Abstract
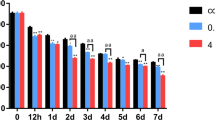
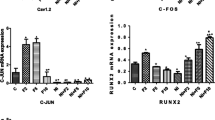
The gap junction protein plays an important role in the bone formation and alteration of these proteins leading to cause bone development. Aim to determine the effects of different concentration of fluoride on gap-junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) related genes and proteins in the rats’ osteoblast cells. We treated the osteoblast cells with various concentrations (0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 mM) NaF for 24 and 72 h. We used the scrape loading and dye transfer technique to research the intracellular connectivity. Moreover, the mRNA expression levels of connexin 43 (Cx43), connexin45 (Cx45), collagen I, and osteocalcin (OCN) were analyzed by qRT-PCR, the protein expression levels of connexin43 (Cx43) were analyzed by western blotting and immunofluorescence. Our results suggested that the osteoblast proliferations were decreased in the 0.5 and 1 mM NaF groups, after 24 and 72 treatments. The scrape loading and dye transfer experiment showed that the GJIC were increased in the 0.01 mM NaF group and decreased in the 0.5 and 1 mM NaF groups. In addition, the mRNA expressions of Cx43, Cx45, and OCN, and the protein expressions of Cx43 were increased in the 0.01 mM NaF group and decreased in the 0.5 and 1 mM NaF groups. In summary, these results suggest that the low concentration NaF is good for the GJIC, but the high concentration NaF damages the GJIC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ge Y, Niu R, Zhang J, Wang J (2011) Proteomic analysis of brain proteins of rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Arch Toxicol 85(1):27–33
Yamazaki S, Ichimura S, Iwamoto J, Takeda T, Toyama Y (2004) Effect of walking exercise on bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with osteopenia/osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 22(5):500–508
Niu R, Xue X, Zhao Y, Sun Z, Yan X, Li X, Feng C, Wang J (2015) Effects of fluoride on microtubule ultrastructure and expression of Tubalpha 1a and Tubbeta 2a in mouse hippocampus. Chemosphere 139:422–427
Krishnamachari KA (1986) Skeletal fluorosis in humans: a review of recent progress in the understanding of the disease. Prog Food Nutr Sci 10(3–4):279–314
Cao J, Chen J, Wang J, Jia R, Xue W, Luo Y, Gan X (2013) Effects of fluoride on liver apoptosis and Bcl-2, Bax protein expression in freshwater teleost, Cyprinus carpio. Chemosphere 91(8):1203–1212
Kim J, Kwon WS, Rahman MS, Lee JS, Yoon SJ, Park YJ, You YA, Pang MG (2015) Effect of sodium fluoride on male mouse fertility. Andrology 3(3):544–551
Yan X, Hao X, Nie Q, Feng C, Wang H, Sun Z, Niu R, Wang J (2015) Effects of fluoride on the ultrastructure and expression of type I collagen in rat hard tissue. Chemosphere 128:36–41
Yan X, Feng C, Chen Q, Li W, Wang H, Lv L, Smith GW, Wang J (2009) Effects of sodium fluoride treatment in vitro on cell proliferation, apoptosis and caspase-3 and caspase-9 mRNA expression by neonatal rat osteoblasts. Arch Toxicol 83(5):451–458
Centeno VA, Fontanetti PA, Interlandi V, Ponce RH, Gallará RV (2015) Fluoride alters connexin expression in rat incisor pulp. Arch Oral Biol 60(2):313–319
Solan JL, Lampe PD (2014) Specific Cx43 phosphorylation events regulate gap junction turnover in vivo. FEBS Lett 588(8):1423–1429
Grimston SK, Fontana F, Watkins M, Civitelli R (2017) Heterozygous deletion of both sclerostin (Sost) and connexin43 (Gja1) genes in mice is not sufficient to impair cortical bone modeling. PLoS One 12(11):e0187980
Shapiro F (1997) Variable conformation of GAP junctions linking bone cells: a transmission electron microscopic study of linear, stacked linear, curvilinear, oval, and annular junctions. Calcif Tissue Int 61(4):285–293
Tsai CF, Cheng YK, Lu DY, Wang SL, Chang CN, Chang PC, Yeh WL (2018) Inhibition of estrogen receptor reduces connexin 43 expression in breast cancers. Toxicol Appl Pharm 338:182–190
