of the ABCB1/Pgp and ABCG2/BCRP/MXR transporters. Biochemical Pharmacology, 78(2), 153–161.
Nilotinib, T., Dan, H., Jin, L., & Cheng, L. (2016). Nilotinib reverses ABCB1/P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance but increases cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in a MDR xenograft model. Toxicology Letters, 30(259), 124–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francisco, A.R.G., Alves, D., David, C. et al. Cardiotoxicity in Hematological Diseases: Are the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Imatinib and Nilotinib Safe?. Cardiovasc Toxicol 18, 431–435 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9453-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9453-3