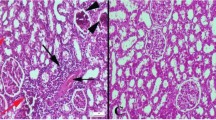
Abstract
Selenium is a trace element that has antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of selenium in reducing ischemia-reperfusion injury of the gastrocnemius muscle. In this experimental study, 80 adult male Wistar rats weighing 250–300 g were divided into ten groups (N = 8 per group). Group 1 is control group (without ischemia-reperfusion). Group 2 received 0.2 mg/kg selenium. Group 3 received ischemia + 3 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg selenium, group 4 received ischemia + 3 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg placebo, group 5 received ischemia + 7 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg selenium, group 6 received ischemia + 7 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg placebo, group 7 received ischemia + 14 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg selenium, group 8 received ischemia + 14 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg placebo, group 9 received ischemia + 28 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg selenium and group 10 received ischemia + 3 d reperfusion + 0.2 mg/kg placebo. External iliac artery blocked for 3 h. After reperfusion, rats killed and gastrocnemius muscle removed, fixed, and tissue processing performed. Samples stained with hematoxylin-eosin for edema evaluation, toluidine blue for mast cell infiltration evaluation and immunohistochemistry for detection TNF-alpha and NF-kappa B proteins. Comparison of mast cell infiltration, edema of the interstitial fluid on the tissue, expression of TNF-alpha protein, and expression of NF-kappa B protein in the groups that received selenium with corresponding placebo group showed that selenium can reduce edema, mast cell infiltration, and TNF-alpha expression and inactivated NF-kappa B. The use of selenium simultaneously with creating ischemia can reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury of the gastrocnemius muscle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robbins SL, Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2012) Robbins basic pathology. Elsevier Health Sciences
Walker PM (1991) Ischemia/reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. Ann Vasc Surg 5(4):399–402
Subramanian P, Mirunalini S, Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Cardinali D (2007) Melatonin treatment improves the antioxidant status and decreases lipid content in brain and liver of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 571(2):116–119
Nayler WG, Poole-Wilson P, Williams A (1979) Hypoxia and calcium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 11(7):683–706
Mccord J (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312(3):159–163
Hellberg P, Kallskog T (1989) Neutrophil-mediated post-ischemic tubular leakage in the rat kidney. Kidney Int 36(4):555–561
Jefayri M, Grace P, Mathie R (2000) Attenuation of reperfusion injury by renal ischaemic preconditioning: the role of nitric oxide. BJU Int 85(9):1007–1013
Araki M, Fahmy N, Zhou L, Kumon H, Krishnamurthi V, Goldfarb D, Modlin C, Flechner S, Novick AC, Fairchild RL (2006) Expression of IL-8 during reperfusion of renal allografts is dependent on ischemic time. Transplantation 81(5):783–788
Schoenber MH, Berger HG (1993) Reperfusion injury after intestinal ischemia. Crit Care Med 21(9):1376–1386
Sinatra ST, DeMarco J (1995) Free radicals, oxidative stress, oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL), and the heart: antioxidants and other strategies to limit cardiovascular damage. Conn Med 59:579
Kohen R, Tirosh O, Kopolovich K (1992) The reductive capacity index of saliva obtained from donors of various ages. Exp Gerontol 27(2):161–168
Ostadalova I, Vobecky M, Chvojkova Z, Mikova D, Hampl V, Wilhelm J, Ostadal B (2007) Selenium protects the immature rat heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem 300(1–2):259–267
Gholami MR, Abolhassani F, Pasbakhsh P, Akbari M, Sobhani A, Sohrabi D, Mehrania K (2007) The effects of simvastatin on functional recovery of rat reperfused sciatic nerve. Pak J Biol Sci 10(23):4256–4260
Gholami MR, Abolhassani F, Pasbakhsh P, Akbari M, Sobhani A, Eshraghian MR, Kamalian N, Amoli FA, Dehpoor AR, Sohrabi D (2008) The effects of simvastatin on ischemia–reperfusion injury of sciatic nerve in adult rats. Eur J Pharmacol 590(1):111–114
Alipour M, Gholami MR, Anarkooli IJ, Sohrabi D, Tajki J, Pourheidar M (2011) Intraperitoneal Aminoguanidine improves sciatic nerve ischemia–reperfusion injury in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31(5):765–773
Andrade-Silva AR, Ramalho FS, Ramalho LN, Saavedra-Lopes M, Jordão AA Jr, Vanucchi H, Piccinato CE, Zucoloto S (2009) Effect of NFκB inhibition by CAPE on skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 153(2):254–262
Zendedel A, Ahmadvand H, Ghanadi K, Gholami M (2015) Effects of selenium on antioxidant activity and recovery from sciatic nerve ischemia–reperfusion in adult rats.Zha J Res Med Sci. In Press
Black RA (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34(1):1–5
Palladino MA, Bahjat FR, Theodorakis EA, Moldawer LL (2003) Anti-TNF-α therapies: the next generation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(9):736–746
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K, Scheurich P (2003) Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ 10(1):45–65
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-κB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 1(6):a001651
Starkie R, Ostrowski SR, Jauffred S, Febbraio M, Pedersen BK (2003) Exercise and IL-6 infusion inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-α production in humans. FASEB J 17(8):884–886
Gius D, Spitz DR (2006) Redox signaling in cancer biology. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(7–8):1249–1252
AL-Rasheed NM, Attia HA, Mohamed RA, Al-Rasheed NM, Al-Amin MA (2014) Preventive effects of selenium yeast, chromium picolinate, zinc sulfate and their combination on oxidative stress, inflammation, impaired angiogenesis and atherogenesis in myocardial infarction in rats. J Pharm Pharm Sci 16(5):848–867
Acknowledgements
This study approved with grant 591 in the Lorestan University of Medical Sciences. Special thanks to Lorestan University of Medical Sciences for the financial support, khorramabad, Iran. The authors thank the head and staff of Razi Herbal Drugs Research Center of Lorestan Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholami, M., Zendedel, A., Khanipour khayat, Z. et al. Selenium Effect on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Gastrocnemius Muscle in Adult Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 164, 205–211 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0218-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0218-y