Flenniken AM, Osborne LR, Anderson N, Ciliberti N, Fleming C, Gittens JE, Gong XQ, Kelsey LB, Lounsbury C, Moreno L, Nieman BJ, Peterson K, Qu D, Roscoe W, Shao Q, Tong D, Veitch GI, Voronina I, Vukobradovic I, Wood GA, Zhu Y, Zirngibl RA, Aubin JE, Bai D, Bruneau BG, Grynpas M, Henderson JE, Henkelman RM, McKerlie C, Sled JG, Stanford WL, Laird DW, Kidder GM, Adamson SL, Rossant J (2005) A Gja1 missense mutation in a mouse model of oculodentodigital dysplasia. Development 132(19):4375–4386
McLachlan E, Plante I, Shao Q, Tong D, Kidder GM, Bernier SM, Laird DW (2009) ODDD-linked Cx43 mutants reduce endogenous Cx43 expression and function in osteoblasts and inhibit late stage differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 23(6):928–938
Gramsch B, Gabriel HD, Wiemann M, Grummer R, Winterhager E, Bingmann D, Schirrmacher K (2001) Enhancement of connexin 43 expression increases proliferation and differentiation of an osteoblast-like cell line. Exp Cell Res 264(2):397–407
Izumi K, Lippa AM, Wilkens A, Feret HA, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH (2013) Congenital heart defects in oculodentodigital dysplasia: report of two cases. Am J Med Genet A 161a(12):3150–3154
Steinberg TH, Civitelli R, Geist ST, Robertson AJ, Hick E, Veenstra RD, Wang HZ, Warlow PM, Westphale EM, Laing JG et al (1994) Connexin43 and connexin45 form gap junctions with different molecular permeabilities in osteoblastic cells. EMBO J 13(4):744–750
Laing JG, Manley-Markowski RN, Koval M, Civitelli R, Steinberg TH (2001) Connexin45 interacts with zonula occludens-1 and connexin43 in osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 276(25):23051–23055
Miao Q, Xu M, Liu B, You B (2002) In vivo and in vitro study on the effect of excessive fluoride on type I collagen of rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 31(3):145–147
Hakami T, O'Brien TJ, Petty SJ, Sakellarides M, Christie J, Kantor S, Todaro M, Gorelik A, Seibel MJ, Yerra R, Wark JD (2016) Monotherapy with Levetiracetam versus older AEDs: a randomized comparative trial of effects on bone health. Calcif Tissue Int 98(6):556–565
Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E, Ferron M, Ahn JD, Confavreux C, Dacquin R, Mee PJ, McKee MD, Jung DY, Zhang Z, Kim JK, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2007) Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell 130(3):456–469
Hinoi E, Nakatani E, Yamamoto T, Iezaki T, Takahata Y, Fujita H, Ishiura R, Takamori M, Yoneda Y (2012) The transcription factor paired box-5 promotes osteoblastogenesis through direct induction of osterix and osteocalcin. J Bone Miner Res 27(12):2526–2534
Lee JS, Kim ME, Seon JK, Kang JY, Yoon TR, Park YD, Kim HK (2018) Bone-forming peptide-3 induces osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells via regulation of the ERK1/2 and Smad1/5/8 pathways. Stem Cell Res 26:28–35
Elfouly MH, Trosko JE, Chang CC (1987) Scrape-loading and dye transfer: a rapid and simple technique to study gap junctional intercellular communication. J Experimental Cell Research 168(2):422–430
Denbesten P, Li W (2011) Chronic fluoride toxicity: dental fluorosis. Monogr Oral Sci 22:81–96
Zhang J, Li Z, Qie M, Zheng R, Shetty J, Wang J (2016) Sodium fluoride and sulfur dioxide affected male reproduction by disturbing blood-testis barrier in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 94:103–111
Lau KH, Goodwin C, Arias M, Mohan S, Baylink DJ (2002) Bone cell mitogenic action of fluoroaluminate and aluminum fluoride but not that of sodium fluoride involves upregulation of the insulin-like growth factor system. Bone 30(5):705–711
Perumal E, Paul V, Govindarajan V, Panneerselvam L (2013) A brief review on experimental fluorosis. Toxicol Lett 223(2):236–251
Wang Z, Yang X, Yang S, Ren G, Ferreri M, Su Y, Chen L, Han B (2011) Sodium fluoride suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis through decreased insulin-like growth factor-I expression and oxidative stress in primary cultured mouse osteoblasts. Arch Toxicol 85(11):1407–1417
Yan X, Yan X, Morrison A, Han T, Chen Q, Li J, Wang J (2011) Fluoride induces apoptosis and alters collagen I expression in rat osteoblasts. Toxicol Lett 200(3):133–138
Chiba H, Sawada N, Oyamada M, Kojima T, Nomura S, Ishii S, Mori M (1993) Relationship between the expression of the gap junction protein and osteoblast phenotype in a human osteoblastic cell line during cell proliferation. Cell Struct Funct 18(6):419–426
Schiller PC, D’Ippolito G, Balkan W, Roos BA, Howard GA (2001) Gap-junctional communication is required for the maturation process of osteoblastic cells in culture. Bone 28(4):362–369
Upham BL, Suzuki J, Chen G, Wang Y, McCabe LR, Chang CC, Krutovskikh VA, Yamasaki H, Trosko JE (2003) Reduced gap junctional intercellular communication and altered biological effects in mouse osteoblast and rat liver oval cell lines transfected with dominant-negative connexin 43. Mol Carcinog 37(4):192–201
Zhang YD, Zhao SC, Zhu ZS, Wang YF, Liu JX, Zhang ZC, Xue F (2017) Cx43- and Smad-mediated TGF-beta/BMP signaling pathway promotes cartilage differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits osteoblast differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem 42(4):1277–1293
Koval M, Geist ST, Westphale EM, Kemendy AE, Civitelli R, Beyer EC, Steinberg TH (1995) Transfected connexin45 alters gap junction permeability in cells expressing endogenous connexin43. J Cell Biol 130(4):987–995
Lecanda F, Warlow PM, Sheikh S, Furlan F, Steinberg TH, Civitelli R (2000) Connexin43 deficiency causes delayed ossification, craniofacial abnormalities, and osteoblast dysfunction. J Cell Biol 151(4):931–944
Misu A, Yamanaka H, Aramaki T, Kondo S, Skerrett IM, Iovine MK, Watanabe M (2016) Two different functions of Connexin43 confer two different bone phenotypes in zebrafish. J Biol Chem 291(24):12601–12611
Suzuki J, Na HK, Upham BL, Chang CC, Trosko JE (2000) Lambda-carrageenan-induced inhibition of gap-junctional intercellular communication in rat liver epithelial cells. Nutr Cancer 36(1):122–128
Pramanik S, Saha D (2017) The genetic influence in fluorosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 56:157–162
Suuriniemi M, Mahonen A, Kovanen V, Alen M, Cheng S (2003) Relation of PvuII site polymorphism in the COL1A2 gene to the risk of fractures in prepubertal Finnish girls. Physiol Genomics 14(3):217–224
Willing MC, Torner JC, Burns TL, Janz KF, Marshall T, Gilmore J, Deschenes SP, Warren JJ, Levy SM (2003) Gene polymorphisms, bone mineral density and bone mineral content in young children: the Iowa bone development study. Osteoporos Int 14(8):650–658
Duan X, Xu H, Wang Y, Wang H, Li G, Jing L (2014) Expression of core-binding factor alpha1 and osteocalcin in fluoride-treated fibroblasts and osteoblasts. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28(3):278–283
Song YE, Tan H, Liu KJ, Zhang YZ, Liu Y, Lu CR, Yu DL, Tu J, Cui CY (2011) Effect of fluoride exposure on bone metabolism indicators ALP, BALP, and BGP. Environ Health Prev Med 16(3):158–163
Lecanda F, Towler DA, Ziambaras K, Cheng SL, Koval M, Steinberg TH, Civitelli R (1998) Gap junctional communication modulates gene expression in osteoblastic cells. Mol Biol Cell 9(8):2249–2258
Li Z, Zhou Z, Saunders MM, Donahue HJ (2006) Modulation of connexin43 alters expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(4):C1248–C1255
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 31672623, 31372497) of China and Veterinary Environmental Lab (Shanxi Key Lab).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
In this study, all experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Ethics committee, China.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, G., Li, Y. et al. The Effects of Fluoride on the Gap-Junctional Intercellular Communication of Rats’ Osteoblast. Biol Trace Elem Res 193, 195–203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01692-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01692-9